Home>Gardening News and Trends>Gardening Trends>What Is The Best Method Of Irrigation


Gardening Trends
What Is The Best Method Of Irrigation
Modified: February 10, 2024
Discover the latest gardening trends and learn about the best method of irrigation for your plants. Improve your gardening skills with expert advice and techniques.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of gardening! Whether you are a seasoned green thumb or just starting out, understanding the latest gardening trends is essential for cultivating a beautiful and thriving garden. One key aspect of successful gardening is implementing the right irrigation method. Adequate water supply is crucial for the health and growth of plants, and choosing the best irrigation method can make all the difference.
In this article, we will explore the various types of irrigation methods and discuss the factors to consider when selecting the best technique for your garden. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the different irrigation options available, and be equipped with the knowledge to make an informed decision.
When it comes to irrigation methods, it’s important to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The best method for your garden will depend on factors such as the type of plants you are growing, the climate in your region, the soil conditions, and your personal preferences. However, understanding the pros and cons of different irrigation techniques will help you make an educated choice.
So let’s dive in and explore the various irrigation methods available!
Types of Irrigation Methods
There are several different irrigation methods used in gardening and agriculture. Each method delivers water to plants in a unique way, targeting specific areas or distributing water evenly across the entire field. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common types of irrigation methods:
-
Surface Irrigation
Surface irrigation is one of the oldest and most traditional methods of irrigation. It involves flooding or manually distributing water over the soil surface, allowing it to infiltrate and reach the plant roots. This method is often used for crops like rice or in fields with a gentle slope.
-
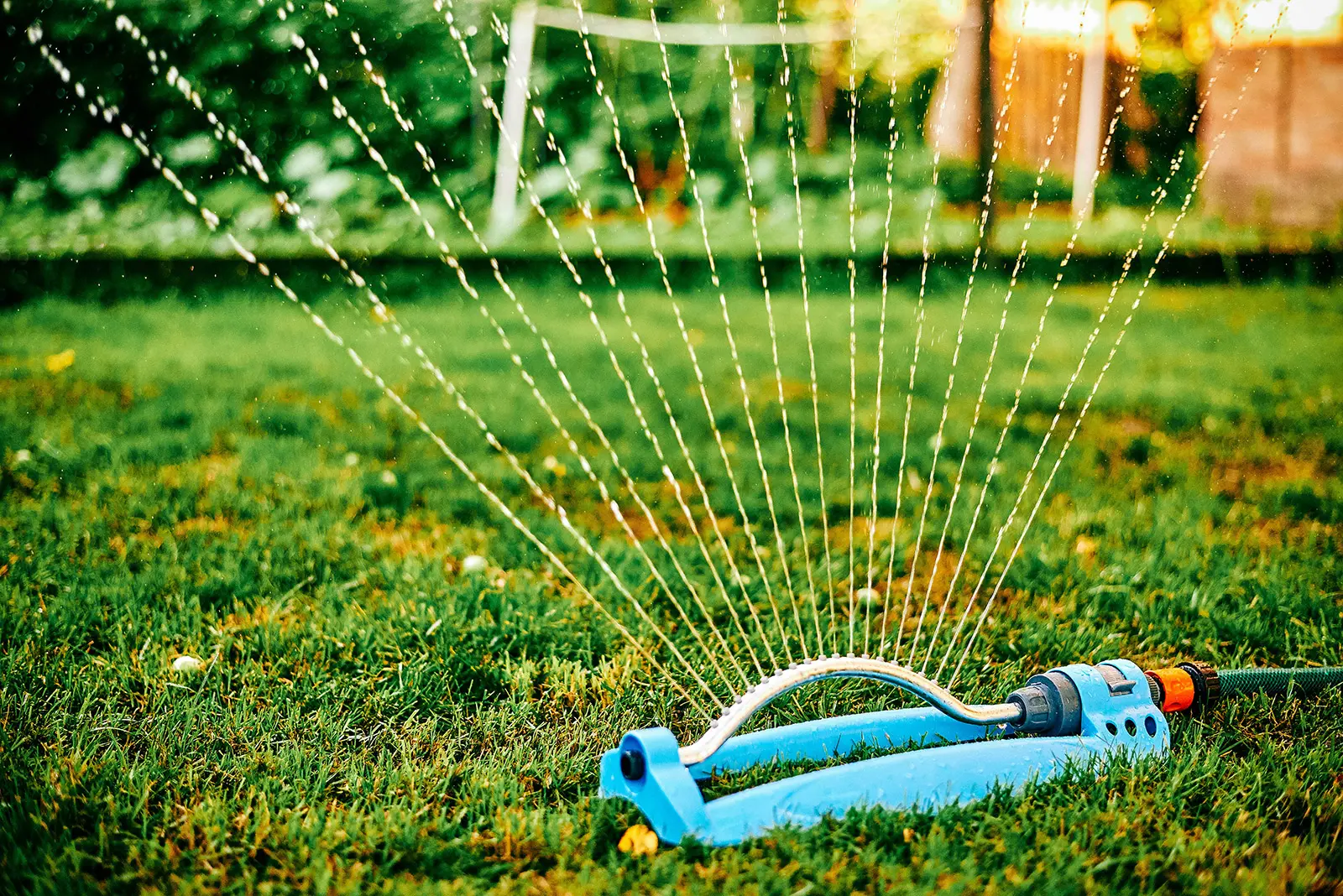
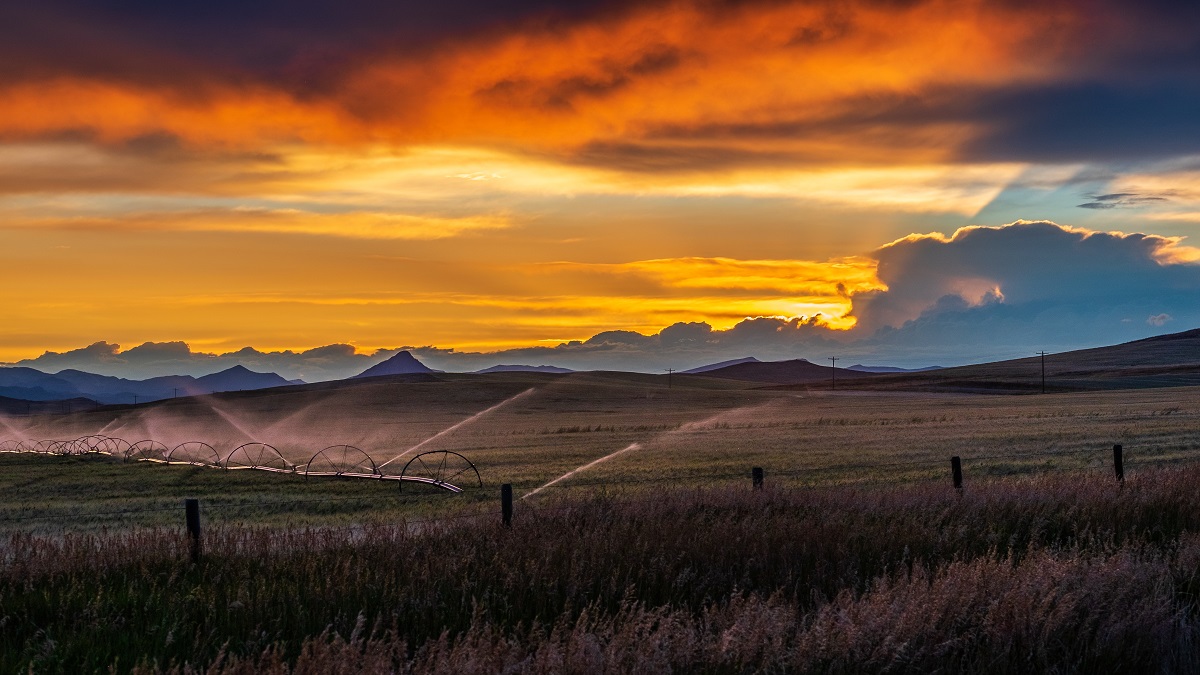
Sprinkler Irrigation
Sprinkler irrigation is a popular method that involves spraying water over the plants using sprinkler heads or spray nozzles. The water is distributed in a manner similar to rainfall, covering the plants from above. This method is effective for both small gardens and large agricultural fields.
