Home>Gardening News and Trends>Latest News>What Is Sea Vegetables


Latest News
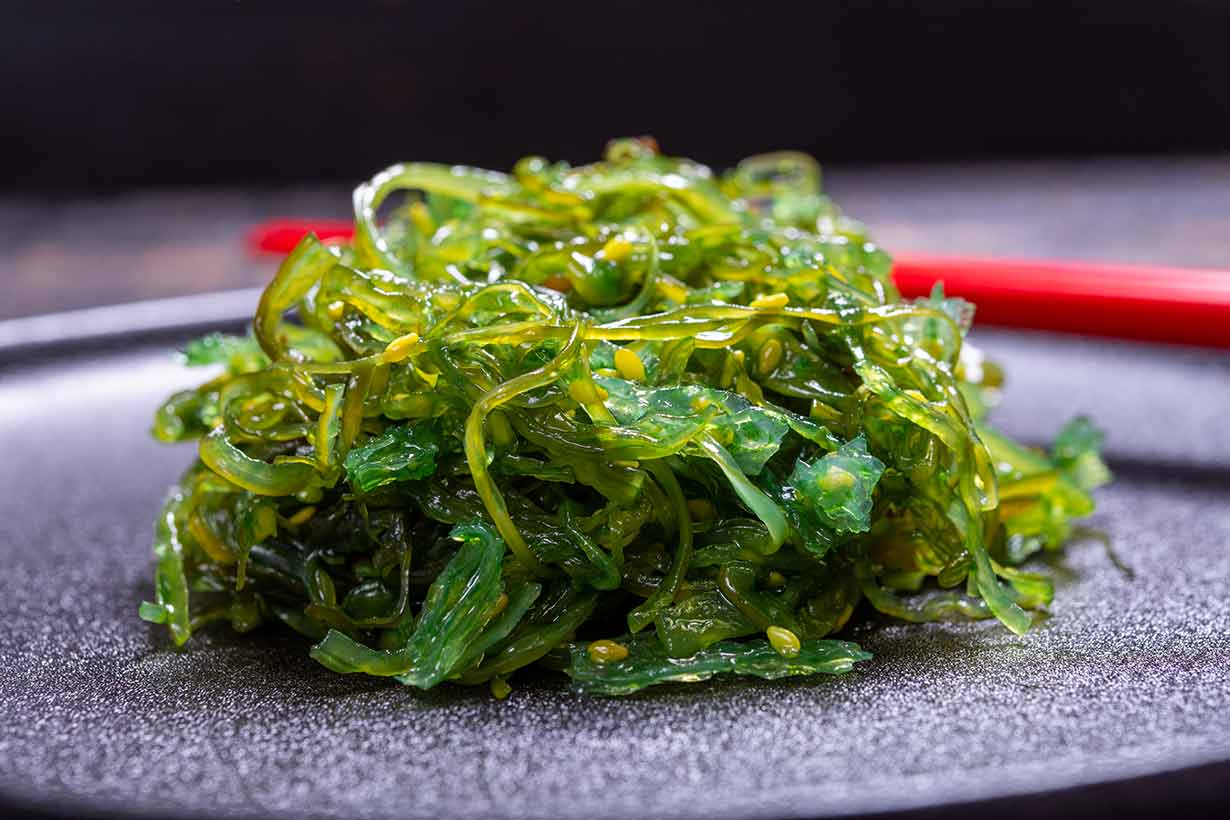
What Is Sea Vegetables
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the latest news and benefits of sea vegetables, including their nutritional value and how to incorporate them into your diet.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Sea vegetables, also known as seaweeds, have been consumed by various cultures for centuries. These marine plants grow in the shallow waters of oceans and have gained popularity in recent years due to their numerous health benefits. From their unique flavors to their impressive nutrient profiles, sea vegetables offer a versatile and nutritious addition to any diet.
Sea vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a valuable source of nutrition. They are known for their high iodine content, which is essential for thyroid function and overall metabolism. Additionally, sea vegetables are low in calories and fat, making them a great option for those seeking to maintain a healthy weight.
