Home>Gardening Tips and Tricks>Eco-Friendly Gardening>How To Lower pH In Hydroponics


Eco-Friendly Gardening
How To Lower pH In Hydroponics
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn how to lower pH in hydroponics with eco-friendly gardening methods. Optimize nutrient uptake and promote healthier plant growth for your hydroponic system.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding pH in Hydroponics
- The Importance of pH Control in Hydroponics
- Factors Affecting pH in Hydroponic Systems
- Testing the pH of Hydroponic Solutions
- Methods for Lowering pH in Hydroponics
- Using pH Adjusters in Hydroponics
- Organic Alternatives for Lowering pH in Hydroponics
- Maintaining Optimal pH Levels in Hydroponic Systems
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of eco-friendly gardening! If you’re passionate about gardening and want to make a positive impact on the environment, then eco-friendly gardening is the way to go. One aspect of eco-friendly gardening that deserves special attention is hydroponics, a soilless gardening method that uses mineral nutrient solutions in water.
Hydroponics offers a range of advantages over traditional soil-based gardening, including greater control over plant nutrition, reduced water usage, and increased crop yields. However, to successfully grow plants hydroponically, it is crucial to understand and manage the pH level of the nutrient solution.
In this article, we will delve into the world of pH in hydroponics, exploring its importance and the factors that affect it. We will also discuss different methods for testing and adjusting pH levels in hydroponic systems. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced hydroponic gardener, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to maintain optimal pH levels and achieve successful and eco-friendly hydroponic gardening results.
Understanding pH in Hydroponics
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, and it plays a crucial role in hydroponics. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being considered neutral. A pH value below 7 indicates acidity, while a pH value above 7 indicates alkalinity. In hydroponics, maintaining a specific pH range is essential for optimal plant growth and nutrient absorption.
Plants have specific pH preferences for nutrient uptake, and deviating too far from their ideal pH range can result in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. Different plants have different pH requirements, but most hydroponic crops thrive in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 5.5 to 6.5.
A pH level that is too high (alkaline) can lead to nutrient lockout, where certain essential nutrients become less available to the plants. On the other hand, a pH level that is too low (acidic) can cause nutrient imbalances and damage to plant roots. It is crucial to monitor and adjust the pH of the hydroponic solution to ensure optimal nutrient uptake and prevent plant stress.
The pH level in hydroponics can fluctuate due to various factors such as the type of water used, nutrient solution composition, temperature, and biological activity in the system. Understanding these factors is key to effectively managing and maintaining pH levels in your hydroponic setup.
When it comes to water sources, tap water can vary in pH depending on the region. Some tap water sources are naturally acidic or alkaline, while others may undergo treatment that alters their pH. Therefore, it is important to test and adjust the pH of your water before using it in your hydroponic system.
The nutrient solution’s composition also affects pH levels. Hydroponic nutrients are typically formulated to be pH balanced, but as plants absorb nutrients over time, the pH of the solution can change. This is why regular monitoring and adjustment are necessary to maintain an ideal pH range.
Temperature can also influence pH in hydroponics. Higher temperatures can cause the pH to rise, while lower temperatures can cause it to decrease. It is essential to monitor and adjust the pH according to temperature changes to ensure optimal nutrient availability for your plants.
The Importance of pH Control in Hydroponics
pH control is of utmost importance in hydroponics because it directly affects plant health and nutrient absorption. Maintaining the proper pH level in the nutrient solution ensures that plants can access essential nutrients for their growth and development.
One of the main reasons why pH control is crucial in hydroponics is because nutrient availability is pH-dependent. Each nutrient has a specific pH range in which it is most soluble and readily available to plants. Deviating from this optimal pH range can lead to nutrient imbalances or deficiencies, impairing plant growth and overall productivity.
For instance, at high pH levels, certain nutrients like iron and manganese tend to precipitate and become insoluble. This makes them less accessible to plants, ultimately leading to deficiencies. On the other hand, at low pH levels, nutrients such as calcium and magnesium can become more available but can also lead to imbalances and toxicity, affecting plant health.
