Home>Gardening Basics>Getting Started>What Weeds Does 2,4-D Kill


Getting Started
What Weeds Does 2,4-D Kill
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover which weeds 2,4-D can effectively target and eliminate. Learn more about getting started with 2,4-D for weed control. Gain insights now!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the Potent Herbicide: 2,4-D
Welcome to the world of weed control, where the battle against invasive plants rages on. In this guide, we’ll delve into the powerful herbicide known as 2,4-D. As we explore its properties, target weeds, and effectiveness, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of this widely used solution for weed management.
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, commonly referred to as 2,4-D, stands as one of the most widely utilized herbicides in the world. Its effectiveness in controlling broadleaf weeds has made it a staple in the arsenal of both agricultural professionals and homeowners seeking to maintain pristine lawns and gardens. This synthetic auxin has been in use since the 1940s, and its popularity endures due to its remarkable efficacy in combating a broad spectrum of stubborn weeds.
As we embark on this exploration, we’ll uncover the specific weeds that succumb to the potent effects of 2,4-D, as well as the considerations for its application. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge needed to harness the weed-fighting prowess of 2,4-D effectively and responsibly. Let’s dive into the world of weed management and discover the impact of 2,4-D on targeted plant species.
Understanding 2,4-D
To comprehend the potency of 2,4-D as a herbicide, it’s essential to grasp its mode of action and the factors contributing to its effectiveness. 2,4-D functions as a synthetic auxin, a class of plant hormones that regulate growth and development. When applied to target weeds, 2,4-D disrupts their normal growth patterns, leading to uncontrolled and unsustainable growth, ultimately resulting in the demise of the plant.
One of the key attributes of 2,4-D is its selective nature, primarily affecting broadleaf plants while sparing grasses and other monocots. This selectivity allows for precise weed control without harming desirable grass species, making it an invaluable tool for maintaining lush lawns and productive agricultural fields.
The formulation of 2,4-D varies, with options including amine, ester, and choline formulations. Each formulation exhibits unique properties, such as volatility and compatibility with different environmental conditions, influencing its efficacy and application methods. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimizing the impact of 2,4-D while minimizing unintended consequences.
Furthermore, the timing of 2,4-D application plays a pivotal role in its effectiveness. Applying the herbicide during the active growth stage of target weeds maximizes its absorption and translocation within the plant, leading to more pronounced and sustained control. By aligning the application with the growth stage of the weeds, users can harness the full potential of 2,4-D to combat invasive species effectively.
As we delve deeper into the world of 2,4-D, it becomes evident that a comprehensive understanding of its mechanisms and formulations is essential for successful weed management. Armed with this knowledge, users can leverage the power of 2,4-D to achieve optimal results in their ongoing battle against unwanted vegetation.
Target Weeds
2,4-D is renowned for its efficacy in combating a wide array of broadleaf weeds that pose significant challenges to agricultural productivity and the aesthetic appeal of lawns and landscapes. Its broad-spectrum control capabilities make it a versatile solution for addressing diverse weed species. Some of the primary target weeds susceptible to the potent effects of 2,4-D include:
- Dandelions: These pervasive and resilient weeds are a common nuisance in lawns and open spaces. 2,4-D effectively disrupts their growth, leading to their gradual elimination.
