Home>Gardening News and Trends>Latest News>What Insects Are Good For Gardens


Latest News
What Insects Are Good For Gardens
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the Latest News on What Insects Are Good for Gardens and how they can benefit your garden. Learn about natural pest control and promoting a healthy ecosystem.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Gardens are not just a patch of land; they are dynamic ecosystems that support a myriad of plant and animal life. While insects can often be seen as pests, harmful to our beloved plants, many insects actually play a vital role in maintaining a healthy garden ecosystem. These insects contribute to various ecological processes, such as pollination, decomposition, and natural pest control.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of insects in gardens and how they can positively impact your gardening endeavors. From predatory insects that keep pest populations in check, to pollinators that help plants reproduce, and decomposers that break down organic matter, we will uncover their crucial roles and the advantages they bring to your garden.
By understanding the importance of these insects and learning how to attract them, you can create a thriving and sustainable garden that flourishes with life. So, let’s dive in and discover the incredible contributions of insects to our gardens.
Benefits of Insects in Gardens
Insects are not just mere creatures that inhabit our gardens; they are integral players in maintaining the natural balance of these ecosystems. Here are some of the key benefits that insects bring to our gardens:
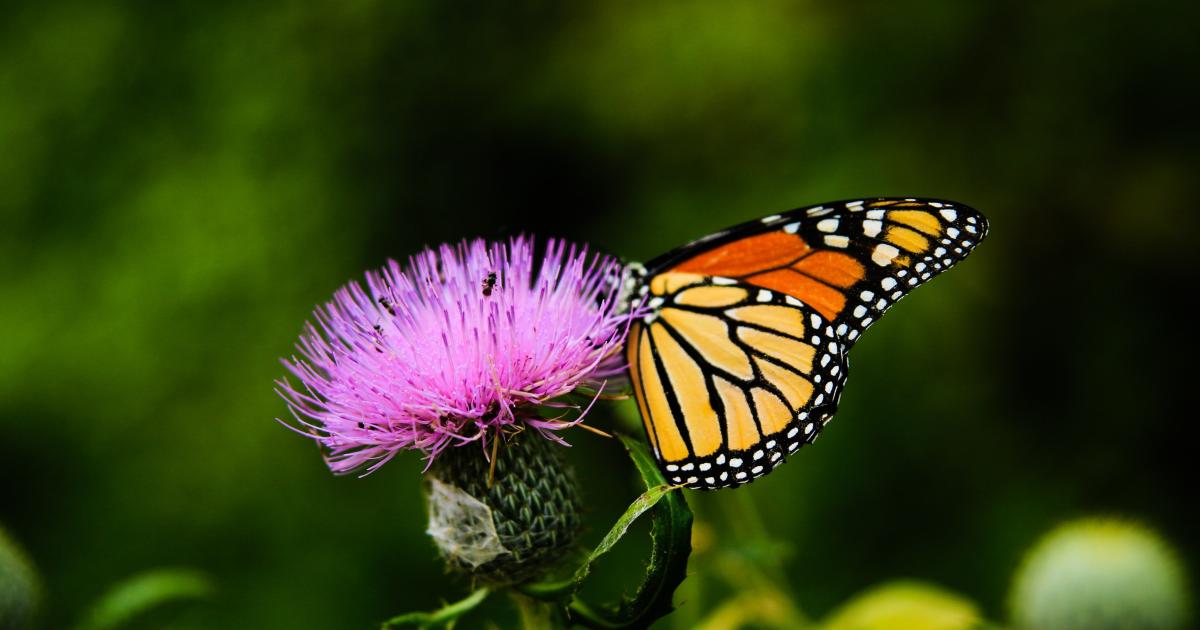
- Pollination: One of the most important contributions of insects is their role as pollinators. Bees, butterflies, and other insects transfer pollen from one flower to another, facilitating the reproduction of plants. This enables the plants to produce fruits, vegetables, and seeds, ensuring the growth and abundance of various plant species in your garden.
- Natural Pest Control: Certain insects act as natural pest controllers by preying on harmful garden pests. Ladybugs, for example, feed on aphids, which are notorious for damaging plants. By attracting these beneficial insects, you can reduce the need for chemical pesticides, creating a more environmentally friendly and sustainable garden.
- Decomposition: Decomposer insects, such as earthworms and beetles, play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter, such as fallen leaves and dead plants. They help in the process of decomposition and nutrient cycling, enriching the soil with vital nutrients that are essential for plant growth.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: By promoting the presence of various insect species in your garden, you contribute to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem. This, in turn, attracts a diverse range of birds and other wildlife, creating a harmonious and thriving habitat.