The popularity of sea vegetables has also increased due to their sustainable and environmentally friendly nature. Unlike land-based crops, sea vegetables require no fresh water, fertilizers, or pesticides to grow. They play a crucial role in marine ecosystems, acting as habitat and food for various species. Therefore, incorporating sea vegetables into our diets not only benefits our health but also supports the health of our planet.
In this article, we will explore the nutritional benefits of sea vegetables, the different types available, how to cook with them, and potential health risks to consider.
What are Sea Vegetables?
Sea vegetables are a type of marine algae that grow in saltwater environments. They are commonly referred to as seaweeds and come in different varieties, shapes, and colors. These edible plants have been a staple in Asian cuisines for centuries and are gaining popularity in Western countries for their unique flavors and nutritional benefits.
Sea vegetables are rich in essential minerals, including iodine, calcium, iron, and magnesium. They are also a good source of vitamins such as vitamin C, vitamin K, and B vitamins. Their unique nutritional profile sets them apart from land vegetables, making them a valuable addition to any diet.
One of the key features of sea vegetables is their high iodine content. Iodine is crucial for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland, which plays a vital role in regulating metabolism and supporting overall health. Sea vegetables can be especially beneficial for those following a plant-based diet or living in iodine-deficient areas, as they provide a natural and sustainable source of this essential mineral.
Sea vegetables can be classified into three main categories: brown, red, and green. Brown seaweeds, such as kelp and kombu, are known for their rich umami flavor and are commonly used in soups, stews, and sushi rolls. Red seaweeds, like nori and dulse, are often used to wrap sushi or as a garnish for salads and rice dishes. Green seaweeds, including sea lettuce and ulva, have a delicate taste and are used in salads, smoothies, and as a topping for soups.
These versatile marine plants can be consumed in various forms, including dried, powdered, or as part of processed foods. They can be used to add flavor, texture, and visual appeal to a wide range of dishes. Sea vegetables can be purchased from health food stores, Asian markets, or online retailers.
While sea vegetables offer numerous health benefits, it is essential to consume them in moderation. Some individuals may be sensitive to the high iodine content, so it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating sea vegetables into your diet, especially if you have thyroid conditions or are taking medication.
Nutritional Benefits of Sea Vegetables
Sea vegetables are a powerhouse of nutrients, offering a wide array of health benefits. They provide a rich source of minerals, vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber, making them a valuable addition to a healthy diet. Let’s explore some of the key nutritional benefits of sea vegetables:
1. Rich in Iodine: Sea vegetables are one of the best natural sources of iodine, a mineral essential for thyroid function. Iodine plays a crucial role in the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, growth, and development. Including sea vegetables in your diet can help ensure adequate iodine intake, especially for individuals following a plant-based or low-iodine diet.
2. Abundance of Minerals: Sea vegetables are packed with an impressive array of minerals, including calcium, magnesium, potassium, iron, and zinc. These minerals are vital for numerous bodily functions, such as maintaining bone health, supporting nerve and muscle function, and promoting a healthy immune system.
3. Excellent Source of Vitamins: Sea vegetables contain a range of vitamins, including vitamin C, vitamin K, and various B vitamins. Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant, helping protect cells from damage caused by harmful free radicals. Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health, while B vitamins play a role in energy production and support brain function.
4. Antioxidant Powerhouses: Sea vegetables are rich in antioxidants, which help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. These antioxidants include carotenoids, flavonoids, and phycocyanins, which may have protective effects against chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
5. High in Fiber: Sea vegetables are a good source of dietary fiber, promoting a healthy digestive system and aiding in weight management. Fiber helps regulate bowel movements and can contribute to feelings of fullness, reducing overeating and supporting healthy digestion.
6. Low in Calories and Fat: Sea vegetables are naturally low in calories and fat, making them an excellent choice for those watching their weight or following a calorie-controlled diet. They provide a satisfying and nutritious alternative to calorie-dense foods.