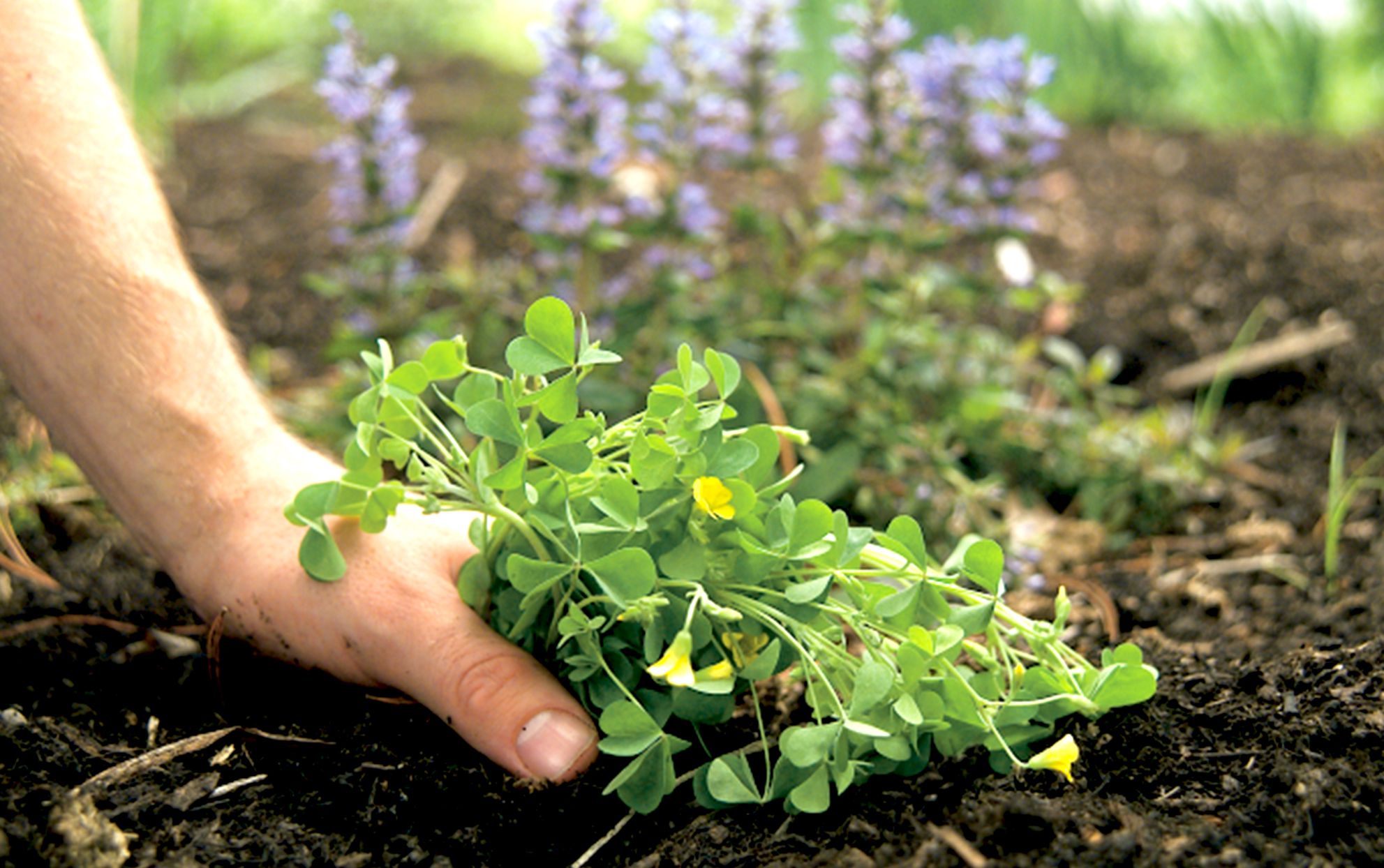
- Clover: With its rapid spread and ability to outcompete desirable grass species, clover is a persistent foe for lawn enthusiasts. 2,4-D provides an effective means of curbing its proliferation.
- Thistles: Known for their tenacious nature and robust growth, thistles can quickly overtake pastures and agricultural fields. 2,4-D offers reliable control, mitigating the impact of these troublesome weeds.
- Wild Carrot (Queen Anne’s Lace): This invasive species, with its intricate and widespread root system, poses a challenge to land managers. 2,4-D serves as a potent tool in managing its encroachment.
- Plantains: Commonly found in lawns and disturbed areas, plantains can detract from the visual appeal of landscapes. 2,4-D effectively targets these weeds, restoring the pristine appearance of treated areas.
