Home>Gardening Tips and Tricks>Eco-Friendly Gardening>What Should The pH Level Be For Hydroponics


Eco-Friendly Gardening
What Should The pH Level Be For Hydroponics
Published: September 22, 2023
Learn about the ideal pH level for hydroponics in eco-friendly gardening. Discover how to maintain optimal conditions for your hydroponic system.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to gardening, there is a growing trend towards eco-friendly practices that not only promote a healthier environment but also yield impressive results. One such practice gaining popularity is eco-friendly gardening, which aims to minimize the use of harmful chemicals and maximize sustainability. One important aspect of eco-friendly gardening is maintaining a balanced pH level in your garden, especially in hydroponic systems.
pH, which stands for “potential of Hydrogen,” is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. It is an essential factor in maintaining optimal plant health and growth as it affects nutrient absorption and overall plant metabolism. In hydroponics, a soil-less method of gardening where plants are grown in nutrient-rich water solutions, proper pH management is crucial for the success of your garden.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of pH in hydroponics, explore the optimal pH range for this gardening technique, discuss the various factors that influence pH levels, and provide valuable insights into how to monitor and adjust pH in hydroponic systems. We will also highlight some common pH problems and their solutions, ensuring that you have all the necessary knowledge to create a thriving and environmentally friendly hydroponic garden.
What is pH?
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance and is based on a scale ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, while values below 7 are acidic and values above 7 are alkaline. The pH scale is logarithmic, which means that each unit represents a tenfold difference in acidity or alkalinity. For example, a substance with a pH of 6 is ten times more acidic than a substance with a pH of 7.
pH is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. When acids dissolve in water, they release hydrogen ions, increasing the concentration of H+ and lowering the pH. Conversely, when bases or alkalis dissolve in water, they release hydroxyl ions (OH-) which combine with hydrogen ions, reducing their concentration and raising the pH.
In gardening, understanding pH is essential as it directly affects plant health and nutrient availability. Different plants have varying pH preferences, with some thriving in acidic conditions, and others preferring alkaline environments. It is crucial to match the pH level of the growing medium or nutrient solution to the specific needs of the plants being cultivated to ensure optimum growth and nutrient uptake.
Importance of pH in Hydroponics
Maintaining the appropriate pH level is vital for the success of any hydroponic system. In hydroponics, plants receive nutrients directly from water, without the use of soil as a medium. Consequently, the pH of the nutrient solution greatly influences the availability and absorption of essential nutrients required for plant growth. Here are some key reasons why pH is crucial in hydroponics:
- Nutrient availability: Different nutrients are more readily available to plants at specific pH levels. For example, iron is best absorbed by plants in slightly acidic conditions, while calcium is more accessible in slightly alkaline conditions. By adjusting the pH, you can ensure that all necessary nutrients are readily available to your plants.
- Nutrient uptake: pH level affects the ability of plants to take up nutrients effectively. When the pH deviates from the optimal range, certain essential elements may become unavailable due to precipitation or complex chemical reactions. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies and hinder plant growth.
- Plant metabolism: pH influences enzymatic activity and overall plant metabolism. Enzymes play a vital role in various biological processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, and nutrient uptake. Maintaining the appropriate pH range helps regulate enzyme activity and ensures proper plant functioning.
- Microorganisms: pH affects the balance of beneficial microorganisms in the hydroponic system. These microorganisms help break down organic matter and contribute to nutrient cycling. Maintaining a suitable pH range promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms, fostering a healthy and sustainable hydroponic ecosystem.
- Preventing nutrient lockout: Extreme pH levels can lead to nutrient lockout, where plants are unable to absorb certain nutrients, even if they are present in the solution. This can cause nutrient deficiencies, stunted growth, and poor yield. Regular pH monitoring and adjustment are necessary to prevent nutrient lockout.
Optimal pH Range for Hydroponics
Finding and maintaining the optimal pH range is essential for the successful growth of plants in hydroponics. The ideal pH range may vary slightly depending on the types of plants being grown, but generally falls between 5.5 and 6.5. Here’s why this range is considered optimal for hydroponics:
- Nutrient availability: Most essential nutrients required for plant growth are most readily available within the pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. This ensures that plants can absorb nutrients efficiently, maximizing their growth potential.