The benefits of insects in gardens extend beyond these key aspects. They also contribute to soil aeration, seed dispersal, and even serve as indicators of ecological health. Therefore, fostering a healthy insect population in your garden is not only beneficial for your plants but also for the overall ecosystem.
Predatory Insects
Predatory insects are the superheroes of the garden, silently working to keep harmful pest populations under control. These insects, armed with their sharp senses and voracious appetites, target and consume pests that can wreak havoc on your plants. Here are some notable predatory insects that you should welcome into your garden:
- Ladybugs: Ladybugs, also known as ladybirds, are a familiar sight in gardens. These small, colorful beetles feed on aphids, mites, and other soft-bodied insects. A single ladybug can consume hundreds of aphids in a day, making them an effective natural defense against these destructive pests.
- Praying Mantids: Praying mantids are fascinating insects that rely on camouflage and lightning-fast reflexes to capture their prey. They feast on a wide range of insects, including flies, grasshoppers, and even small spiders. Their unique appearance and hunting behavior make them a welcome presence in gardens.
- Hoverflies: Hoverflies resemble bees or wasps but are harmless and serve as valuable pollinators. Their larval stage, known as “rat-tailed maggots,” feed on aphids and other small insects, while the adults visit flowers for nectar, aiding in the pollination process.
- Ground Beetles: Ground beetles are nocturnal predators that inhabit the soil. They prey on a wide range of pests, including slugs, snails, caterpillars, and even weed seeds. These beetles can consume multiple times their body weight in pests every night, making them an invaluable asset to your garden.
These are just a few examples of the many predatory insects that can help you maintain a balanced garden ecosystem. By making your garden a welcoming environment for these beneficial insects, you can reduce the need for harmful pesticides and ensure the health and well-being of your plants.
Pollinating Insects
Pollinating insects are the unsung heroes of the plant world, playing a vital role in the reproduction and survival of countless plant species. These insects facilitate the transfer of pollen from the male parts of the flower to the female parts, allowing fertilization to occur. Here are some important pollinating insects that contribute to the success of your garden:
- Bees: Bees are perhaps the most well-known and efficient pollinators. They have specialized hairs that collect pollen as they move from flower to flower in search of nectar. As bees travel, they inadvertently transfer pollen, enabling plants to reproduce and produce fruits and seeds.
- Butterflies: Butterflies are not only admired for their beauty but also for their role as pollinators. As they feed on nectar, their long tongues collect pollen, which they transfer from flower to flower. Butterflies are particularly attracted to brightly colored, fragrant flowers and play a significant role in pollinating these species.
- Moths: Moths are nocturnal pollinators, attracted to white, pale, or fragrant flowers that open in the evening. They are equipped with long tongues that allow them to access nectar, all while picking up and dispersing pollen in the process.
- Hoverflies: In addition to their predatory capabilities, hoverflies also contribute to pollination. As they hover near flowers, they inadvertently pick up and transfer pollen while feeding on nectar. Their fuzzy bodies help facilitate the pollen transfer, making them important pollinators in the garden.
By attracting and supporting these pollinating insects in your garden, you can ensure the successful reproduction and fruiting of your plants. Planting a diverse range of flowers that bloom at different times throughout the growing season and providing a water source will help attract these valuable pollinators to your garden.
Decomposer Insects
While pollinators and predators often steal the spotlight, decomposer insects play a crucial role in maintaining the health and fertility of your garden’s soil. These insects specialize in breaking down organic matter, such as fallen leaves, dead plants, and animal remains, into nutrient-rich compost. Here are some notable decomposer insects that contribute to the decomposition process:
- Earthworms: Earthworms are soil-dwelling decomposers that play a significant role in improving soil structure and fertility. As they tunnel through the soil, they consume organic matter and excrete nutrient-rich castings, also known as worm castings. These castings are an excellent source of organic matter and essential nutrients for plants.
- Beetles: Beetles, including dung beetles and carrion beetles, are important decomposers that facilitate the breakdown of animal waste and carcasses. They help recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem and prevent the spread of diseases by disposing of decaying organic matter.
- Millipedes and Springtails: These tiny decomposer insects feed on decaying plant matter, fungi, and bacteria. They assist in breaking down organic material into smaller pieces, accelerating the decomposition process. Their feeding activities also contribute to the aeration and moisture balance of the soil.
- Woodlice: Woodlice, also known as pillbugs or sowbugs, are commonly found in decomposing wood or organic debris. They help in the breakdown of dead plant material and contribute to the nutrient cycling process in the garden.
