Home>Types of Gardening>Edible Gardening>What Are Brassica Vegetables


Edible Gardening
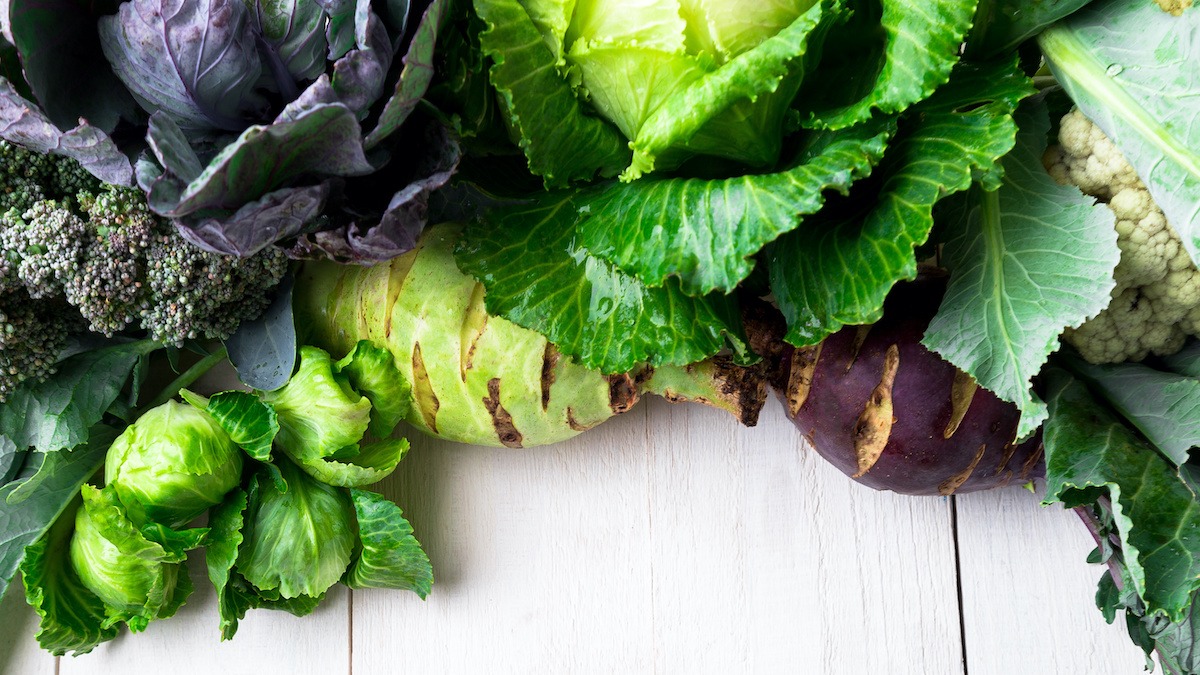
What Are Brassica Vegetables
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the benefits and varieties of Brassica vegetables for your edible gardening journey. Enhance your garden with nutrient-rich crops like kale, cabbage, broccoli, and more.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of edible gardening! There’s nothing quite as rewarding as growing your own food, and one area of edible gardening that has gained popularity in recent years is cultivating brassica vegetables. Whether you’re an experienced gardener or just starting out, adding brassicas to your garden can be a fantastic way to enjoy the satisfaction of fresh, homegrown produce.
But what exactly are brassica vegetables? Well, brassicas are a family of plants that belong to the Brassicaceae family, also known as the mustard family. These vegetables are known for their versatility, distinctive flavors, and abundant health benefits. From delicious leafy greens like kale and cabbage to crunchy delights such as broccoli and radishes, brassicas offer a wide variety of flavors, colors, and textures to enhance your culinary repertoire.
One of the great things about brassicas is their nutritional value. These vegetables are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can contribute to a healthy diet. They are low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great choice for weight management. Additionally, brassica vegetables are a rich source of vitamin C, folate, and various phytochemicals, which have been linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
From a gardening perspective, brassicas are known for their hardiness and resilience. They can tolerate a wide range of climatic conditions and are relatively easy to grow, making them an excellent choice for both seasoned gardeners and beginners. With a bit of attention and care, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of these flavorful and nutritious vegetables.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the world of brassica vegetables. We will explore the different types of brassicas, their nutritional benefits, methods of cooking and preparation, the positive impact they can have on your health, as well as tips for cultivation and harvesting. We will also share some delicious and simple recipes for you to savor the flavors of brassica vegetables.
