Home>Types of Gardening>Ornamental Gardening>What Are Coniferous Trees


Ornamental Gardening
What Are Coniferous Trees
Modified: February 8, 2024
Discover the beauty of coniferous trees in ornamental gardening. Learn about their characteristics, benefits and how to incorporate them into your landscape for a stunning visual appeal.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating world of coniferous trees! If you have ever marveled at the natural beauty of towering evergreens or been awed by the serenity of a pine forest, then you have encountered the enchanting presence of coniferous trees. These iconic trees, with their needle-like leaves and cone-bearing structures, are an integral part of our natural environment and have captivated the imaginations of gardeners, nature enthusiasts, and artists for centuries.
Coniferous trees, also known as evergreen trees or gymnosperms, belong to the botanical group Coniferales. They are characterized by their unique features, including needle or scale-like leaves, resinous sap, and the production of cones containing seeds. These remarkable trees exhibit a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors, from the towering Douglas fir to the bushy juniper.
While coniferous trees are prominent in regions with colder climates, such as boreal forests, they can also be found in various habitats around the world. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in diverse ecosystems, including mountainous regions, coastal areas, and even arid deserts.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of coniferous trees, delving into their unique characteristics, the different types of conifers, their importance in the ecosystem, and their various economic uses. Join us on this journey to discover the magic and significance of these magnificent trees.
Definition of Coniferous Trees
Coniferous trees, also known as evergreen trees or gymnosperms, are a group of trees belonging to the botanical order Coniferales. They are distinguished by their unique reproductive structures, including cones and needle or scale-like leaves. Unlike deciduous trees, which shed their leaves in the fall, conifers retain their foliage year-round, giving them the characteristic evergreen appearance.
The term “coniferous” is derived from the Latin words “conus,” meaning cone, and “ferre,” meaning to bear. This name accurately describes the reproductive structures of these trees, known as cones. Cones are formations that house the seeds of conifers, with male and female cones typically found on separate trees.
An important characteristic of coniferous trees is their needle or scale-like leaves. While some species have long, slender needles, others have shorter and softer needles or even flattened, scale-like foliage. This adaptation helps reduce water loss and prevents damage from harsh weather conditions.
Coniferous trees are able to thrive in a variety of habitats, from cold boreal forests to dry, rocky slopes. Their ability to survive in harsh conditions is due in part to their resinous sap, which acts as a natural protection against pests and diseases. Additionally, many conifers have shallow root systems that allow them to access both surface and deep soil moisture.
Overall, coniferous trees are a diverse and fascinating group of plants that play a vital role in our natural environment. Their unique characteristics and adaptability have made them an integral part of many ecosystems and a beloved feature of ornamental gardens around the world.
Characteristics of Coniferous Trees
Coniferous trees possess several distinctive characteristics that set them apart from other types of trees. These features contribute to their resilience and success in various habitats:
- Needle or Scale-like Leaves: One of the defining features of coniferous trees is their needle or scale-like leaves. These leaves are adapted to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures and low moisture. The needles or scales also have a reduced surface area, minimizing water loss through transpiration.
- Evergreen Foliage: Unlike deciduous trees, which shed their leaves in the fall, conifers retain their foliage year-round. This evergreen characteristic allows them to photosynthesize and produce food throughout the year, even in colder climates.