-
Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a precise and efficient method that delivers water directly to the plant’s root zone. It involves the use of a network of tubes or pipes with small emitters that release water slowly and directly onto the soil. Drip irrigation is ideal for conserving water and reducing weed growth.
-
Subsurface Irrigation
Subsurface irrigation, also known as subsurface drip irrigation (SDI), involves placing water emitters below the soil surface. This method allows water to be delivered directly to the plant’s root zone, reducing evaporation and minimizing water loss. It is commonly used in orchards, vineyards, and horticultural applications.
Each of these irrigation methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. Surface irrigation is simple and affordable but may lead to water wastage and uneven distribution. Sprinkler irrigation is versatile but can be less water-efficient. Drip irrigation is highly efficient but requires careful planning and maintenance. Subsurface irrigation is also efficient but requires proper installation and management.
It’s important to consider the specific needs of your garden or agricultural field when choosing the most suitable irrigation method. Factors such as soil type, plant types, and water availability will play a significant role in determining the ideal irrigation technique for your specific needs.
Surface Irrigation
Surface irrigation is one of the oldest and simplest methods of irrigation, commonly used in agriculture and gardening. It involves the controlled flooding or manual distribution of water over the soil surface, allowing it to infiltrate and reach the plant roots.
There are different techniques of surface irrigation, including furrow irrigation, flood irrigation, and border irrigation. Furrow irrigation involves creating small trenches or furrows between rows of plants and allowing water to flow along the furrows, effectively irrigating the plants. Flood irrigation involves flooding the entire field with water and allowing it to gradually infiltrate the soil. Border irrigation is similar to flood irrigation, but the field is divided into smaller sections or borders to facilitate better water distribution.
Surface irrigation is a popular choice for certain crops, especially those with deep root systems or crops that require high water availability. It is often used for crops like rice, corn, and wheat, as well as in orchards and vineyards.
One of the advantages of surface irrigation is its simplicity and low cost. It does not require sophisticated equipment or complex infrastructure, making it accessible to small-scale farmers and gardeners. Additionally, surface irrigation can help improve soil fertility by distributing sediment and nutrients carried by the water along the field.
However, there are some drawbacks to consider. One potential issue with surface irrigation is uneven water distribution. Factors such as soil type, slope, and field layout can affect the distribution of water, leading to waterlogging in some areas and insufficient irrigation in others. Additionally, surface irrigation can result in water wastage due to evaporation, especially in warm and dry climates.
To enhance the efficiency of surface irrigation, adopting techniques such as contour plowing, leveling the field, and using check gates or bunds can help improve water flow and distribution. Regular monitoring of the irrigation process and adjusting the water application rate can also enhance efficiency.
In summary, surface irrigation is a simple and cost-effective method of irrigation that is commonly used in agriculture. While it has some limitations, proper planning and management can help maximize its effectiveness and minimize water wastage. Understanding the specific needs of your plants and the characteristics of your soil will guide you in determining whether surface irrigation is the best method for your garden.
Sprinkler Irrigation
Sprinkler irrigation is a widely used method of delivering water to plants by spraying it over the foliage or soil surface. This method resembles natural rainfall, providing even coverage and ensuring that plants receive the required amount of water.
Sprinkler irrigation systems consist of a network of pipes, sprinkler heads, and valves. The water is pressurized and released through the sprinkler heads, effectively distributing water over the targeted area.
One of the main advantages of sprinkler irrigation is its versatility. It can be used in various settings, from small garden beds to large-scale agricultural fields. The flexibility in design and layout options allows for precise water application, catering to the specific needs of different plants and soil types.
Another benefit of sprinkler irrigation is its ability to distribute water evenly, reducing the risk of over-watering or under-watering. This uniformity aids in promoting healthy plant growth and minimizing the occurrence of diseases caused by over- or under-watering.