- Avoiding nutrient deficiencies: When the pH strays too far from the optimal range, certain nutrients may become less available to plants, leading to deficiencies. By maintaining the pH within the recommended range, you can help prevent nutrient imbalances and deficiencies.
- Microbial activity: The optimal pH range also supports a healthy microbial population in the hydroponic system. Beneficial microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and maintaining a balanced ecosystem. The pH range of 5.5 to 6.5 promotes the growth of these beneficial microorganisms.
- Minimizing pathogen risk: Extreme pH levels can create an environment favorable to the growth of harmful pathogens, such as fungi and bacteria. By keeping the pH within the optimal range, you reduce the risk of pathogen infestations, ensuring the health and wellbeing of your plants.
It is important to note that the optimal pH range can vary slightly depending on the specific needs of the plants being grown. Some plants, like tomatoes and peppers, prefer a slightly more acidic pH, while others, like lettuce and herbs, tolerate a slightly more alkaline pH. Consult plant-specific guidelines or conduct pH preference research for the crops you are growing to fine-tune the pH levels within the optimal range.
Maintaining the optimal pH range is crucial, but it is equally important to avoid rapid and drastic pH fluctuations. Sudden pH changes can cause stress to plants and disrupt nutrient uptake. Regular monitoring and gradual adjustments to maintain a stable and suitable pH environment will promote healthy growth and maximize the potential of your hydroponic garden.
Factors Affecting pH in Hydroponics
Several factors can influence the pH levels in a hydroponic system. Understanding these factors is essential for maintaining the optimal pH range and ensuring the health and productivity of your plants. Here are some key factors that can affect pH in hydroponics:
- Source water: The pH of your source water can have a significant impact on the initial pH of your nutrient solution. Some water sources naturally have high or low pH levels, which may need adjustment to match the optimal range for hydroponics.
- Nutrient solutions: The pH of nutrient solutions can vary based on the specific formulation and the ratios of different nutrients. It is important to use high-quality, pH-balanced nutrient solutions to avoid any imbalances that may impact the pH of the system.
- Plant uptake: As plants absorb nutrients from the solution, the pH can be affected. Different plants have varying nutrient uptake rates, which can influence pH levels. It is important to monitor pH regularly and make necessary adjustments to maintain a stable environment for optimal plant growth.
- Nutrient deficiencies or excesses: Certain nutrient deficiencies or excesses can impact the pH of the hydroponic system. For example, an excess of certain nutrients can increase acidity, while deficiencies can lead to alkalinity. Proper nutrient management is essential to maintaining a balanced pH.
- Plant respiration: During respiration, plants release carbon dioxide, which can affect the pH of the surrounding solution. Increased carbon dioxide levels can lead to a decrease in pH. Proper aeration and ventilation in the hydroponic system can help regulate pH fluctuations caused by plant respiration.
- Microbial activity: The presence of beneficial microorganisms in the hydroponic system can impact pH levels. Some microorganisms produce acidic or alkaline byproducts as part of their metabolic processes, which can influence the pH of the solution. Maintaining a healthy microbial balance is important for pH stability.
