Home>Types of Gardening>Ornamental Gardening>What Are Deciduous Trees


Ornamental Gardening
What Are Deciduous Trees
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn about deciduous trees in ornamental gardening. Discover their beauty and benefits in landscapes. Enhance your gardening knowledge!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Deciduous Trees
- Characteristics of Deciduous Trees
- Life Cycle of Deciduous Trees
- Types of Deciduous Trees
- Importance and Benefits of Deciduous Trees
- Environmental Impact of Deciduous Trees
- Seasonal Changes in Deciduous Trees
- Common Deciduous Trees in Different Regions
- Cultivation and Care of Deciduous Trees
- Conclusion
Introduction
Ornamental gardening is a delightful hobby that allows you to create an aesthetically pleasing and visually appealing outdoor space. One of the key elements in achieving a beautiful garden is the inclusion of deciduous trees. These magnificent trees not only provide shade and shelter but also add color and texture to your landscape throughout the changing seasons.
Deciduous trees, as the name suggests, are trees that undergo a natural process of shedding their leaves during specific times of the year. This cycle of leaf shedding and re-growth is closely tied to the changing seasons, and it plays a vital role in the life cycle and adaptation of these trees.
In this article, we will explore the characteristics and life cycle of deciduous trees, the wide variety of tree species that fall into this category, and the importance of incorporating them into your ornamental garden. We will also delve into the environmental impact of deciduous trees, their seasonal changes, commonly found species in different regions, and tips for cultivating and caring for these trees to ensure their optimal growth and health.
So, whether you are an avid gardener or simply interested in learning more about these captivating trees, read on to discover the wonders of deciduous trees and how they can enhance the beauty and vitality of your garden.
Definition of Deciduous Trees
Deciduous trees are a classification of trees that undergo a natural process of shedding their leaves in response to seasonal changes. Unlike evergreen trees, which retain their leaves throughout the year, deciduous trees go through a distinct leaf-changing cycle that is dictated by the environmental conditions they grow in.
During the warmer months, deciduous trees produce an abundance of leaves that serve several important functions. These leaves harness energy from the sun through photosynthesis, converting sunlight into nutrients that fuel the tree’s growth and development. The leaves also provide a surface for gas exchange, allowing the tree to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen into the atmosphere.
However, as the days grow shorter and temperatures drop, deciduous trees prepare for winter by entering a dormant phase. To conserve energy and protect themselves from the harsh winter conditions, they shed their leaves. This shedding process, known as abscission, involves the tree detaching the leaf from its stem and sealing off the wound with a protective layer.
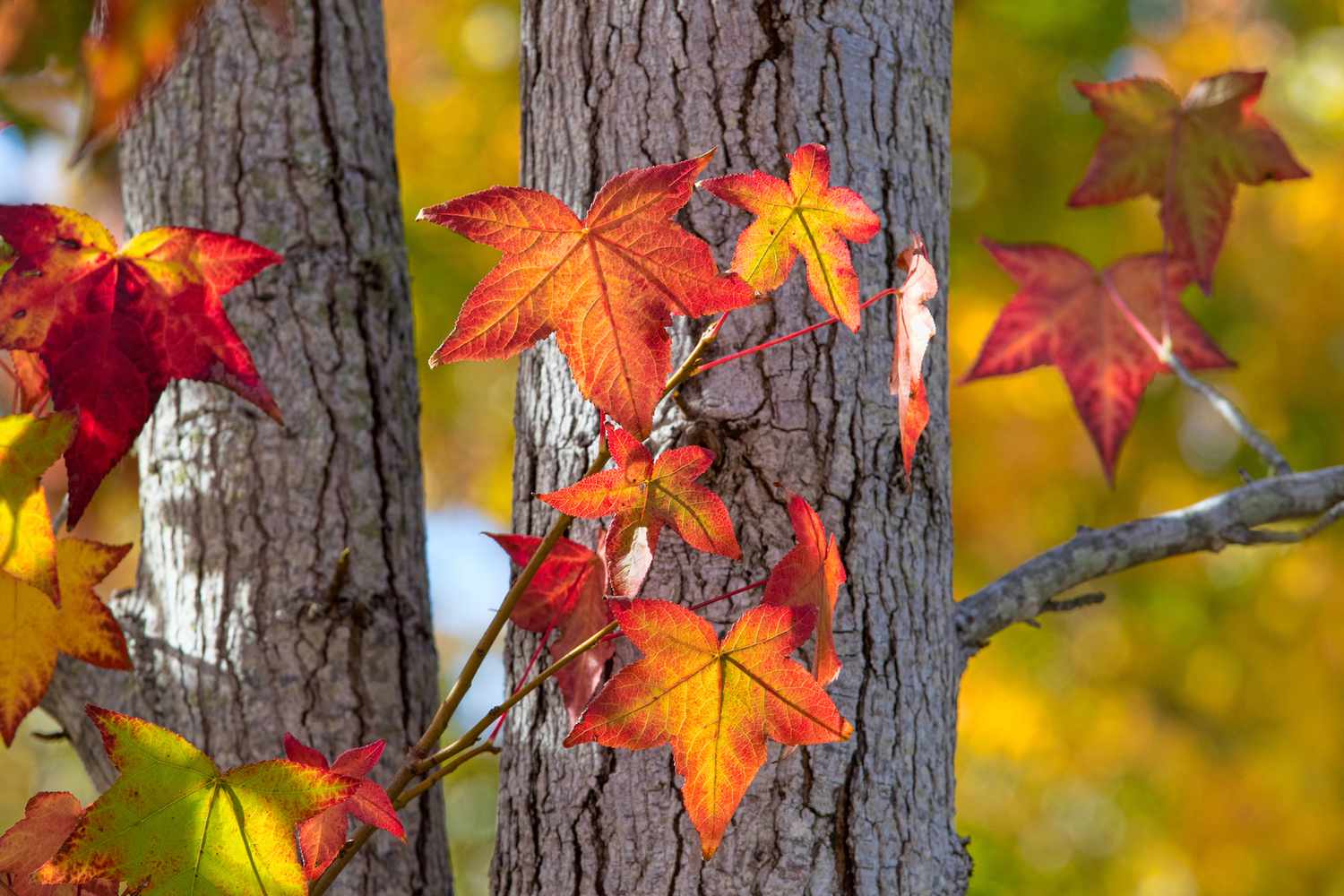
This characteristic of deciduous trees is especially noticeable during the fall season, when the leaves change color before ultimately falling off. This mesmerizing display of vibrant hues, including shades of red, orange, and yellow, is a result of the chlorophyll pigment breaking down and revealing the underlying pigments present in the leaves.
Once the leaves have fallen, the deciduous tree enters a period of rest, conserving its energy until the arrival of spring. As the days become longer and temperatures rise, the tree begins its leafing-out stage, where new leaves emerge from buds, signaling the start of a new growing season.