Sprinkler irrigation systems also have the advantage of being adjustable and adaptable. The spray radius, angle, and intensity can be modified to accommodate different plant heights, shapes, and growth stages. Additionally, modern sprinkler systems often come equipped with timers and sensors, enabling automated watering and efficient water management.
However, there are a few considerations to keep in mind when using sprinkler irrigation. One potential downside is the potential for water loss due to evaporation. In hot and arid climates, a significant amount of water may evaporate before reaching the plants. Proper timing of irrigation, typically during cooler hours, can help minimize water loss.
Another challenge is the potential for water splashing onto leaves, which can increase the risk of disease. To mitigate this, it is important to choose sprinkler heads that produce fine droplets and to avoid watering during windy conditions.
Overall, sprinkler irrigation is a popular and effective method of watering plants. Its adaptability, even water distribution, and ability to cover larger areas make it a preferred choice for many gardeners and farmers. By considering factors such as plant type, soil conditions, and climate, you can determine whether sprinkler irrigation is the best method for your garden or agricultural needs.
Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a precise and efficient method of delivering water directly to the root zone of plants. In this method, water is slowly emitted through a network of tubes or pipes with small emitters or drippers that are strategically placed near the base of the plants.
Drip irrigation offers several advantages over other methods. One of the major benefits is its water efficiency. Drip irrigation minimizes water loss due to evaporation or runoff, as water is delivered directly to the roots where it is needed most. This targeted application of water helps reduce water waste and promotes optimal plant growth.
Another advantage of drip irrigation is its ability to reduce weed growth. By delivering water precisely to the plant roots, the surrounding soil remains dry, creating an unfavorable environment for weeds to grow. This reduces the need for manual weeding or the use of herbicides.
Drip irrigation is also highly versatile and adaptable. It can be used in various settings, from small home gardens to large agricultural fields. The flexibility of the system allows for easy customization, such as adding more emitters or adjusting the flow rate, to meet the specific water requirements of different plants.
In addition to these benefits, drip irrigation promotes better nutrient uptake by the plants. Nutrients can be applied directly to the irrigation water, allowing them to be efficiently delivered to the root zone. This helps prevent nutrient leaching and ensures that plants receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth.
While drip irrigation offers numerous advantages, it does require careful planning and maintenance. Proper installation of the system is essential to ensure uniform water distribution and prevent clogging of the emitters. Regular maintenance, such as checking for leaks, unclogging the emitters, and monitoring the water flow, is necessary to keep the system functioning optimally.
Drip irrigation is particularly useful in areas with water scarcity or high water costs. It allows for precise water management, enabling growers to optimize water usage and reduce their water footprint. Additionally, the controlled application of water in the root zone helps prevent soil erosion and nutrient runoff, contributing to better environmental sustainability.
In summary, drip irrigation is a highly efficient and effective method of delivering water to plants. Its water-saving benefits, weed control advantages, and nutrient management capabilities make it a popular choice among gardeners and farmers. By considering factors such as the size of your garden or field, the water availability, and the specific needs of your plants, you can determine whether drip irrigation is the best method for your irrigation needs.
Subsurface Irrigation
Subsurface irrigation, also known as subsurface drip irrigation (SDI), is a method that delivers water directly to the root zone of plants below the soil surface. This technique involves the installation of water emitters or drippers beneath the soil, which release water slowly and evenly to the plant roots.
Subsurface irrigation offers several advantages over other irrigation methods. One of the main benefits is its high water efficiency. By delivering water directly to the roots, subsurface irrigation minimizes water loss due to evaporation and surface runoff. This targeted application of water ensures that plants receive the necessary moisture while conserving water resources.
Another advantage of subsurface irrigation is its ability to prevent weed growth. Since the water is delivered directly to the root zone, the soil surface remains dry, creating an unfavorable environment for weeds to germinate and grow. This reduces the need for herbicides or manual weeding, resulting in time and labor savings.