Definition of Brassica Vegetables
Brassica vegetables, also known as cruciferous vegetables, are a group of plants that belong to the Brassicaceae family. These vegetables are characterized by their distinctive cross-shaped flowers, from which they get their name “cruciferous.” Brassicas are widely cultivated for their edible leaves, stems, flowers, or roots, and are cherished for their unique flavors and culinary versatility.
Common examples of brassica vegetables include broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, kale, Brussels sprouts, turnips, radishes, and mustard greens. Each of these vegetables has its own distinct taste, texture, and culinary uses, but they all share common characteristics that set them apart from other plant families.
One defining characteristic of brassica vegetables is their rich nutritional profile. They are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to overall health and well-being. Brassicas are particularly known for their high levels of vitamins C, K, and A, as well as folate and fiber.
Another notable aspect of brassica vegetables is their sulfur-containing compounds, such as glucosinolates. These compounds are responsible for the distinct aroma and flavor of brassicas, and they also have potential health benefits. Glucosinolates have been studied for their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer properties.
Brassicas are also revered for their versatility in the kitchen. They can be enjoyed raw in salads, stir-fried, boiled, steamed, roasted, or even fermented. Their robust flavors and textures make them excellent additions to a wide range of dishes, from comforting soups and stews to vibrant stir-fries and side dishes.
In summary, brassica vegetables are a diverse group of plants that encompass a wide range of nutritious and flavorful vegetables. From the crunchy bite of broccoli to the hearty richness of kale, brassicas offer a world of culinary possibilities. Their nutritional benefits and culinary versatility make them a valuable addition to any vegetable garden or kitchen.
Types of Brassica Vegetables
The world of brassica vegetables is incredibly diverse, offering a range of flavors, textures, and colors. Here are some of the most popular varieties of brassicas:
- Broccoli: Known for its dense florets and thick stalks, broccoli is a staple in many households. It can be eaten raw in salads, steamed, sautéed, or roasted, and is packed with vitamins C and K, as well as fiber.
- Cauliflower: This versatile vegetable comes in various colors, including classic white, orange, green, and purple. Cauliflower can be enjoyed raw, roasted, mashed, or even used as a low-carb alternative to rice or pizza crusts.
- Cabbage: Cabbage is a leafy brassica that comes in different varieties, such as green, red, and Savoy. It can be used in salads, stir-fries, soups, or fermented to make sauerkraut or kimchi. Cabbage is an excellent source of vitamin C and fiber.
- Kale: Known as a nutritional powerhouse, kale is a leafy green brassica that is rich in vitamins A, C, and K. It can be enjoyed raw in salads, sautéed as a side dish, or blended into smoothies for an added nutritious boost.
- Brussels Sprouts: Brussels sprouts are small, compact cabbage-like vegetables that grow in clusters along the stem. They can be roasted, sautéed, or steamed and are a good source of fiber, vitamins C and K, as well as folate.
- Turnips: Turnips are root vegetables that come in various shapes and sizes. They can be eaten raw, boiled, mashed, or roasted. Both the root and the greens of turnips are packed with nutrients and provide a great source of antioxidants.
- Radishes: Radishes are known for their crisp texture and spicy flavor. They can be eaten raw in salads, pickled, or used in stir-fries. Radishes are low in calories and provide a good source of vitamin C and other antioxidants.
- Mustard Greens: Mustard greens have a distinctive peppery flavor and are often used in salads, stir-fries, or sautéed as a side dish. They are an excellent source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as calcium and iron.
These are just a few examples, but the world of brassica vegetables is extensive, offering an abundance of flavors and textures to explore in your culinary endeavors.