In addition to nutrient availability, pH control also plays a crucial role in the functioning of beneficial microbes in hydroponic systems. These beneficial microbes, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria, mycorrhizal fungi, and other beneficial bacteria, contribute to nutrient cycling and plant health. However, their activity and effectiveness can be greatly influenced by pH. Maintaining an optimal pH range ensures that these beneficial microbes can thrive and support the overall health of the plants.
Furthermore, pH control is essential for preventing the growth of harmful pathogens and diseases in hydroponic systems. Many plant pathogens have specific pH requirements for growth and reproduction. By maintaining a pH level outside of their optimal range, you can create an unfavorable environment for these pathogens, reducing the risk of infection and disease outbreaks.
Overall, proper pH control is vital for maximizing nutrient availability, supporting beneficial microbial activity, and preventing the proliferation of harmful pathogens in hydroponic systems. By carefully monitoring and adjusting the pH of your nutrient solution, you can ensure optimal plant health, growth, and overall success in your eco-friendly hydroponic garden.
Factors Affecting pH in Hydroponic Systems
Several factors can influence the pH level in hydroponic systems. Understanding these factors is essential to effectively manage and control the pH of the nutrient solution. Let’s explore some of the key factors that can affect pH in hydroponics:
1. Water source: The source of water used in hydroponics can have a significant impact on pH. Tap water can vary in pH depending on the region and treatment processes. Some tap water sources are naturally acidic or alkaline, while others may have undergone treatment that alters their pH. It is crucial to test the pH of your water source and adjust it if necessary before using it in your hydroponic system.
2. Nutrient solution composition: The composition of the nutrient solution itself can impact pH levels. Hydroponic nutrient formulations are typically designed to be pH balanced. However, as plants uptake nutrients over time, the pH of the solution can shift. Different nutrient formulations can also have different pH effects. Monitoring and adjusting the nutrient solution’s pH regularly is crucial to maintain optimal nutrient availability.
3. Temperature: Temperature plays a role in pH levels in hydroponics. Higher temperatures can cause the pH to rise, while lower temperatures can lower the pH. This is due to the influence of temperature on chemical reactions and the solubility of certain compounds. It is essential to monitor the pH closely and make adjustments if needed based on temperature changes in your hydroponic system.
4. Plant uptake and nutrient interactions: The uptake of nutrients by plants and their interactions with each other can also impact the pH of the nutrient solution. As plants absorb nutrients, the pH can fluctuate due to changes in nutrient concentrations. Different nutrients can also interact with each other, affecting pH levels. Regular monitoring of the pH and nutrient levels allows for timely adjustments to maintain a stable and optimal pH range.
5. Biological activity: The presence of beneficial microbes and other microorganisms in the hydroponic system can influence pH levels. These microorganisms can have metabolic processes that can impact pH, either by producing acids or by changing nutrient availability. Maintaining a well-balanced microbial population and a healthy ecosystem in the hydroponic system is essential for pH stability.
By taking into account these factors and monitoring the pH regularly, hydroponic gardeners can maintain a stable and optimal pH range for their plants. This ensures that plants can access the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and maximizes their overall productivity in eco-friendly gardening.
Testing the pH of Hydroponic Solutions
Regularly testing the pH of your hydroponic nutrient solution is crucial to maintaining optimal plant health and nutrient availability. Fortunately, there are several methods available to accurately measure the pH level. Let’s explore some common techniques for testing the pH of hydroponic solutions:
1. pH Test Strips: pH test strips are an affordable and convenient option for testing pH levels in hydroponic systems. These strips are coated with a pH-sensitive indicator that changes color based on the pH of the solution. Simply dip the strip into the nutrient solution and compare the color against a provided chart to determine the pH level. While test strips are easy to use, they may not provide the same level of accuracy as more precise testing methods.