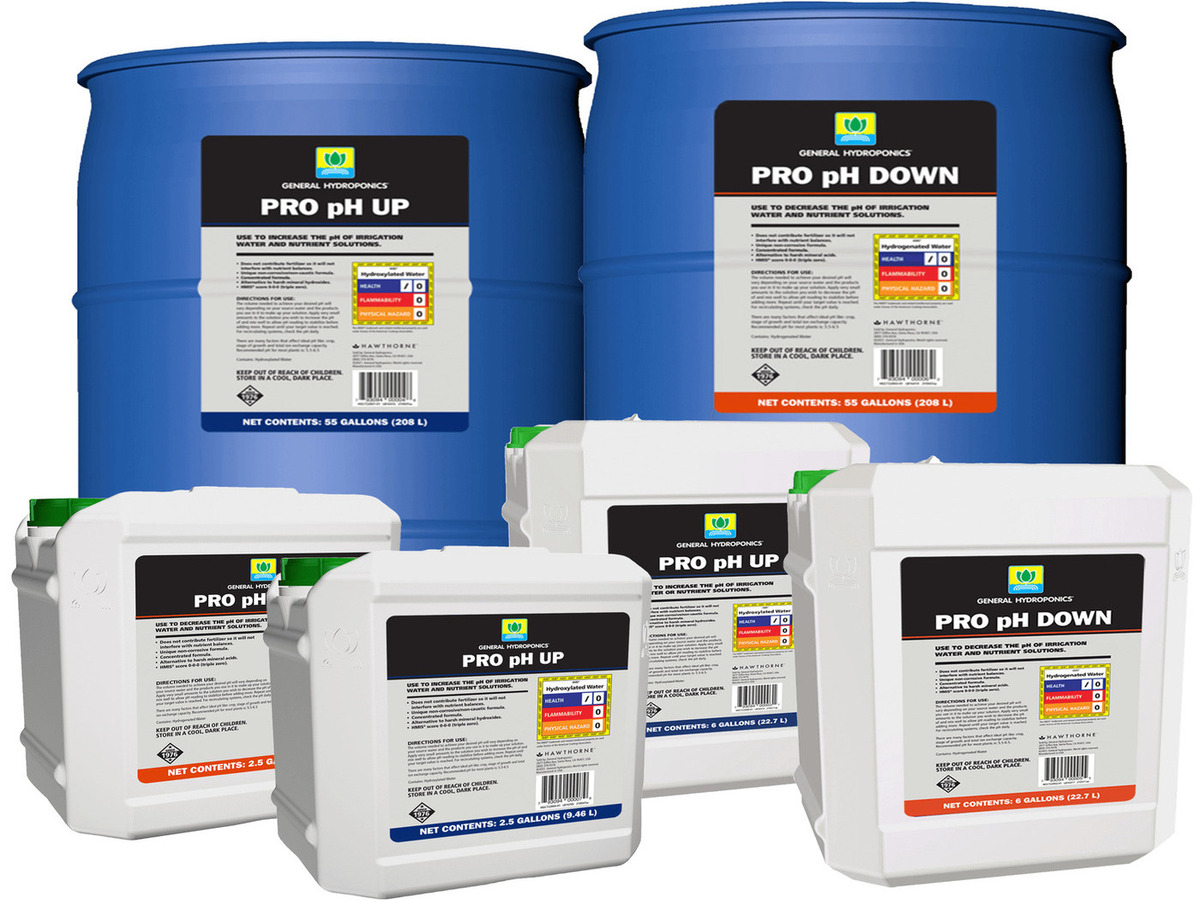
- pH adjustment substances: The use of pH adjustment substances, such as pH up or pH down solutions, can directly impact the pH levels in hydroponics. These substances should be used cautiously and in accordance with the recommended guidelines to prevent drastic pH fluctuations.
By understanding and managing these factors, you can maintain a stable and optimal pH range in your hydroponic system. Regular monitoring, appropriate nutrient management, and attention to water quality will help ensure that your plants have the ideal pH conditions to thrive and reach their full potential.