Nutritional Benefits of Brassica Vegetables
Brassica vegetables are not only delicious but also pack a powerful nutritional punch. Here are some of the key benefits of including brassicas in your diet:
- Rich in Vitamins: Brassicas are excellent sources of essential vitamins. They are particularly high in vitamins A, C, and K. Vitamin A supports healthy vision and immune function, while vitamin C is important for collagen production and immune system function. Vitamin K is necessary for blood clotting and bone health.
- Loaded with Antioxidants: Brassicas are rich in antioxidants, which help protect the body from free radicals and oxidative stress. These antioxidants, including beta-carotene and flavonoids, have been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, certain cancers, and age-related macular degeneration.
- High in Fiber: Fiber is essential for a healthy digestive system and can help promote regular bowel movements, regulate blood sugar levels, and contribute to weight management. Brassica vegetables, such as broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts, are excellent sources of fiber.
- Support Healthy Skin: The vitamins and antioxidants found in brassicas can contribute to healthy skin. Vitamin C, for example, is necessary for collagen synthesis, which helps maintain the elasticity and firmness of the skin. The antioxidants in brassicas also help protect the skin from damage caused by exposure to environmental pollutants and UV radiation.
- Potential Anti-cancer Properties: Brassica vegetables contain compounds called glucosinolates. When these compounds are broken down during digestion, they form bioactive substances that have been shown to have potential anti-cancer effects. Studies suggest that consuming brassica vegetables may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including lung, colorectal, and breast cancer.
- Heart Health Support: The fiber, antioxidants, and other bioactive compounds found in brassicas can contribute to heart health. A diet rich in brassica vegetables has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and elevated cholesterol levels.
Including a variety of brassica vegetables in your diet can provide a wide range of essential nutrients and support overall health and well-being. Whether it’s the vibrant purple of cabbage or the deep green of kale, these vegetables offer a delicious and nutritious addition to any plate.
Cooking and Preparation of Brassica Vegetables
Brassica vegetables offer versatility in the kitchen, allowing you to enjoy them through various cooking and preparation methods. Here are some popular ways to cook and prepare these nutritious veggies:
- Steaming: Steaming is a gentle cooking method that helps preserve the nutrients and natural flavors of brassica vegetables. Simply place the vegetables in a steamer basket over boiling water and cook until tender. Steamed brassicas, such as broccoli and cauliflower, make a delicious side dish or can be added to salads and stir-fries.
- Sautéing: Sautéing brassica vegetables in a bit of olive oil or butter can enhance their flavors and create a delicious caramelization. Heat a skillet over medium heat, add your favorite brassica veggies, and cook until they are tender-crisp. Sautéed brassicas are perfect for adding to pasta dishes, stir-fries, or as a side dish.
- Roasting: Roasting brings out the natural sweetness and adds a wonderful depth of flavor to brassica vegetables. Preheat your oven to a high temperature, toss the vegetables in olive oil, season with salt and pepper, and spread them out on a baking sheet. Roast until they are tender and slightly browned. Roasted brassicas like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts make a fantastic addition to any meal.
- Raw: Some brassica vegetables, such as kale, cabbage, and radishes, can be enjoyed raw in salads or slaws. Raw brassicas add a refreshing crunch and provide a great base for a variety of dressings and toppings. To soften the texture and mellow the flavors, you can give them a quick massage with a bit of olive oil and salt before incorporating them into your salad.
- Pickling: Pickling is a popular technique to preserve brassicas and add a tangy flavor to them. You can make quick pickles by submerging sliced brassicas, such as radishes or turnips, in a mixture of vinegar, water, salt, sugar, and spices. Allow them to marinate for a few hours or overnight in the refrigerator, and they will be ready to enjoy as a condiment or addition to sandwiches and salads.
- Blanching: Blanching is a quick cooking method that involves briefly boiling the brassica vegetables and then transferring them to an ice bath to stop the cooking process. Blanching helps maintain the vibrant color and crispness of the vegetables. Blanching is commonly used for broccoli, kale, and Brussels sprouts before using them in stir-fries or freezing them for later use.
Experiment with different cooking methods and flavor combinations to discover your favorite way to enjoy brassica vegetables. Whether they are roasted to perfection or enjoyed raw in a salad, these nutritious and delicious veggies are sure to elevate your culinary creations.