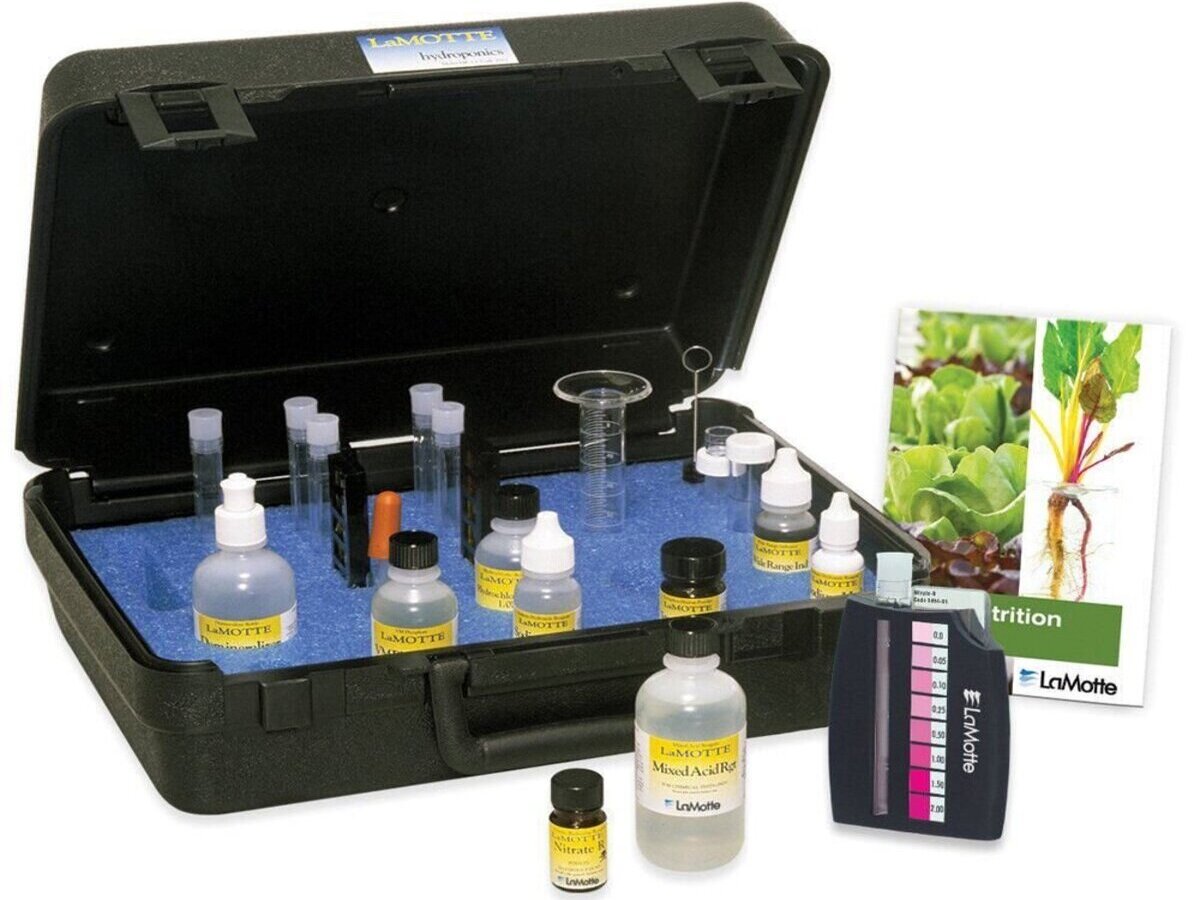
2. pH Test Kits: pH test kits typically include liquid reagents and a color comparison chart. To use a test kit, you’ll need to fill a test tube with a sample of the nutrient solution, add a few drops of the provided reagent, and compare the resulting color to the chart. pH test kits offer a more precise measurement compared to test strips and are suitable for hydroponic gardeners who require greater accuracy.