Monitoring and Adjusting pH in Hydroponic Systems
Monitoring and adjusting pH levels in hydroponic systems is a critical aspect of maintaining optimal plant health and maximizing growth and yield. Here are some key steps to effectively monitor and adjust pH in your hydroponic system:
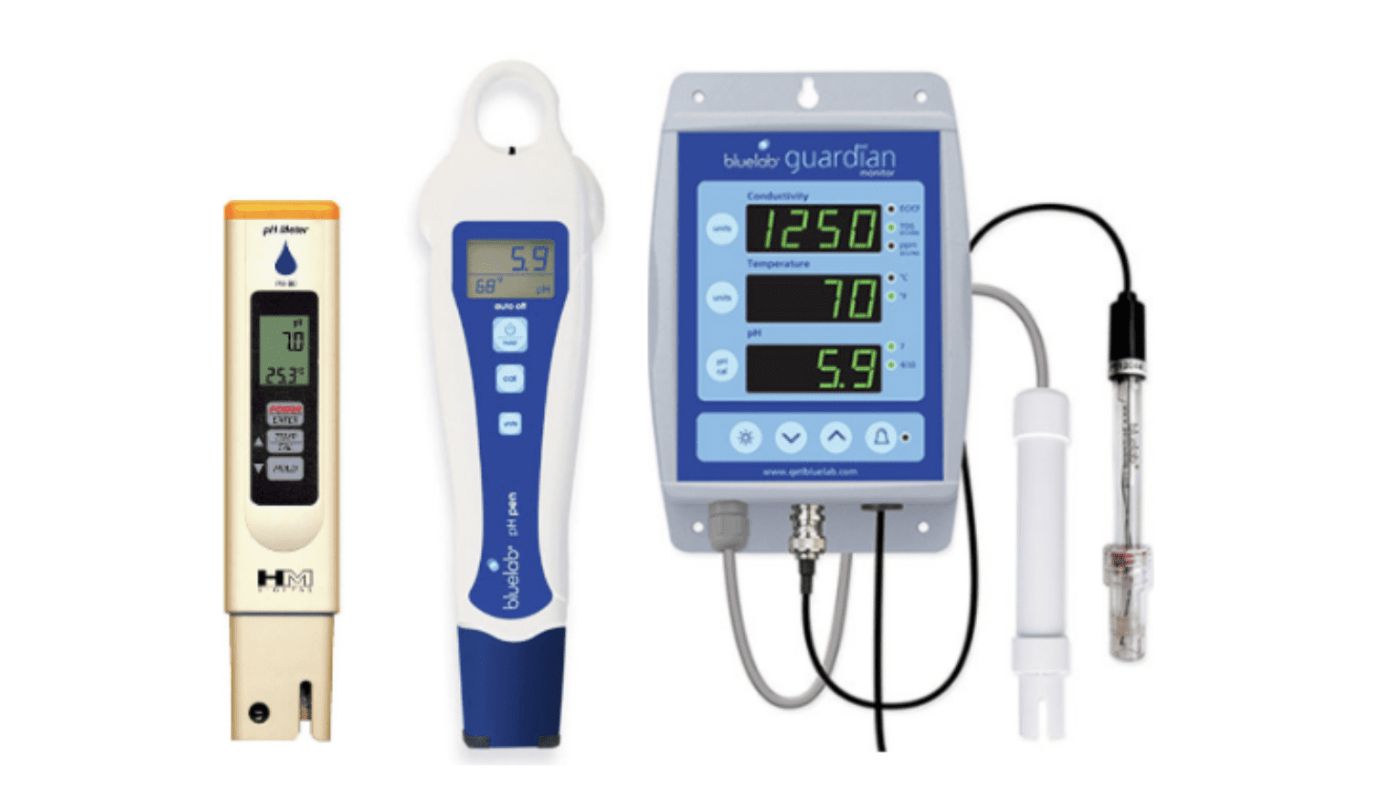
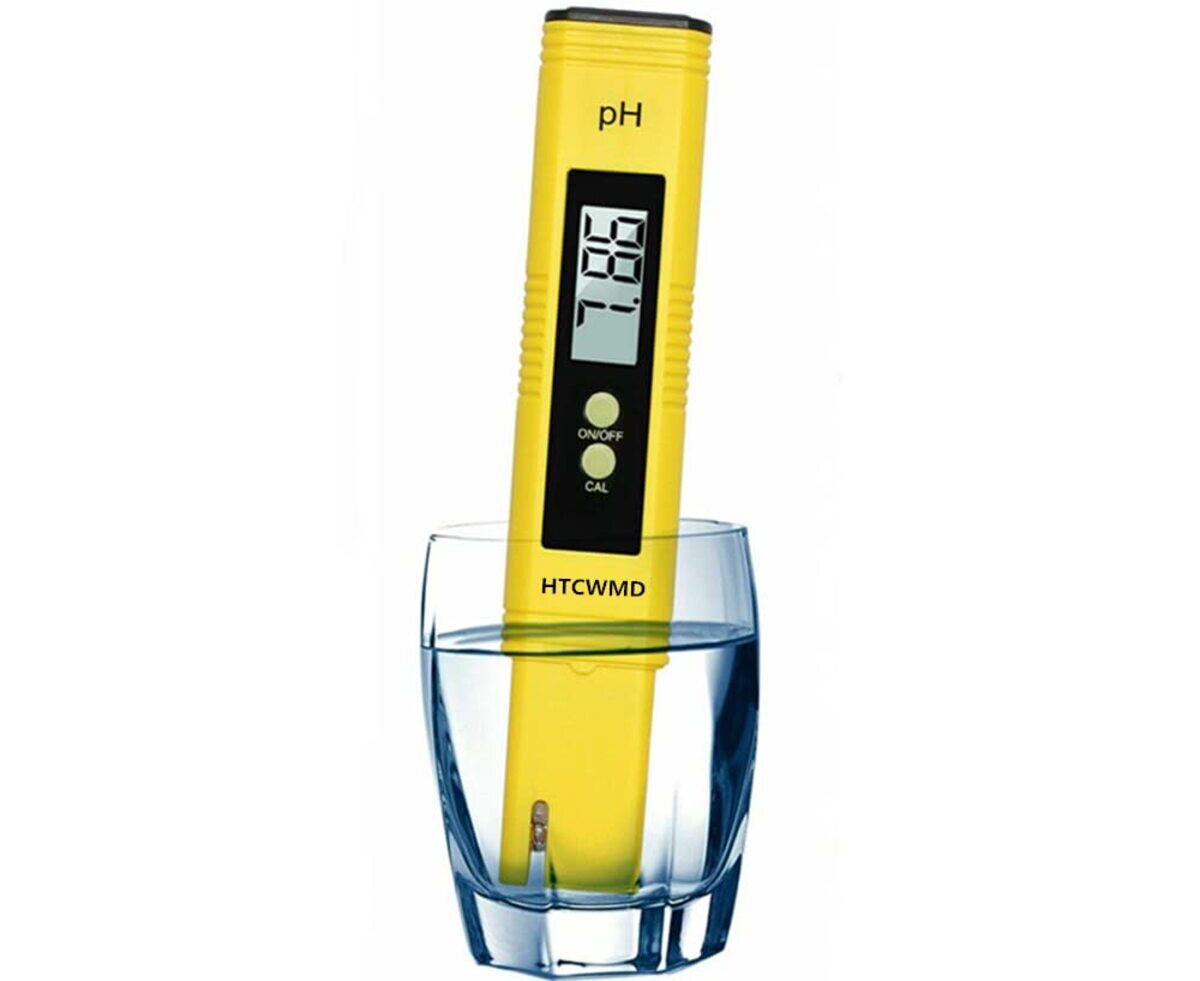
- Regularly test the pH of your nutrient solution using a pH testing kit or pH meter. The frequency of testing may vary depending on the specific needs of your plants and the stability of your system. Aim to test the pH at least once a day, preferably during the same time each day.
- If the pH falls outside the optimal range, use pH adjustment substances like pH up or pH down to bring it back into the desired range. Be cautious when adjusting the pH as small increments are typically more effective and prevent overshooting the target range.
- pH buffering agents can be used to stabilize the pH levels and prevent rapid fluctuations. These buffering agents help maintain a more stable pH by resisting changes caused by acidification or alkalization. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully when using pH buffering agents.
- Invest in a reliable pH meter for accurate and precise measurement of pH levels. pH meters provide digital readings and are more reliable and convenient compared to pH testing kits. Regularly calibrate your pH meter according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accurate readings.
- As plants uptake nutrients, the pH in the system can change. Monitor the pH daily and make the necessary adjustments to keep it within the optimal range. Be patient and make small adjustments over time, as sudden and drastic pH changes can stress the plants and disrupt nutrient uptake.
- Keep a record of your pH monitoring and adjustment activities. This will help you identify patterns or trends and make informed decisions for maintaining the pH of your hydroponic system. Note any changes in nutrient solutions, water sources, or other factors that may impact pH levels.