Health Effects of Brassica Vegetables
Brassica vegetables offer numerous health benefits, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Here are some of the health effects associated with consuming these nutritious veggies:
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Brassica vegetables contain compounds called glucosinolates, which have anti-inflammatory effects on the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and some types of cancer. Including brassicas in your diet may help reduce inflammation and promote overall health.
- Cancer Prevention: Brassicas are known for their potential anti-cancer properties. The glucosinolates in these vegetables are broken down into bioactive compounds, such as sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol, during digestion. These compounds have been shown to have anti-cancer effects and may help inhibit the growth of cancer cells, particularly in the digestive system, lungs, and breast.
- Heart Health: The fiber, antioxidants, and other compounds in brassica vegetables contribute to heart health. High intake of brassicas has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and elevated cholesterol levels. The vitamins and minerals found in brassicas, such as potassium and folate, also support heart health.
- Weight Management: Brassica vegetables are low in calories and high in fiber, making them an excellent choice for weight management. The fiber in brassicas helps promote feelings of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Additionally, the high fiber content aids in digestion and supports a healthy metabolism.
- Digestive Health: Brassica vegetables are rich in fiber, which promotes a healthy digestive system. Fiber helps prevent constipation, improves bowel regularity, and supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Additionally, brassicas contain compounds that may help protect against gastric ulcers and promote a healthy gut environment.
- Eye Health: Certain brassica vegetables, such as kale and Brussels sprouts, are rich in antioxidants and other nutrients that support eye health. These vegetables contain lutein and zeaxanthin, which are beneficial for the retina and can help reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
- Immune Support: Brassicas are loaded with vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, which plays a vital role in supporting the immune system. Vitamin C contributes to the production of white blood cells, which help the body fight off infections and illnesses.
By incorporating brassica vegetables into your diet, you can enjoy a wide array of health benefits, ranging from inflammation reduction to cancer prevention and heart health support. These versatile and nutritious veggies offer a powerful boost to overall well-being.
Cultivation and Harvesting of Brassica Vegetables
If you’re interested in growing your own brassica vegetables, you’ll be pleased to know that they are relatively easy to cultivate. Here are some key tips for successfully growing and harvesting brassicas:
- Choose the right location: Brassicas thrive in full sun, so select a site in your garden that receives at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Ensure that the soil is well-draining and rich in organic matter.
- Start from seeds or seedlings: Brassicas can be started from seeds indoors or directly sown into the garden. If starting indoors, begin 4 to 6 weeks before the last frost date in your area. Transplant the seedlings outdoors once they have a few sets of true leaves.
- Plant at the right time: Brassicas can be grown in both cool-season and warm-season climates. In cool-season areas, such as early spring or fall, start planting in late winter or early spring for a spring harvest, or in late summer for a fall harvest. In warm-season areas, plant in late summer or early fall for a winter harvest.
- Space properly: Give each brassica plant enough space to grow. Space broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower plants about 18 to 24 inches apart. Brussels sprouts and kale require more space and should be planted 24 to 36 inches apart.
- Water adequately: Brassicas require consistent moisture to thrive. Water deeply and regularly, ensuring that the soil remains evenly moist but not waterlogged. Avoid overhead watering to prevent the spread of fungal diseases.
- Fertilize appropriately: Brassicas are heavy feeders and benefit from regular applications of fertilizer. Work compost or well-rotted manure into the soil before planting, and use a balanced organic fertilizer during the growing season to promote healthy growth.
- Protect from pests: Brassica plants are susceptible to pests such as cabbage worms, aphids, and flea beetles. Implement organic pest control methods such as hand picking, using insecticidal soaps, or applying natural pest deterrents like neem oil or row covers.
- Harvest at the right time: Brassica vegetables can be harvested once they reach the desired size and have formed tight heads or mature leaves. Harvest broccoli and cauliflower when the heads are still compact, cabbage when the heads are firm, and kale and Brussels sprouts when they have developed their characteristic textures and colors. Use a sharp knife or pruning shears to avoid damaging the plants.
- Extend the harvest: For some brassicas, such as kale and Brussels sprouts, you can extend the harvest by picking individual leaves or sprouts as needed, allowing the plants to continue producing.