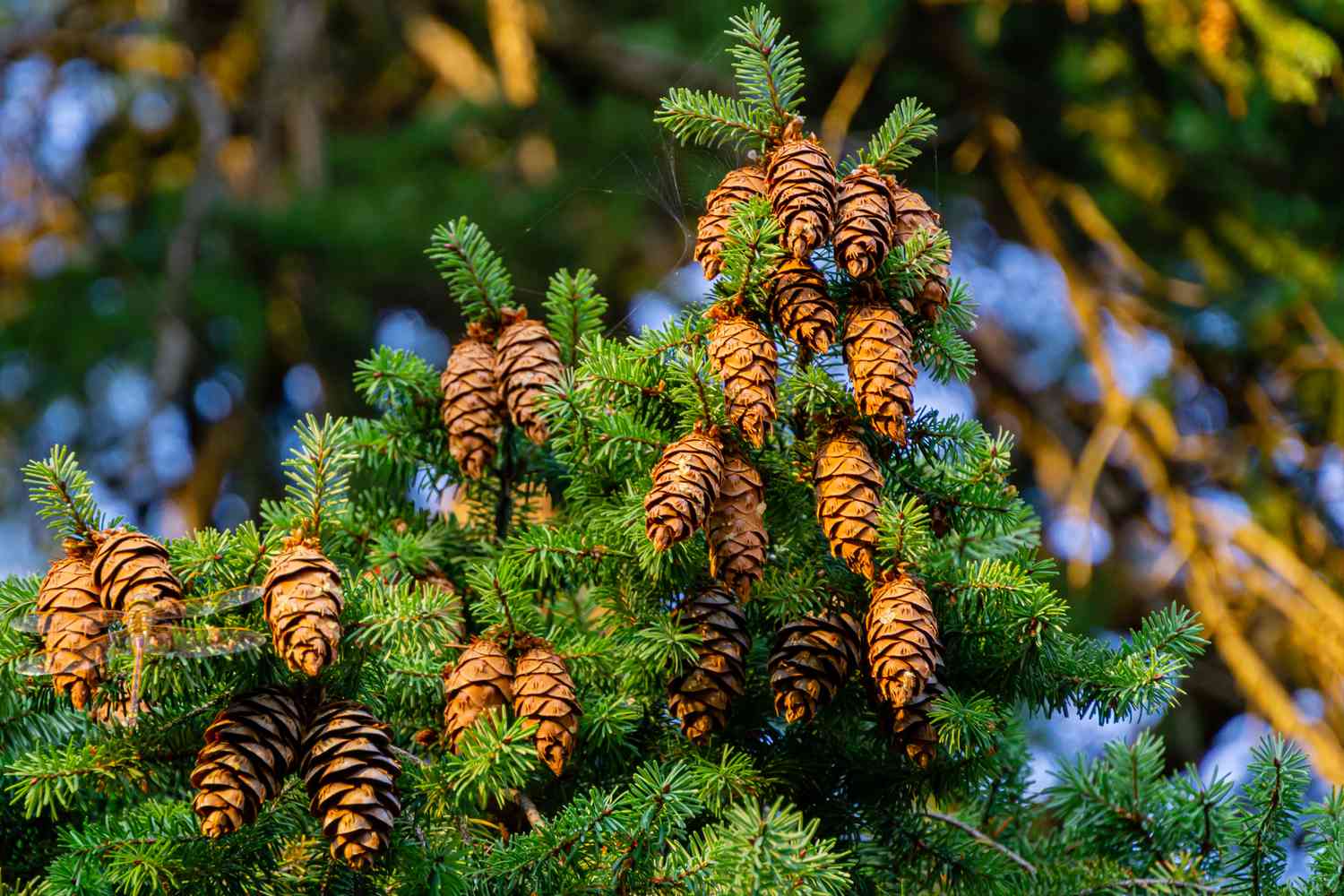
- Cones: Conifers produce cones as their reproductive structures. These cones contain the tree’s seeds and can be either male cones or female cones. Male cones produce pollen, which is carried by the wind to fertilize the female cones. The female cones, once fertilized, develop into seed-bearing structures.
- Resinous Sap: Conifers produce a sticky and fragrant resinous sap. This sap serves as a natural defense mechanism against insects, fungus, and other potential threats to the tree. It also helps seal wounds and prevents excessive moisture loss.
- Conical Shape: Many coniferous trees exhibit a conical shape, with a broad base and a pointed top. This shape enables them to efficiently shed snow and withstand heavy winds, making them well-suited for harsh winter conditions.
- Shallow Root System: Conifers typically have shallow and widespread root systems. While this may make them more susceptible to windthrow, it also allows them to efficiently gather moisture from the upper layers of the soil. Moreover, their shallow roots often form a dense network that helps stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
These characteristics make coniferous trees identifiable and contribute to their ability to thrive in various environments. They are not only aesthetically appealing but also provide essential ecological and economic benefits.
Types of Coniferous Trees
Coniferous trees encompass a wide variety of species, each with its own unique characteristics and habitat preferences. Here are some of the most common types of conifers:
- Pine Trees: Pine trees are perhaps the most recognizable type of conifers. They have long, slender needles grouped in bundles and typically produce large, woody cones. There are numerous species of pine trees found throughout the world, including the Eastern White Pine, Scots Pine, and Ponderosa Pine.