In essence, the defining characteristic of deciduous trees is their ability to undergo cyclical leaf growth and shedding, adapting to the changing seasons and environmental conditions. This unique behavior sets them apart from evergreen trees and contributes to their charm and allure in ornamental gardening.
Characteristics of Deciduous Trees
Deciduous trees possess a range of distinctive characteristics that set them apart from other types of trees. These characteristics contribute to their beauty, ecological importance, and adaptability to various environments. Understanding these features can help you make informed decisions when selecting and caring for deciduous trees.
1. Leaf Shedding: One of the most notable characteristics of deciduous trees is their ability to shed their leaves. This process occurs during the fall season when the tree withdraws valuable nutrients from the leaves and seals off the leaf stems to conserve energy and protect against cold temperatures. The shedding of leaves not only marks the transition to winter but also allows the tree to go into a dormant state until the arrival of spring.
2. Seasonal Changes: The changing colors of deciduous tree leaves during the fall season are a sight to behold. The vibrant hues of red, orange, and yellow create a stunning visual display that adds to the beauty of any landscape. This seasonal change is a result of the breakdown of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the green color in leaves, which reveals underlying pigments such as carotenoids and anthocyanins.
3. Height and Structure: Deciduous trees come in a wide range of sizes, from small ornamental varieties to towering giants. Their height and structure contribute to the overall design and functionality of a garden. Tall deciduous trees can provide shade, privacy, and natural borders, while smaller varieties are suitable for smaller spaces or as focal points within a garden. The branching patterns and forms of deciduous trees also create unique shapes and textures, adding visual interest throughout the year.
4. Environmental Adaptability: Deciduous trees have developed various adaptations to thrive in different climates and environments. Their ability to shed leaves helps them conserve water during dry periods and protect against frost during the winter. Additionally, deciduous trees are adaptable to a wide range of soil types and can tolerate varying light conditions, making them versatile for different garden settings.
5. Lifespan: While the lifespan of deciduous trees can vary depending on the species and environmental factors, many have relatively long lifespans. Some deciduous trees can live for several decades or even centuries, providing long-lasting beauty and environmental benefits to the landscape.
6. Habitat Support: Deciduous trees play a crucial role in supporting diverse ecosystems. They provide shelter, nesting sites, and food sources for a wide range of birds, insects, and other wildlife. Their fallen leaves also contribute to the nutrient cycling process and enrich the soil, promoting the growth of other plants and organisms.
Overall, the unique characteristics of deciduous trees make them a popular choice for ornamental gardening. Their seasonal changes, diverse forms, and ecological significance add depth and beauty to any landscape, making them an essential element in creating a visually appealing and sustainable garden space.
Life Cycle of Deciduous Trees
The life cycle of deciduous trees is a fascinating process that reflects their adaptation to the changing seasons and environmental conditions. Understanding the different stages of their life cycle can provide valuable insights into their growth and survival strategies.