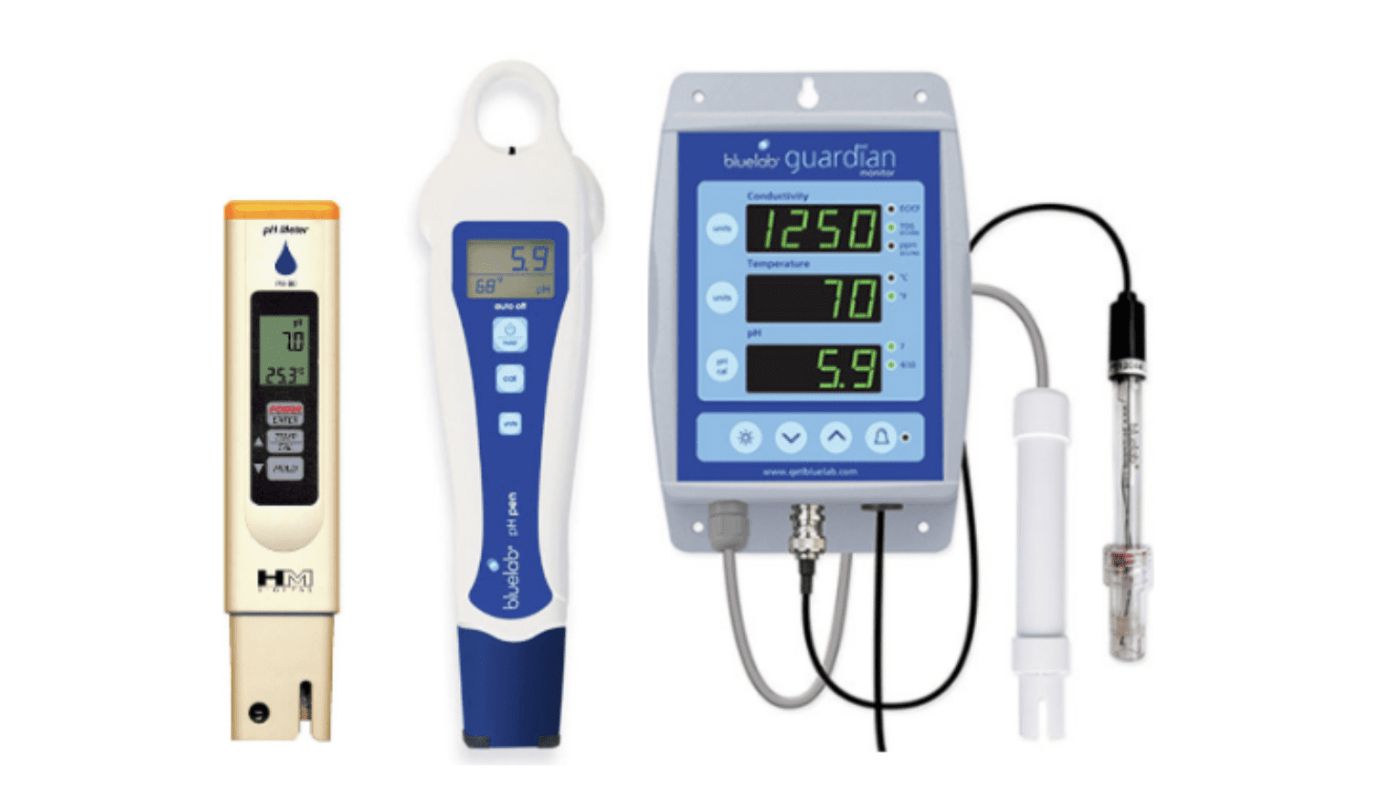
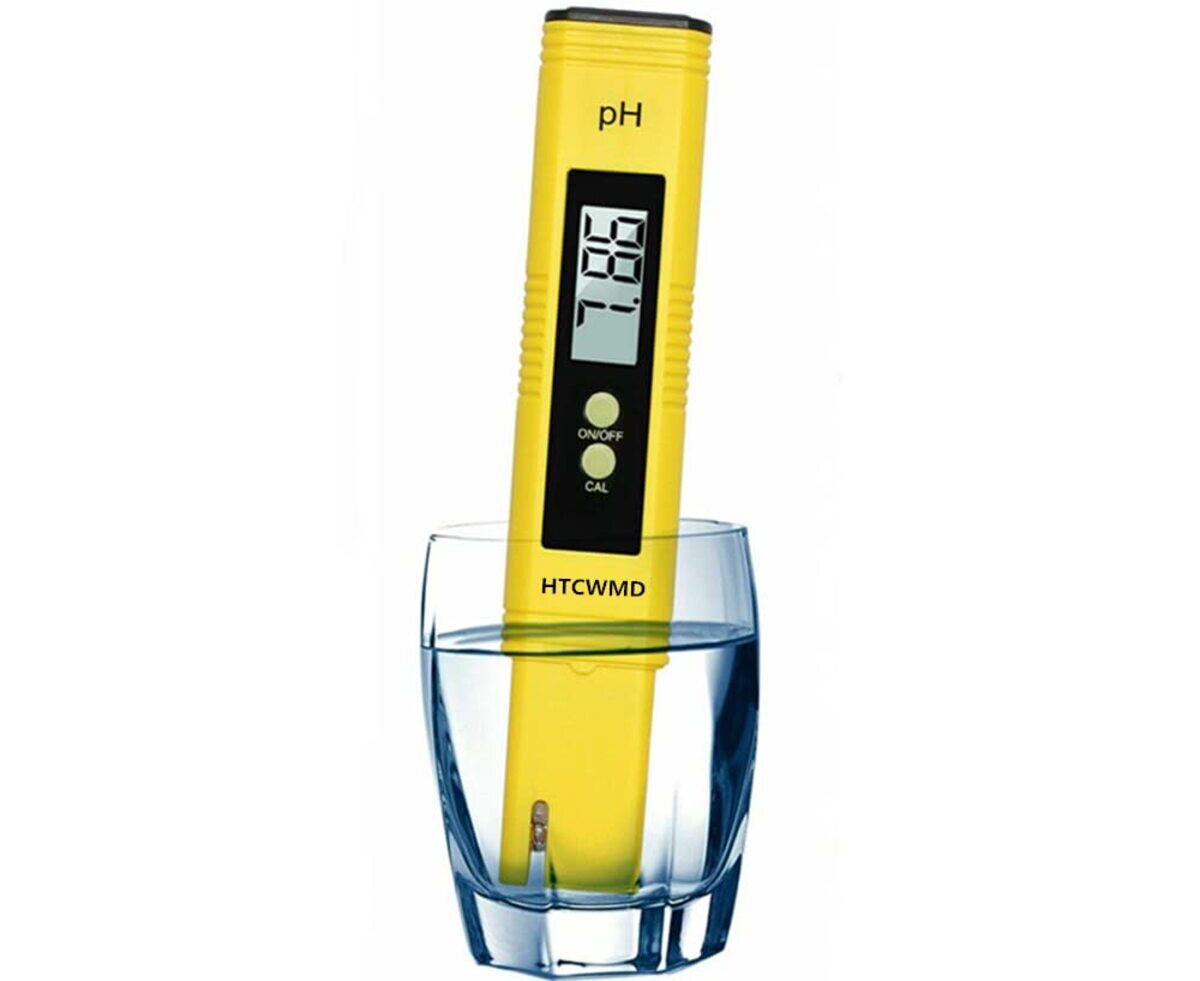
3. Digital pH Meters: Digital pH meters are highly accurate instruments for measuring pH levels in hydroponic solutions. These meters consist of a probe that is submerged directly into the nutrient solution, and they provide an instant digital readout of the pH value. Digital pH meters are easy to use and offer precise measurements, making them a popular choice for serious hydroponic gardeners. However, they require regular calibration and maintenance to ensure accurate readings.
When testing the pH of your hydroponic solution, it’s important to take multiple readings across different areas of the system to ensure consistency. pH levels can vary within a hydroponic setup, so testing different points such as the reservoir, nutrient solution, and runoff can provide a comprehensive understanding of the overall pH conditions.