Subsurface irrigation also helps in reducing the risk of plant diseases. By avoiding the wetting of above-ground foliage, this method lowers the chances of fungal and bacterial diseases, which thrive in moist environments. Additionally, subsurface irrigation minimizes leaf burn caused by water droplets, which can magnify the sun’s rays and scorch plants.
Furthermore, subsurface irrigation is suitable for a variety of soil types and topographies. It can be used in different field conditions, including sloping terrain or areas with high clay content. This flexibility makes it a preferred choice for orchards, vineyards, and horticultural applications.
However, subsurface irrigation does require proper installation and management. The installation process involves careful placement of the emitters at the correct depth and spacing to ensure uniform water distribution. Monitoring and regular maintenance, such as checking for clogging or damage to the emitters, are necessary to keep the system functioning effectively.
Additionally, it is important to consider the specific needs of the plants being irrigated when using subsurface irrigation. While this method is effective, certain plants may prefer different irrigation techniques. Factors such as plant species, root depth, and water requirements should be taken into account to ensure optimal growth and yield.
In summary, subsurface irrigation is a highly efficient and effective method of delivering water directly to the root zone of plants. Its water-saving benefits, weed control advantages, and reduced disease risk make it an attractive option for growers. By considering factors such as the soil type, topography, and specific plant requirements, you can determine whether subsurface irrigation is the best method for your gardening or agricultural needs.
Factors to Consider in Choosing the Best Irrigation Method
When it comes to choosing the best irrigation method for your garden or agricultural field, several factors should be taken into consideration. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision. Here are some key considerations:
-
Water Efficiency
Efficient water usage is essential for sustainable irrigation. Consider the water efficiency of each irrigation method. Drip and subsurface irrigation are typically the most water-efficient, as they deliver water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
-
Crop Suitability
Different crops have specific water requirements. Consider the water needs of the plants you are growing. For example, surface irrigation may be suitable for crops like rice or corn, while sprinkler or drip irrigation may be better for fruit trees or vegetable gardens.
-
Soil Type and Topography
Understand the soil type and topography of your garden or field. Some irrigation methods, like surface irrigation, are better suited for flat landscapes, while drip or subsurface irrigation can accommodate different inclines and soil conditions.
-
Cost and Maintenance
Consider the cost and maintenance requirements of each irrigation method. Some methods may require more initial investment in equipment and installation, while others may necessitate regular maintenance and monitoring.
-
Environmental Impact
Think about the environmental impact of the irrigation method. Some methods may conserve water and reduce soil erosion, while others may contribute to water wastage or have a higher carbon footprint. Choose a method that aligns with your sustainability goals.
Ultimately, the best irrigation method for your garden or agricultural field will depend on a combination of these factors. It’s important to assess your specific needs and goals, weigh the advantages and limitations of each method, and choose the approach that will provide the most effective and efficient water management for your plants.
Water Efficiency
Water efficiency is a crucial factor to consider when choosing the best irrigation method for your garden or agricultural field. Efficient water usage not only helps conserve this valuable resource but also ensures that plants receive the optimal amount of water for healthy growth. Let’s explore the importance of water efficiency and how different irrigation methods compare in this aspect.
When it comes to water efficiency, two irrigation methods stand out: drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation. These methods deliver water directly to the plant’s root zone, minimizing water loss due to evaporation or runoff. By targeting the root zone, the water is efficiently absorbed by the plants without wastage.
Drip irrigation is considered one of the most water-efficient methods available. It uses a network of tubes or pipes with small emitters that release water slowly and directly onto the soil. This targeted application prevents water from being wasted on non-essential areas like pathways or between rows of plants. Drip irrigation also allows for precise control over the amount of water applied, making it ideal for conserving water in water-scarce regions.
Similarly, subsurface irrigation delivers water below the soil surface, directly to the plant roots. This method also minimizes water loss to evaporation and surface runoff. Moreover, subsurface irrigation reduces the exposure of water to the air, reducing the risk of weed growth and allowing for more efficient water absorption by the plants.