- Spruce Trees: Spruce trees are known for their short, sharp needles that cover their branches in a dense tufted fashion. They often have distinctive cones that hang downward, providing a unique visual appeal. Examples of spruce trees include the Norway Spruce, Colorado Spruce, and Blue Spruce.
- Fir Trees: Fir trees have flat, flexible needles that are typically softer to the touch than those of other conifers. They produce upright cones that disintegrate when mature, releasing their seeds. Popular fir tree species include the Balsam Fir, Douglas Fir, and Noble Fir.
- Cedar Trees: Cedar trees are known for their aromatic wood and scale-like foliage. They often have a pyramid-like shape and produce small, woody cones. Cedar trees are valued for their durable timber and are commonly used in the construction industry. Examples include the Eastern Red Cedar, Western Red Cedar, and Atlantic White Cedar.
- Cypress Trees: Cypress trees are typically found in wetland areas and have scale-like or feathery foliage. They are characterized by their unique knee-like projections that emerge from their root systems. The Bald Cypress and Leyland Cypress are familiar examples of cypress trees.
- Juniper Trees: Juniper trees are known for their hardy nature and their berry-like cones. They have needle or scale-like leaves, often with a unique blue or gray hue. Juniper trees are commonly used in landscaping and can be found in various forms, including shrubs and tall trees.
These are just a few examples of the vast array of coniferous tree species that exist worldwide. Each one offers its own beauty, resilience, and ecological benefits, contributing to the diversity and splendor of our natural landscapes.
Importance of Coniferous Trees
Coniferous trees play a significant role in our environment and have a multitude of benefits that make them invaluable. Here are some of the key reasons why coniferous trees are important:
- Environmental Protection: Coniferous forests act as vital green lungs, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen through photosynthesis. They help mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The dense foliage of coniferous trees also provides a habitat for numerous animal species, promoting biodiversity and preserving ecological balance.
- Soil Stabilization: The extensive root systems of coniferous trees help prevent soil erosion, especially on slopes and in areas with fragile soil. The dense network of shallow roots holds the soil in place, reducing the risk of landslides and runoff.
- Water Conservation: Coniferous trees contribute to water conservation by reducing evaporation and retaining moisture in the soil. Their needle or scale-like leaves help slow down water loss through transpiration, preserving water resources in arid regions.
- Wildlife Habitat: Coniferous forests provide vital habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna. The dense canopy of these trees provides shelter and nesting sites for birds, mammals, and insects. Many animal species rely on coniferous forests for food, protection, and breeding grounds.
- Wood and Timber: Coniferous trees are economically significant for their wood and timber production. The strong and durable wood of coniferous species is used in construction, furniture making, and paper production. Sustainable management of coniferous forests ensures a renewable source of timber and contributes to the economy.
- Recreation and Aesthetics: Coniferous forests are popular destinations for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and wildlife watching. Many people find solace and tranquility in the serenity of coniferous landscapes. Their beauty and majestic presence add to the aesthetic appeal of parks, gardens, and natural landscapes.
From their environmental contributions to their economic and recreational value, coniferous trees have a profound impact on our world. Their conservation and sustainable management are essential to preserve these invaluable benefits for future generations.
Environmental Impact of Coniferous Trees
Coniferous trees have a significant environmental impact, shaping the health and well-being of our ecosystems. Let’s explore some of the key environmental contributions of these remarkable trees:
- Carbon Sequestration: Coniferous forests play a crucial role in mitigating climate change. They act as carbon sinks, absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. The accumulated carbon is then stored in the tree trunks, branches, and roots, helping to reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Air Purification: Coniferous trees remove pollutants from the air, improving air quality and promoting human health. Through the process of photosynthesis, they absorb harmful carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide, while releasing oxygen into the atmosphere. The dense foliage of conifers also acts as a physical barrier, trapping dust and particulate matter, and filtering the air we breathe.
- Water Regulation: Coniferous trees have a significant impact on water regulation within ecosystems. Their dense canopies intercept rainfall, reducing erosion and allowing water to infiltrate into the soil. The extensive root systems of conifers help to improve soil structure and increase water retention, reducing the risk of flooding and preserving water resources.
- Biodiversity Support: Coniferous forests provide critical habitat for a multitude of plant and animal species. The complex structure of these forests, with their layers of understory vegetation, deadwood, and tree canopies, supports diverse ecosystems. Many species of birds, mammals, insects, and fungi rely on coniferous forests for shelter, food, and breeding grounds, contributing to overall biodiversity.