Incorporating sea vegetables into your diet can be as simple as adding them to salads, soups, stir-fries, or sushi rolls. However, it is essential to consume in moderation, as excessive intake of iodine from sea vegetables can have adverse effects on thyroid health. As with any dietary changes, it is always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating sea vegetables, especially if you have specific health concerns or conditions.
Types of Sea Vegetables
Sea vegetables come in a variety of types, each with its own unique characteristics, flavors, and culinary uses. Here are some common types of sea vegetables:
1. Nori: Nori is perhaps one of the most well-known sea vegetables. It is a red seaweed that is typically used to wrap sushi rolls or used as a crunchy topping for salads and rice dishes. Nori has a slightly sweet and salty flavor.
2. Kelp: Kelp is a type of brown seaweed known for its complex umami flavor. It is commonly used in Japanese cuisine, particularly in soups and stews. Kelp can also be dried and powdered, sprinkled onto dishes as a seasoning, or used as a natural thickening agent.
3. Wakame: Wakame is another popular brown seaweed that is often used in Asian cuisine. It has a mild flavor and tender texture that works well in salads, miso soup, and stir-fries.
4. Dulse: Dulse is a red seaweed with a slightly smoky and salty taste. It can be eaten both dried and raw. Dulse is commonly used as a snack or added to salads, soups, and sandwiches for a flavor boost.
5. Hijiki: Hijiki is a brown seaweed with a strong, nutty flavor and a slightly crunchy texture. It is commonly used in Japanese dishes, such as salads, stir-fries, and sushi rolls.
6. Sea Lettuce: Sea lettuce is a green seaweed that resembles leafy lettuce. It has a mild and delicate flavor, making it a popular choice for salads or as a garnish for seafood dishes.
7. Kombu: Kombu is a thick and dark brown seaweed commonly used in Japanese cuisine as a flavor enhancer for broths, stocks, and soups. Its umami-rich taste adds depth to dishes while providing essential minerals.
These are just a few examples of the many sea vegetables available. Each type offers unique flavors and textures, allowing for culinary creativity and experimentation in the kitchen.
When purchasing sea vegetables, it is essential to ensure their quality and safety. Look for reputable sources that offer organic, sustainably harvested sea vegetables to minimize the risk of contaminants. Proper storage is also important to maintain their freshness and flavor.
Whether you are an experienced cook or new to sea vegetables, exploring the different types can add diversity to your meals and provide a wide range of health benefits.
Cooking with Sea Vegetables
Sea vegetables offer a unique and nutritious addition to a variety of dishes. From soups and salads to stir-fries and sushi rolls, there are countless ways to incorporate these versatile marine plants into your culinary repertoire. Here are some ideas and tips for cooking with sea vegetables:
1. Sushi Rolls: Nori, a type of seaweed traditionally used for sushi rolls, adds a subtle flavor and texture. Fill nori sheets with cooked rice, vegetables, and protein of your choice, then roll and slice for a delicious homemade sushi experience.
2. Salads: Sea vegetables can bring a unique twist to your salads. Add a handful of chopped seaweed, such as wakame or dulse, to your fresh green or grain-based salads for added nutrition and a touch of umami.
3. Broths and Stocks: Kelp and kombu are often used to flavor broths and stocks due to their rich umami taste. Add a strip of kelp or kombu to your soup base to infuse it with depth and complexity.
4. Stir-fries: Incorporate sea vegetables into your stir-fries for a burst of flavor and nutrients. Add small pieces of wakame, hijiki, or thinly sliced kombu to your favorite stir-fry recipe for a delightful twist.
5. Seasonings and Condiments: Dry and crush sea vegetables such as nori, dulse, or kombu to create flavorful seasonings. Sprinkle these seaweed flakes over roasted vegetables, popcorn, or even homemade fries for a delicious and nutritious seasoning option.
6. Soups and Stews: Sea vegetables can add depth and richness to soups and stews. Use chopped or powdered seaweed as a natural thickener or simmer kombu or kelp in broths to infuse them with a savory taste.