Other irrigation methods, such as surface irrigation and sprinkler irrigation, are generally less water-efficient. Surface irrigation, while simple and commonly used, can result in significant water loss due to evaporation and uneven distribution. Sprinkler irrigation, although versatile and widely used, can also suffer from water loss through evaporation and wind drift. However, adopting water-saving practices like proper timing of irrigation and using efficient sprinkler heads can help improve water efficiency.
It’s important to note that water efficiency is not solely determined by the irrigation method but also by other factors such as the design of the system, maintenance practices, and the water management strategies employed. Regularly monitoring and adjusting the irrigation system, based on plant needs and weather conditions, can further enhance water efficiency regardless of the irrigation method employed.
Overall, water efficiency should be a primary consideration when selecting the best irrigation method. Factors such as the availability of water, climate conditions, and the specific needs of your plants should be taken into account to ensure sustainable and responsible water usage. By choosing an irrigation method that maximizes water efficiency, you can contribute to the conservation of this vital resource while promoting healthier plant growth.
Crop Suitability
When choosing the best irrigation method, it is important to consider the suitability of different methods for the specific crops you are growing. Each crop has unique water requirements, and selecting an irrigation method that aligns with those needs will contribute to the overall success of your garden or agricultural field.
Some crops, such as rice or corn, have higher water requirements and may benefit from irrigation methods that provide ample water coverage, such as surface irrigation or sprinkler irrigation. These methods distribute water over a larger area, ensuring that the water reaches the root zone of the plants and meets their thirst for moisture.
On the other hand, certain crops, including fruit trees, vegetables, and ornamental plants, may benefit from more precise and targeted water application. Drip irrigation is especially suitable for these types of crops. With its small emitters that release water directly to the root zone, drip irrigation provides a controlled and efficient means of delivering water, ensuring that the crops receive the necessary moisture without excess water reaching the surrounding soil surface.
Subsurface irrigation, with its ability to deliver water directly to the root zone, is also suitable for a variety of crops. Orchards, vineyards, and horticultural crops often benefit from subsurface irrigation as it allows for efficient water uptake and reduced water loss through evaporation.
When considering crop suitability, it is crucial to understand the specific water needs of the plants at different growth stages. Some plants, such as young seedlings, may require more frequent irrigation to establish their roots, while established plants may have different requirements depending on their growth stage or fruiting period. Adjusting the irrigation schedule and water application rate accordingly will ensure that the crops receive the optimal amount of water for their growth and development.
Additional factors to consider when determining crop suitability include the type of soil in your garden or field and the overall climate conditions. Some crops are better suited for certain soil types, and certain irrigation methods may work more effectively in specific climates. For example, in sandy or well-draining soils, drip irrigation can help prevent excessive water loss, while in areas with high winds, sprinkler irrigation may be less effective.
By evaluating the water requirements of your crops and understanding the irrigation methods available, you can make an informed decision on the best irrigation method for optimal crop suitability. Consider factors such as water distribution, ease of adjustment, and adaptability to different planting patterns or row spacings to ensure that your chosen method meets the specific needs of your crops.
Soil Type and Topography
Soil type and topography are important factors to consider when selecting the best irrigation method for your garden or agricultural field. Different soil types have varying water-holding capacities, drainage properties, and nutrient availability, which can influence the effectiveness of different irrigation techniques. Likewise, the topography of your land can impact water distribution and the suitability of certain irrigation methods.
The first consideration is soil type. Soil texture, such as sandy, loamy, or clay soils, plays a significant role in water movement and retention. Sandy soils have high drainage rates but low water-holding capacity, which may require more frequent irrigation. In contrast, clay soils have higher water-retention capacities but poorer infiltration rates, potentially leading to waterlogging or runoff if not managed properly. Loamy soils, which have a balanced combination of sand, silt, and clay, are generally considered ideal for plant growth and water management.
In terms of irrigation methods, surface irrigation is often suited for permeable soils like sandy soil, as it can evenly distribute water across the surface and allow for sufficient infiltration. However, caution should be taken to prevent excess water from pooling or washing away in sandy soils with high permeability.
Drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation are well-suited for clay soils as they deliver water more directly to the plant roots, minimizing water loss through evaporation and promoting efficient water uptake. These methods also help prevent surface runoff in clay soils, ensuring that water reaches the root zone without excessive flooding.