By fostering a healthy population of decomposer insects in your garden, you can improve soil fertility and nutrient availability for your plants. Creating a compost pile or using leaf litter as mulch can provide them with ample organic matter to decompose, enhancing the overall health of your garden ecosystem.
Natural Pest Control
Dealing with pests in the garden can be a frustrating and challenging task. However, relying on natural pest control methods can help manage pest populations effectively while minimizing the use of harmful chemical pesticides. By harnessing the power of beneficial insects, you can create a balanced and sustainable garden ecosystem. Here are some ways in which natural pest control can be achieved:
- Encouraging Predatory Insects: As discussed earlier, attracting predatory insects such as ladybugs, praying mantids, and ground beetles can help keep pest populations in check. These natural predators feed on plant-damaging pests, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
- Companion Planting: Companion planting involves strategically placing certain plants together to repel pests or attract beneficial insects. For example, marigolds emit a scent that repels aphids, while attracting hoverflies, which are natural predators of aphids.
- Physical Barriers: Implementing physical barriers can prevent pests from damaging your plants. Using row covers, netting, or fences can keep out pests like birds, rabbits, and larger insects, reducing the necessity for chemical deterrents.
- Crop Rotation: Rotating your crops each season can help break the pest life cycle. Pests that are specific to certain plants may not survive or thrive if the plants are moved to a different location in subsequent growing seasons.
- Planting Diversity: Planting a diverse range of plant species in your garden not only adds visual interest but also discourages the buildup of specific pest populations. Diversity disrupts pest cycles and creates a more balanced ecosystem that can better withstand pest pressures.
By employing these natural pest control methods, you can minimize the need for chemical pesticides, which can be harmful to both beneficial insects and the environment. Embracing these techniques contributes to the overall health and resilience of your garden.
Attracting Beneficial Insects to Your Garden
If you want to reap the benefits of beneficial insects in your garden, it’s essential to create an inviting environment that encourages their presence. By implementing specific strategies, you can attract and retain these helpful insects, ensuring a thriving garden ecosystem. Here are some tips for attracting beneficial insects to your garden:
- Provide Food Sources: Plant a variety of flowering plants with different shapes, sizes, and bloom times to offer a continuous supply of nectar and pollen. Native plants are particularly attractive to beneficial insects as they have evolved together over time.
- Include a Water Source: Ensure your garden provides a water source, such as a shallow dish filled with fresh water or a birdbath. Beneficial insects need water for hydration, especially during hot and dry periods.
- Plant in Clusters: Planting flowers in clusters or blocks rather than scattered throughout the garden makes it easier for beneficial insects to locate and navigate between food sources. This also increases the chances of successful pollination and pest control efforts.
- Create Shelter: Incorporate elements in your garden that provide shelter and refuge for beneficial insects. This can include tall grasses, shrubs, rock piles, or even insect hotels. These areas will offer protection and resting places for beneficial insects.
- Minimize Pesticide Use: Avoid or minimize the use of chemical pesticides in your garden, as they can harm not only harmful pests but also beneficial insects. Opt for organic pest control methods and integrated pest management techniques instead.
- Be Mindful of Seasonal Needs: Different beneficial insects have different seasonal activity patterns. Plan and plant your garden to provide a continuous source of food and shelter throughout the year, catering to the needs of different beneficial insects at different times.
By implementing these practices, you can create an ecosystem that attracts and supports an abundance of beneficial insects. The presence of these helpful insects will contribute to increased pollination, natural pest control, and overall garden health.
Conclusion
Insects are often seen as pests, but they play vital roles in the garden ecosystem. From pollination to natural pest control and decomposition, insects contribute to the health and abundance of plant life. By understanding the benefits of insects in gardens and implementing strategies to attract beneficial insects, you can create a thriving and sustainable garden.
Predatory insects like ladybugs, praying mantids, and hoverflies help keep pest populations in check by feeding on harmful insects. Pollinating insects such as bees, butterflies, and hoverflies facilitate the reproduction of plants and ensure the production of fruits and seeds. Decomposer insects like earthworms and beetles break down organic matter, enriching the soil with nutrients for plant growth.
Embracing natural pest control methods, including encouraging beneficial insects, companion planting, crop rotation, and physical barriers, can reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides and promote a healthier garden ecosystem. Creating a garden with diverse plant species, providing food sources, water, and shelter, and being mindful of seasonal needs can attract and support a wide range of beneficial insects.
By fostering a balanced and biodiverse garden ecosystem, you not only enhance the beauty and productivity of your garden but also contribute to the overall health of the environment. So, embrace the presence of insects in your garden, and let them work their magic to create a harmonious and flourishing outdoor space.