7. Snacks: Enjoy sea vegetables as a healthy snack option. Roast nori sheets in the oven for a crispy seaweed snack or snack on dried dulse for a flavorful and nutrient-packed treat.
When cooking with sea vegetables, it’s essential to remember a few tips. Firstly, rinse dried sea vegetables to remove any excess salt or debris before using them. Secondly, follow the recipe recommendations for the amount of seaweed to ensure a balanced flavor profile. Additionally, avoid overcooking sea vegetables to retain their texture and nutritional value.
By experimenting with different cooking methods and combinations, you can explore the unique flavors and textures offered by sea vegetables. They not only provide a nutritional boost but also infuse your dishes with a touch of the ocean’s goodness.
Potential Health Risks of Sea Vegetables
While sea vegetables offer numerous health benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and exercise moderation when incorporating them into your diet. Here are some potential health risks associated with sea vegetables:
1. Iodine Overconsumption: Sea vegetables, particularly brown seaweeds like kelp and kombu, are high in iodine. While iodine is essential for thyroid health, excessive intake can have negative effects on thyroid function. Individuals with thyroid disorders or those taking medications affecting thyroid function should be cautious about their iodine intake and consult with a healthcare professional before consuming large amounts of sea vegetables.
2. Heavy Metal Contamination: Sea vegetables can absorb heavy metals, such as mercury, arsenic, and lead, from the ocean. While most sea vegetables have shown to have low levels of contamination, it’s important to source them from reputable suppliers that ensure rigorous testing for heavy metal contamination.
3. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to certain types of sea vegetables. Allergic reactions can manifest as skin irritation, rash, digestive issues, or respiratory symptoms. If you have a known seaweed or iodine allergy, it’s necessary to avoid consuming sea vegetables or products containing them.
4. Risk of Excess Sodium: Sea vegetables naturally contain sodium, which can contribute to increased salt intake. Individuals with hypertension, kidney disease, or other conditions that require a low-sodium diet should monitor their consumption of sea vegetables and consider low-sodium options.
5. Potential Interactions with Medications: Sea vegetables contain compounds that may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, anticoagulants, or medications for thyroid conditions. It’s important to discuss your sea vegetable consumption with your healthcare provider if you are on any medications to minimize potential interactions.
While these potential health risks should be considered, they should not discourage the consumption of sea vegetables in moderation. Adhering to the recommended daily intake guidelines and sourcing high-quality sea vegetables from reputable suppliers can help mitigate these risks and allow individuals to enjoy the nutritional benefits they offer.
If you have any specific health concerns or underlying medical conditions, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, including the incorporation of sea vegetables.
Conclusion
Sea vegetables, or seaweeds, are a nutritious and versatile addition to any diet. Packed with an array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, sea vegetables offer numerous health benefits. From supporting thyroid function to providing essential minerals and fiber, they are a valuable source of nutrition.
With their unique flavors and textures, sea vegetables can be incorporated into various dishes, including sushi, salads, soups, and stir-fries. They add a touch of umami, enhance the nutritional profile of meals, and bring the goodness of the ocean to your plate.
While sea vegetables offer many advantages, it’s essential to be mindful of potential health risks. The high iodine content, heavy metal contamination, allergic reactions, and interactions with medications are factors to consider. Moderation, sourcing from reputable suppliers, and consulting with healthcare professionals can help mitigate these risks.
Incorporating sea vegetables into your diet can be a delicious and sustainable way to boost your overall health and well-being. Whether you’re seeking to explore new flavors, follow a plant-based diet, or simply introduce more nutrient-dense ingredients into your meals, sea vegetables provide a unique opportunity to dive into the world of marine plants.
Remember to explore the various types of sea vegetables available, experiment with different cooking methods, and enjoy the diverse flavors and textures they offer. And as with any dietary changes, it’s important to listen to your body, pay attention to how you feel, and make adjustments accordingly.
So go ahead and embrace the wonders of sea vegetables, adding a healthy twist and a taste of the ocean to your culinary adventures!