Topography, or the slope and contour of your land, influences water movement and the choice of irrigation method. For flat or gently sloping terrain, surface irrigation can be effective as water can flow evenly across the field. However, it is necessary to properly level the field and manage water distribution to avoid water pooling or uneven irrigation.
In areas with steep slopes or uneven topography, drip irrigation or subsurface irrigation may be more suitable. These methods allow for controlled and targeted water application directly to the root zone, reducing the risk of water runoff on slopes and preventing soil erosion.
Understanding the soil type and topography of your garden or agricultural field will help you select an irrigation method that aligns with these characteristics. It is also important to consider any variations in soil type or topography within your land and adjust the irrigation accordingly.
Conducting a soil analysis and consulting with agricultural experts can provide valuable insights into the specific soil type, properties, and moisture-holding capacities. Observing the natural drainage patterns of your land and identifying any areas prone to waterlogging or erosion can also inform your irrigation decision-making process.
By considering the soil type and topography, you can choose an irrigation method that optimizes water penetration, minimizes water loss, and promotes healthy plant growth in your specific garden or agricultural setting.
Cost and Maintenance
Cost and maintenance are important factors to consider when selecting the best irrigation method for your garden or agricultural field. These factors can have a significant impact on your budget, as well as the long-term viability and sustainability of your irrigation system.
When it comes to cost, it’s important to consider both the initial investment and the ongoing expenses associated with each irrigation method. Some methods may require a higher upfront cost due to the need for specialized equipment or infrastructure. For example, subsurface irrigation systems may involve the installation of underground pipes or emitters, which can incur higher initial costs compared to other methods. On the other hand, surface irrigation or sprinkler irrigation generally have lower upfront costs, as they may require less equipment and simpler setups.
However, it’s essential to look beyond the initial investment and consider the long-term costs of maintenance and operation. Drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation, although they may have higher upfront costs, are typically more cost-effective in the long run. They deliver water directly to the root zone, minimizing water waste and reducing the need for additional resources or treatments. These methods also tend to have lower energy requirements and may save on water costs, especially in areas with high water prices.
In terms of maintenance, each irrigation method comes with specific maintenance needs. Some methods, like surface irrigation or sprinkler irrigation, may require regular checks for clogged nozzles, damaged equipment, or misaligned sprinkler heads. Periodic adjustments and repairs may be necessary to ensure optimal water distribution and minimize water loss.
Drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation generally require less maintenance, as the water is released through emitters below the soil surface. However, it is still essential to monitor the system for any clogs or leaks and promptly address any issues to prevent water loss or damage to the system. Routine inspections and occasional cleanings may be needed to maintain the efficiency of the emitters or drippers.
Considering the cost and maintenance requirements, it is important to find a balance between your budget and the long-term sustainability of your irrigation system. Evaluate the specific needs of your garden or agricultural field, including the size, soil type, crop requirements, and water availability, to determine which irrigation method aligns with your financial and maintenance capabilities.
It is also worth exploring any available incentives, rebates, or grants offered by local or regional authorities, as these programs can help offset some of the initial costs of installing water-efficient irrigation systems. Additionally, consulting with irrigation specialists or local agricultural extension services can provide valuable advice on cost-effective irrigation solutions and proper maintenance practices for your specific needs.
By carefully considering the cost and maintenance factors associated with each irrigation method, you can choose the most financially viable and sustainable option for your garden or agricultural operation.
Environmental Impact
Considering the environmental impact of an irrigation method is vital for sustainable and responsible water management in gardening and agriculture. Different irrigation methods have varying effects on the environment, including water conservation, soil health, energy usage, and carbon footprint. Let’s explore the environmental considerations associated with different irrigation techniques.
Water conservation is a primary environmental concern in irrigation. Methods that minimize water loss through evaporation and runoff, such as drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation, are highly efficient in water usage. These methods deliver water directly to the plant roots, reducing wastage and ensuring that water reaches the intended target without unnecessary exposure to the atmosphere. By conserving water, not only are valuable water resources preserved, but the strain on local water supplies is also minimized.