In addition to regular pH testing, it is recommended to keep a log of your pH readings. This allows you to track pH trends over time and identify any potential issues or fluctuations that may arise. By keeping accurate and organized records, you can make precise adjustments to maintain the optimal pH range for your hydroponic crop.
Remember that maintaining a stable pH range is crucial for successful hydroponic gardening. By regularly testing the pH of your nutrient solution using these various methods, you can ensure that your plants have the ideal pH conditions for optimal nutrient uptake and growth.
Methods for Lowering pH in Hydroponics
Lowering the pH of your hydroponic nutrient solution is essential when it becomes too alkaline for optimal plant growth. Fortunately, there are several effective methods available to lower the pH in hydroponics. Let’s explore some common techniques:
1. pH Down Solutions: pH down solutions are commercially available products that are specifically designed to lower the pH of hydroponic nutrient solutions. These solutions are usually concentrated acids, such as phosphoric acid or citric acid, that can easily and safely lower the pH. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper dosage and gradually adjust the pH while monitoring closely to avoid overshooting the desired pH range.
2. Vinegar or Citric Acid: Natural acids like vinegar or citric acid can be used to lower the pH in hydroponics. They are cost-effective and readily available options. When using vinegar, choose white distilled vinegar with 5% acidity. However, it’s important to use these acids carefully and in moderation, as excessive amounts can harm plants. Begin by adding small amounts and test the pH regularly until the desired range is achieved.
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Injection: Carbon dioxide injection is another effective method for lowering pH in hydroponics. When carbon dioxide is dissolved in water, it forms carbonic acid, which can naturally lower the pH. CO2 injection systems are available for this purpose and can be controlled using timers or pH controllers. This method not only lowers pH but also provides a boost of carbon dioxide to enhance plant growth and productivity.
4. Acidic Fertilizers: Some organic fertilizers naturally have acidic properties and can be used to lower pH in hydroponic systems. For example, certain formulations of fish emulsion or seaweed extract can help acidify the nutrient solution. However, it is important to carefully monitor the pH when using organic fertilizers, as they can vary in acidity, and excessive use may lead to imbalances or nutrient deficiencies.
5. Reverse Osmosis Water: Using reverse osmosis water as a source for your hydroponic system can help lower the pH. Reverse osmosis removes impurities and minerals from the water, which can contribute to higher pH levels. However, it’s important to note that using reverse osmosis water alone may not be sufficient to significantly lower pH. It should be used in conjunction with other pH-lowering methods for best results.
Remember to test the pH regularly when implementing these methods and make adjustments gradually. Sudden and drastic pH changes can shock plants and cause stress. Aim to achieve a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 5.5 to 6.5, which is ideal for most hydroponic crops.
By utilizing these methods for lowering pH in hydroponics, you can create an optimal growing environment for your plants, ensuring they have access to the right balance of nutrients for healthy and vigorous growth.
Using pH Adjusters in Hydroponics
pH adjusters are essential tools for maintaining the ideal pH range in hydroponic systems. These products help raise or lower the pH of the nutrient solution to ensure optimal nutrient availability for plants. Here are some key considerations and guidelines for using pH adjusters effectively in hydroponics:
1. Understanding pH Adjusters: pH adjusters are typically chemicals or compounds that have acidic or alkaline properties, allowing you to increase or decrease the pH of the nutrient solution. Common pH adjusters include concentrated acids (such as phosphoric acid) to lower pH and alkaline substances (such as potassium hydroxide) to raise pH. It is important to select pH adjusters that are designed specifically for hydroponic use to ensure their safety and compatibility with plant and system requirements.
2. Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Each pH adjuster product has specific instructions for usage, concentrations, and precautions. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure safe and effective application. Improper use or excessive application of pH adjusters can have detrimental effects on plant health and system stability. Always start with smaller doses and gradually adjust as needed, testing the pH frequently to achieve the desired range.
3. pH Monitoring: Regular monitoring of the pH is critical when using pH adjusters. pH levels can fluctuate over time due to nutrient uptake, system changes, and environmental factors. Use a reliable pH meter or test kit to measure the pH of the nutrient solution and make adjustments as necessary. Maintain a consistent pH testing schedule to stay proactive and prevent drastic pH swings that can stress plants and impact nutrient availability.