- Soil Conservation: The extensive root systems of coniferous trees help stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and landslides. The roots bind the soil particles together, reducing the risk of soil degradation and loss. The dense litter layer composed of fallen needles and cones also acts as a natural mulch, protecting the soil from erosion and retaining moisture.
- Climate Regulation: Coniferous forests play a role in regional climate regulation. They have a cooling effect on the environment due to their ability to retain moisture and provide shade. The release of water vapor through the leaves of conifers contributes to local humidity levels and can influence precipitation patterns.
The environmental impact of coniferous trees is far-reaching and essential for maintaining the health of our planet. Protecting and conserving these forests is crucial in combating climate change, preserving biodiversity, and ensuring a sustainable future for both humans and wildlife.
Economic Uses of Coniferous Trees
Coniferous trees have a wide range of economic uses that contribute to various industries and economies worldwide. Let’s explore some of the key economic benefits provided by these valuable trees:
- Timber and Lumber: Coniferous trees are highly valued for their wood, which is used in the production of timber and lumber. The strong, durable nature of coniferous wood makes it ideal for construction, furniture making, and woodworking industries. Species like pine, spruce, and fir are commonly harvested for their timber and contribute substantially to the economy.
- Paper and Pulp Production: Coniferous trees are a vital source of raw material for the paper and pulp industry. The long fibers found in coniferous wood make it suitable for producing high-quality paper products, including printing paper, packaging materials, and tissue paper. Sustainable management practices ensure a renewable supply of pulpwood and support the paper industry.
- Resin and Essential Oils: Some coniferous trees, such as pines and cedars, produce resin with commercial value. Resin can be used in the production of varnishes, adhesives, and as a base for essential oils. The essential oils extracted from coniferous trees are utilized in various industries, including fragrances, cosmetics, and aromatherapy.
- Christmas Trees: Coniferous trees have long been associated with the festive season and are widely used as Christmas trees. The demand for fresh-cut conifers during the holiday season contributes significantly to local economies. Christmas tree farming provides jobs and income for many individuals and boosts tourism in rural areas.
- Landscaping and Ornamental Gardens: Coniferous trees are highly valued for their aesthetic appeal and are widely used in landscaping projects and ornamental gardens. Dwarf and compact varieties of conifers are popular for their unique shapes, colors, and textures, adding beauty and interest to gardens, parks, and public spaces.
- Medicinal and Herbal Uses: Certain coniferous trees have medicinal properties and are used in traditional medicine and herbal remedies. For example, extracts from juniper trees are used as diuretics, while cedarwood oil is used in natural remedies and aromatherapy. The pharmaceutical and herbal industries benefit from the utilization of coniferous trees for their therapeutic properties.
The economic uses of coniferous trees result in job creation, economic growth, and the support of various industries. Sustainable management and responsible harvesting practices ensure the continued availability of these resources for future generations.
Conclusion
Coniferous trees are a remarkable group of plants that have a profound impact on our environment and economy. Their unique characteristics, ranging from needle or scale-like leaves to cone-bearing structures, make them easily recognizable and beloved by many. These trees are not only aesthetically pleasing but also play vital roles in maintaining ecological balance and contributing to human well-being.
From an environmental perspective, coniferous trees have a range of benefits. They sequester carbon dioxide, purify the air, conserve water, support biodiversity, and stabilize the soil. Coniferous forests act as important habitats for countless plant and animal species, and their preservation is essential to maintain ecosystems and protect our planet.
Economically, coniferous trees have significant value. They provide timber and lumber for construction, contribute to the paper and pulp industries, and yield resin and essential oils used in various commercial products. The cultivation and sale of Christmas trees offer economic opportunities, while the use of conifers in landscaping enhances the aesthetic appeal of gardens and public spaces.
Appreciating the importance of coniferous trees, it is crucial to practice sustainable management and responsible harvesting methods. By implementing conservation efforts and supporting reforestation initiatives, we can ensure the long-term availability of these valuable resources.
In conclusion, coniferous trees are not only captivating in their beauty but also vital components of our ecosystem and economy. Their ability to adapt to different environments, provide essential services, and contribute to a sustainable future makes them truly remarkable. Let us continue to appreciate, conserve, and celebrate the magic of coniferous trees for generations to come.