Another environmental consideration is soil health and nutrient management. Over-irrigation or improper water application methods can lead to nutrient leaching and the depletion of essential nutrients from the soil. Drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation, by supplying water directly to the root zone, can help prevent nutrient loss, as the nutrients are delivered efficiently to the plants’ roots. These methods also contribute to improved soil structure and reduced soil erosion, preserving the health and fertility of the soil.
Energy usage and associated carbon emissions are important environmental factors to evaluate. Some irrigation methods, such as surface irrigation and sprinkler irrigation, may require high energy inputs for pumping water or operating sprinkler systems. These methods can have a higher carbon footprint, especially if fossil fuels are used for energy generation. Drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation generally have lower energy requirements, minimizing the environmental impact related to energy usage.
Furthermore, the use of pesticides and herbicides can have environmental consequences. Certain irrigation methods, like surface irrigation and sprinkler irrigation, may lead to water splashing onto foliage, increasing the risk of plant diseases and promoting weed growth. This may result in a higher dependence on chemical treatments. Drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation, which deliver water directly to the root zone, reduce the chance of foliar diseases and weed proliferation, potentially minimizing the need for chemical interventions.
Additionally, considering the overall ecological impact is important. The choice of irrigation method should align with sustainable land management practices, promoting biodiversity, and minimizing disruptions to natural ecosystems. By reducing water wastage, preventing soil erosion, and promoting healthier plant growth, water-efficient irrigation methods contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to gardening and agriculture.
It is crucial to carefully assess the environmental impact of each irrigation method and weigh the benefits and trade-offs. Local climate, resource availability, and specific environmental goals should be taken into consideration. Engaging with local agricultural extension services or environmental experts can provide valuable insights into the best irrigation practices for minimizing environmental impact and optimizing resource efficiency in your specific region.
By selecting an irrigation method that aligns with environmental considerations, you can contribute to a more sustainable and ecologically responsible approach to water usage in gardening and agriculture.
Conclusion
Choosing the best irrigation method for your garden or agricultural field is crucial for the success and sustainability of your plants. Understanding the different irrigation methods and considering key factors such as water efficiency, crop suitability, soil type and topography, cost and maintenance, and environmental impact, will guide you in making an informed decision.
Water efficiency should be a primary consideration, as it helps conserve water resources and ensures that plants receive the optimal amount of water for healthy growth. Drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation are particularly efficient methods, delivering water directly to the root zone and minimizing water loss through evaporation or runoff.
Considering the specific water requirements of your crops will help determine the most suitable irrigation method. Crops with higher water needs, such as rice or corn, may benefit from surface irrigation or sprinkler irrigation, while drip and subsurface irrigation are well-suited for fruit trees, vegetables, and ornamentals.
Soil type and topography are important factors to consider, as they influence water movement and the effectiveness of different irrigation methods. Sandy soils may benefit from surface irrigation, while clay soils may require drip irrigation or subsurface irrigation to prevent waterlogging or runoff.
Cost and maintenance considerations play a significant role in selecting the irrigation method that aligns with your budget and long-term viability. While some methods may have higher upfront costs, like subsurface irrigation, they may offer long-term cost savings through reduced water usage and maintenance needs. Regular maintenance of any irrigation system is essential to ensure optimal performance and minimize water loss or damage.
Lastly, considering the environmental impact of the chosen irrigation method is crucial for sustainable and responsible water management. Methods that conserve water, promote soil health, and minimize energy usage and carbon emissions are preferred. Drip irrigation and subsurface irrigation demonstrate good environmental characteristics by reducing water wastage, preserving soil fertility, and minimizing the need for chemical treatments.
In conclusion, by carefully evaluating and balancing the factors of water efficiency, crop suitability, soil type and topography, cost and maintenance, and environmental impact, you can select the best irrigation method for your garden or agricultural field. Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution, and understanding the specific needs and conditions of your plants and environment will lead to successful and sustainable irrigation practices.