By following these guidelines, you can enjoy a plentiful harvest of homegrown brassica vegetables. Remember to rotate the planting location each year to prevent soil-borne diseases and pests. With a little care and attention, you’ll reap the rewards of your brassica garden.
Common Recipes for Brassica Vegetables
Brassica vegetables can be used in a wide variety of delicious and nutrient-rich recipes. Here are some popular and easy-to-make recipes that highlight the flavors and versatility of brassica vegetables:
- Roasted Brassica Medley: Toss a mixture of broccoli florets, cauliflower florets, and Brussels sprouts with olive oil, salt, and pepper. Spread them out on a baking sheet and roast in a preheated oven at 425°F (220°C) for 20-25 minutes or until browned and tender. Enjoy as a flavorful side dish or add grilled chicken or roasted chickpeas to turn it into a satisfying main course.
- Kale Caesar Salad: Make a healthy twist on a classic Caesar salad by swapping out romaine lettuce for fresh kale. Massage the kale leaves with a bit of olive oil to soften them, then toss with a homemade Caesar dressing, grated Parmesan cheese, and crunchy croutons. Add some grilled shrimp, chicken, or tofu for a protein-packed meal.
- Cabbage Stir-Fry: Heat a wok or large skillet over high heat and stir-fry shredded cabbage, sliced bell peppers, carrots, and thinly sliced onions until crisp-tender. Season with soy sauce, ginger, and garlic, and stir-fry for a few more minutes. Serve as a flavorful side dish or add cooked shrimp, chicken, or tofu for a complete meal.
- Broccoli and Cheddar Soup: In a large pot, sauté chopped onions and garlic in butter until translucent. Add chopped broccoli florets and cook for a few minutes. Pour in vegetable or chicken broth and bring to a boil. Reduce heat, cover, and simmer until the broccoli is tender. Use an immersion blender to puree the mixture, then stir in shredded cheddar cheese until melted and smooth. Season with salt, pepper, and a pinch of nutmeg. Serve hot with a sprinkle of extra cheese on top.
- Brussels Sprouts Slaw: Slice Brussels sprouts thinly and toss them in a bowl with shredded carrots, thinly sliced red onions, dried cranberries, and chopped walnuts. In a separate small bowl, whisk together olive oil, apple cider vinegar, Dijon mustard, honey, salt, and pepper to make the dressing. Drizzle the dressing over the slaw and toss to combine. Let it sit in the fridge for at least 30 minutes before serving to allow the flavors to meld together.
These are just a few examples of the countless ways to incorporate brassica vegetables into your cooking. Feel free to experiment with different seasonings, sauces, and cooking techniques to suit your taste preferences. Whether you prefer them roasted, stir-fried, in soups, or as a base for salads, brassica vegetables add flavor, texture, and a nutritional boost to your meals.
Conclusion
Brassica vegetables offer a delightful combination of flavors, textures, and nutritional benefits that make them an excellent addition to any edible garden and kitchen. From the versatile and nutrient-rich broccoli to the vibrant and robust kale, these vegetables provide a range of health-boosting properties, from anti-inflammatory effects to potential cancer prevention.
Cultivating brassicas in your garden can be a rewarding experience, as they are relatively easy to grow and harvest. With proper care, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of these nutritious vegetables throughout the growing season.
When it comes to cooking and preparing brassicas, the possibilities are endless. Whether you prefer them roasted to enhance their natural sweetness, sautéed to bring out their flavors, or enjoyed raw in salads for a refreshing crunch, brassicas offer versatility in the kitchen that can elevate your culinary creations.
It’s worth noting that brassica vegetables can vary in taste and texture, allowing for a diverse range of recipes. From creamy soups and hearty stir-fries to vibrant salads and delicious roasted dishes, there is a brassica recipe to please every palate.
So, why not embark on your edible gardening journey and explore the flavors and benefits of brassica vegetables? Whether you have a large garden or just a few containers on a balcony, growing and enjoying these versatile veggies will not only enhance your meals but also promote a healthier lifestyle. So, get your hands dirty, plant some brassicas, and savor the joys of cultivating and consuming these remarkable vegetables.