Maintaining a stable pH range is crucial for the overall success of your hydroponic garden. By implementing regular monitoring, adjusting pH as needed, and using appropriate pH buffering agents, you can ensure that your plants have the ideal pH conditions for optimal growth and nutrient absorption.
Remember, each plant species may have different pH preferences, so it is important to research and understand the specific pH requirements of the crops you are growing. By providing the optimal pH conditions, you’ll enhance the overall health and productivity of your hydroponic garden.
Common pH Problems in Hydroponics
Maintaining a suitable pH range is crucial in hydroponics, as deviations from the optimal pH can lead to various problems for your plants. Here are some of the common pH-related issues that you may encounter in hydroponic systems:
- High or low pH: Extreme pH levels can negatively impact nutrient availability and uptake. A high pH, typically above 7.0, can lead to nutrient deficiencies, particularly for iron, manganese, and phosphorus. Conversely, a low pH, typically below 5.0, can cause nutrient toxicity, especially for manganese, iron, and aluminum.
- pH drift: pH drift occurs when the pH of the nutrient solution gradually shifts away from the desired range over time. This can result from factors such as nutrient dosing, evaporation, plant uptake, or the accumulation of organic acids. pH drift can lead to nutrient imbalances and hinder overall plant growth.
- pH fluctuations: Rapid and drastic fluctuations in pH can stress plants and disrupt nutrient uptake. This can occur due to improper pH adjustment practices or poor pH maintenance. pH fluctuations can result in nutrient lockout, stunted growth, and reduced overall plant health.
- pH imbalance from nutrient solutions: Incorrectly mixed or imbalanced nutrient solutions can lead to pH issues. Using low-quality or inconsistent nutrient solutions can result in pH imbalances and hinder plant growth and development.
- Inadequate pH monitoring: Failing to regularly monitor pH levels can lead to pH-related problems going unnoticed until they become more severe. It is essential to establish a routine for pH testing and record keeping to promptly identify and address any pH issues that arise.
- Impact on beneficial microorganisms: pH imbalances can inhibit the growth and activity of beneficial microorganisms in the hydroponic system. These microorganisms play an important role in nutrient cycling and maintaining a healthy ecosystem. pH-related problems can disrupt the balance of these microorganisms and negatively impact overall system health.
- Plant stress and reduced productivity: When pH levels are outside the optimal range, plant stress can occur, leading to reduced productivity and susceptibility to pests and diseases. Unhealthy plants are more vulnerable to nutrient deficiencies, stunted growth, and lower yields.
To mitigate and prevent these pH-related problems, it is crucial to maintain a regular and consistent pH monitoring and adjustment routine. This includes using high-quality nutrient solutions, monitoring pH levels diligently, making gradual adjustments, and addressing any pH issues promptly. By doing so, you can ensure a healthy and thriving hydroponic garden.
Conclusion
Maintaining the proper pH level in hydroponics is crucial for the success of your eco-friendly gardening endeavors. By understanding the significance of pH and its impact on nutrient availability, plant metabolism, and overall plant health, you can create an optimal environment for your hydroponic plants to thrive.
Throughout this article, we explored the concept of pH and its role in hydroponics. We discussed the ideal pH range for hydroponics, which generally falls between 5.5 and 6.5. We also identified the various factors that can affect pH levels in hydroponic systems, including source water, nutrient solutions, plant uptake, and microbial activity. By monitoring and adjusting pH levels using pH testing tools, pH adjustment substances, and pH buffering agents, you can ensure that your plants have the optimal pH conditions for growth and nutrient absorption.
Furthermore, we highlighted common pH problems that may arise in hydroponics, such as high or low pH, pH drift, fluctuations, and nutrient imbalance. These problems can hinder plant growth, reduce productivity, and stress the plants. Regular pH monitoring, proper nutrient management, and attention to water quality are essential in preventing and addressing these issues.
In conclusion, maintaining a balanced pH level is an important aspect of achieving eco-friendly gardening practices in hydroponics. By providing the ideal pH conditions, you not only promote the health and vitality of your plants but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly gardening approach. Keep in mind the importance of regular pH monitoring, make necessary adjustments, and stay vigilant in providing the best pH environment for your hydroponic garden. Happy hydroponic gardening!