4. Make Gradual Adjustments: It is important to make gradual adjustments to the pH of the nutrient solution. Rapid and drastic pH changes can shock plants and disrupt their nutrient absorption. Start with small increments in pH adjustment and allow sufficient time for the system to stabilize before making further adjustments. Regular monitoring and gradual pH changes promote a stable growing environment for plants.
5. Safety Precautions: When working with pH adjusters, it is crucial to prioritize safety. Wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, to avoid direct contact with the skin or eyes. Store pH adjusters in a cool, dry place and out of reach of children or pets. Follow proper disposal guidelines for pH adjuster waste or unused solutions to minimize environmental impact.
Remember, pH adjusters are valuable tools for maintaining the optimal pH range in hydroponics, but they should be used with caution and in accordance with the instructions provided. Regular monitoring, gradual adjustments, and attention to safety ensure the best results for your hydroponic garden, promoting healthy plant growth and maximal nutrient uptake.
Organic Alternatives for Lowering pH in Hydroponics
For eco-conscious hydroponic gardeners, there are several organic alternatives available for lowering the pH of the nutrient solution. These natural methods provide an environmentally friendly approach to adjust the pH while minimizing the use of synthetic chemicals. Let’s explore some organic alternatives for lowering pH in hydroponics:
1. Citric Acid: Citric acid, derived from citrus fruits, is an organic option for lowering pH in hydroponics. It is a weak acid that can safely and effectively lower pH levels. Citric acid can be found in powdered form and easily dissolved in water. Start with small amounts, gradually adding and testing the pH until you reach the desired range. Citric acid is a popular choice for organic growers due to its availability and gentle nature.
2. Vinegar: Vinegar is another organic option for lowering pH in hydroponics. It contains acetic acid, which can effectively lower pH levels. White distilled vinegar is a commonly used type of vinegar for this purpose. Like citric acid, vinegar should be used in small amounts and added gradually while monitoring the pH. Avoid using vinegars that contain additives or flavorings, as they may not be suitable for hydroponic systems.
3. Ascorbic Acid: Ascorbic acid, also known as vitamin C, is an organic acid that can be used to lower pH in hydroponics. It is available in powdered form and can be dissolved in water. Ascorbic acid is not only an effective pH adjuster but also provides some additional benefits to plants, acting as an antioxidant and promoting healthy growth. Start with small amounts and adjust gradually to achieve the desired pH range.
4. Organic Acidic Fertilizers: Some organic fertilizers have natural acidic properties that can help lower pH in hydroponic systems. For example, humic acid and fulvic acid-based fertilizers can lower the pH while providing essential nutrients and promoting beneficial microbial activity. It is important to choose organic fertilizers that are specifically formulated for hydroponic use and follow the recommended application rates to prevent nutrient imbalances.
5. Sulfur: Sulfur can be used as an organic method to lower pH in hydroponics. Elemental sulfur can be applied to the growing medium or dissolved in water to gradually lower pH over time. The sulfur reacts with moisture and soil microorganisms to produce sulfuric acid, which lowers the pH. This method requires careful monitoring and patience, as it can take several weeks for the pH to stabilize. It is important to avoid excessive sulfur applications, as high sulfur levels can be toxic to plants.
When using organic alternatives to lower pH in hydroponics, it is important to monitor the pH closely and make adjustments gradually. Organic methods may take longer to achieve the desired pH range compared to synthetic alternatives, so patience and regular testing are key. By utilizing these organic options, you can maintain an eco-friendly approach to pH control in your hydroponic garden while promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing nutrient uptake.