These are just a few examples of the many broadleaf weeds that succumb to the targeted action of 2,4-D. Whether in agricultural, residential, or commercial settings, the versatility of this herbicide in controlling a diverse range of invasive plants underscores its significance in weed management practices.
By understanding the specific weeds that 2,4-D effectively targets, users can tailor their weed control strategies to address prevalent species in their respective environments, ensuring the preservation of desired vegetation and the suppression of unwanted plant intruders.
Effectiveness of 2,4-D
The effectiveness of 2,4-D as a herbicide stems from its remarkable ability to disrupt the growth and development of broadleaf weeds while sparing desirable grass species. This selectivity is a defining feature that sets 2,4-D apart as a valuable tool in weed management efforts.
One of the key factors contributing to the efficacy of 2,4-D is its systemic mode of action. Upon application, 2,4-D is absorbed by the leaves and stems of target weeds, where it is then translocated throughout the plant. This systemic translocation ensures comprehensive coverage, reaching even concealed or hard-to-reach plant parts, thus delivering consistent and thorough control.
Furthermore, the versatility of 2,4-D in terms of application methods and formulations enhances its effectiveness in diverse settings. Whether applied as a liquid spray, granular formulation, or in combination with other herbicides, 2,4-D offers flexibility and adaptability to meet the specific needs of varying weed control scenarios.
Another aspect that contributes to the effectiveness of 2,4-D is its rapid action on susceptible weeds. Upon application, visible symptoms of wilting, leaf distortion, and overall decline in weed vigor become apparent within a relatively short timeframe. This rapid onset of action underscores the potent and reliable nature of 2,4-D in combating unwanted vegetation.
Moreover, the residual activity of 2,4-D contributes to sustained weed control, preventing the regrowth and resurgence of treated weeds. This enduring impact minimizes the need for frequent reapplication, offering long-term relief from weed infestations and reducing the overall effort and resources required for weed management.
As we assess the effectiveness of 2,4-D, it becomes evident that its multifaceted attributes, including selectivity, systemic action, versatility, rapid onset of control, and residual activity, collectively contribute to its status as a leading herbicidal solution for addressing a broad spectrum of stubborn broadleaf weeds.
Considerations for Use
While 2,4-D stands as a potent herbicidal ally in the battle against broadleaf weeds, its application necessitates careful considerations to ensure optimal efficacy and environmental responsibility. Understanding the following key factors is essential for harnessing the potential of 2,4-D while mitigating potential risks:
- Application Timing: Timing plays a crucial role in maximizing the impact of 2,4-D. Applying the herbicide during the active growth stage of target weeds enhances its uptake and translocation within the plant, leading to more effective control.
- Weather Conditions: Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed can influence the performance and potential off-target effects of 2,4-D. Adhering to recommended application guidelines under favorable weather conditions is vital for minimizing unintended consequences.
- Adjuvants and Formulations: Selecting appropriate adjuvants and formulations based on the specific weed control objectives and environmental considerations is imperative for optimizing the efficacy of 2,4-D while minimizing environmental impact.
- Environmental Protection: Safeguarding non-target vegetation, water bodies, and sensitive habitats from potential herbicide drift or runoff is a critical aspect of responsible 2,4-D use. Adhering to buffer zones and application best practices is essential for environmental stewardship.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarizing oneself with local regulations, label instructions, and usage restrictions pertaining to 2,4-D is essential for legal compliance and responsible herbicide application.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider the potential impact of 2,4-D on non-target plants, particularly sensitive broadleaf species, and to implement mitigation measures to prevent unintended damage. Additionally, promoting integrated weed management practices, including cultural, mechanical, and biological control methods alongside herbicidal treatments, contributes to sustainable and holistic weed control strategies.
By integrating these considerations into the use of 2,4-D, practitioners can harness its potent weed control capabilities while upholding environmental stewardship and ensuring the preservation of non-target vegetation. Adopting a comprehensive and responsible approach to 2,4-D application is pivotal in maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential risks and ecological impacts.