Maintaining Optimal pH Levels in Hydroponic Systems
Maintaining optimal pH levels in a hydroponic system is crucial for the overall health and productivity of your plants. A stable pH ensures that nutrients are readily available for absorption, promoting vigorous growth and preventing nutrient imbalances. Here are some important steps to help you maintain optimal pH levels in your hydroponic system:
1. Regular pH Monitoring: Regularly monitor the pH of your hydroponic nutrient solution to catch any fluctuations or imbalances early on. Use a reliable pH meter or test kit to accurately measure the pH. Take multiple measurements at different points in the system, such as the reservoir, nutrient solution, and runoff, to ensure consistency. Record your pH readings in a logbook for easy reference and comparison over time.
2. Adjust pH Gradually: When the pH deviates from the desired range, make adjustments gradually to avoid shocking the plants. Whether using pH-adjusting solutions or organic alternatives, add small amounts at a time and thoroughly mix the solution before retesting. It is important to keep in mind that pH adjustments may take some time to stabilize, so patience is key. Aim for a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 5.5 to 6.5, which is suitable for most hydroponic crops.
3. Maintain Proper Water Quality: The quality of the water you use in your hydroponic system can impact pH levels. If using tap water, test its pH and adjust if necessary before adding nutrients. Consider using filtered or reverse osmosis (RO) water to minimize the presence of impurities and avoid potential pH fluctuations caused by minerals in the water.
4. Nutrient Solution Balance: Ensure that your nutrient solution is properly balanced to avoid pH imbalances. Follow the recommended dosages and ratios for your specific crop and growth stage. Overfeeding or underfeeding plants can lead to nutrient imbalances, which in turn can affect pH levels. Regularly monitor nutrient levels and adjust as needed to maintain a balanced and healthy nutrient solution.
5. Promote Beneficial Microbial Activity: Having a diverse and thriving population of beneficial microbes in your hydroponic system can help maintain pH stability. These beneficial microbes contribute to nutrient cycling and assist in maintaining a healthy balance. Consider using microbial inoculants or compost tea to introduce beneficial microorganisms to your system. Regularly monitor the microbial activity and adjust the pH as needed to support their growth and effectiveness.
6. Diligent System Maintenance: Proper system maintenance is key to minimizing pH fluctuations. Regularly clean and sanitize your hydroponic system to remove any potential sources of imbalance or contamination. Check for clogs, leaks, or any other issues that may affect nutrient circulation. A well-maintained system promotes a stable environment for your plants and helps prevent pH deviations.
By following these steps and remaining vigilant in pH monitoring and adjustment, you can maintain optimal pH levels in your hydroponic system. This promotes healthy plant growth, maximizes nutrient availability, and ultimately leads to a successful and productive eco-friendly hydroponic garden.
Conclusion
Maintaining the proper pH level in hydroponics is crucial for the success of your eco-friendly gardening endeavors. By understanding the significance of pH control and the factors that affect pH levels, you can create an optimal growing environment for your plants. Regular testing and monitoring of pH, along with gradual adjustments using pH adjusters or organic alternatives, allow you to maintain the desired pH range for optimal nutrient availability and plant health.
Remember to implement proper pH monitoring techniques, such as using pH meters, test kits, or pH strips, to accurately measure pH levels. Continuously track and record these measurements to detect any deviations and make necessary adjustments. Understand that pH control is an ongoing process, and maintaining a stable pH range requires consistency and attention to detail.
Additionally, consider the use of eco-friendly and organic alternatives for lowering pH, such as citric acid, vinegar, or organic acidic fertilizers, to minimize the use of synthetic chemicals. These options offer a more sustainable approach to pH control in hydroponics while promoting plant health and minimizing environmental impact.
Lastly, don’t overlook the importance of proper system maintenance and promoting beneficial microbial activity. Ensuring a clean and well-maintained hydroponic system, as well as fostering a diverse microbial community, contributes to pH stability and overall plant vitality.
With a solid understanding of pH control, regular monitoring, and the application of appropriate pH adjustment methods, you can cultivate a thriving hydroponic garden that optimizes plant growth and productivity while minimizing ecological impact.
So, embrace the world of eco-friendly gardening through meticulous pH control and embark on an exciting journey of nurturing healthy plants, conserving water, and contributing to a greener future.