1. Germination: The life cycle of a deciduous tree begins with the germination of its seeds. Under favorable conditions, such as adequate moisture and temperature, the seed will sprout, sending out a tiny root, followed by a shoot that develops into the tree’s main stem.
2. Growth: As the seedling continues to grow, it establishes a root system to anchor the tree and absorb nutrients and water from the soil. Simultaneously, the shoot or stem becomes taller and produces leaves, which serve as a vital site for photosynthesis and energy production.
3. Maturity: As the tree matures, it continues to grow in height and width, and its branches extend outwards. During this stage, the tree develops a stronger and more intricate root system to support its increasing size and stability. The tree reaches its maximum growth potential and starts producing flowers, leading to the formation of fruits or seeds.
4. Reproduction: Deciduous trees reproduce through the process of pollination. They rely on external agents, such as wind or insects, to transfer pollen from the male parts of the flower to the female parts, resulting in fertilization. Once fertilized, the tree produces fruits or seeds that contain the genetic information necessary for the next generation.
5. Leaf Shedding: As the seasons change and the days become shorter, deciduous trees undergo a process known as leaf shedding or abscission. The tree withdraws valuable nutrients from the leaves and forms a protective layer at the base of each leaf stem. This process helps the tree conserve energy, withstand the cold winter months, and prepare for the upcoming dormancy period.
6. Dormancy: During the dormant phase, the tree enters a resting state where its metabolic activity slows down significantly. This period allows the tree to conserve energy and protect itself from harsh environmental conditions. The tree remains in the dormant stage until the arrival of spring, triggered by increasing temperatures and longer daylight hours.
7. Leafing-out: With the onset of spring, deciduous trees go through the leafing-out stage. Buds that formed the previous year start to grow and unfurl, giving birth to new leaves. The leaves provide the necessary surface area for photosynthesis, allowing the tree to produce carbohydrates and fuel its growth and development for the upcoming season.
This cycle of germination, growth, maturity, reproduction, leaf shedding, dormancy, and leafing-out repeats throughout the life of a deciduous tree. With each year, the tree adds new layers of growth and continues to contribute to the beauty and ecological balance of its surroundings.
Types of Deciduous Trees
Deciduous trees encompass a vast array of species, each with its unique characteristics, growth habits, and aesthetic qualities. From towering hardwoods to ornamental flowering trees, there is an incredible variety to choose from when selecting deciduous trees for your garden. Here are several notable types:
- Oak Trees: Oak trees are renowned for their majestic size and longevity. They have a strong, sturdy structure and feature distinctive lobed leaves. Oak trees provide ample shade and serve as important habitats for various wildlife species.
- Maple Trees: Maple trees are prized for their vibrant foliage and stunning fall colors. They are known for their distinctive leaves with serrated edges and provide shade and beauty to any landscape. Maple trees are also tapped for their sap, which is used to make maple syrup.
- Birch Trees: Birch trees are recognized for their striking white bark and delicate leaves. They add elegance and texture to a garden and are particularly popular in cooler climates. Birch trees are also known for their tolerance of wet soil conditions.
- Dogwood Trees: Dogwood trees are valued for their splendid springtime display of blossoms. These trees produce clusters of small flowers in various shades of pink, white, or red. In addition to their ornamental value, dogwood trees provide food and cover for birds and other wildlife.
- Willow Trees: Willow trees are known for their graceful appearance and the cascading branches. They thrive near bodies of water and add a tranquil and soothing element to any landscape. Willow trees are also commonly used for their flexibility in craft and basket making.
- Crabapple Trees: Crabapple trees are coveted for their abundant spring blooms and showy fruits. They produce colorful and fragrant flowers that attract pollinators, while their small fruits persist into the winter, providing food for birds. Crabapple trees come in a wide range of sizes and are suitable for various garden settings.
These are just a few examples of the many types of deciduous trees available for your garden. Each species offers unique visual appeal, growth habits, and ecological contributions. When selecting species for your landscape, consider factors such as available space, soil conditions, climate suitability, and the desired purpose, whether it is for shade, privacy, or ornamental value. Consult with local nurseries or horticulturists to identify the best deciduous tree species that can thrive in your specific region.
Importance and Benefits of Deciduous Trees
Deciduous trees hold great importance in our natural environment and provide numerous benefits to both wildlife and humans. Their presence in gardens and landscapes goes beyond their visual appeal, as they offer a host of ecological, environmental, and social advantages. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of deciduous trees:
1. Environmental Impact: Deciduous trees play a vital role in mitigating the impact of climate change. Through the process of photosynthesis, they absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, a greenhouse gas responsible for global warming, and release oxygen, helping to clean the air we breathe. In addition, their root systems reinforce soil stability, thereby reducing soil erosion and preventing landslides.
2. Habitat Creation: Deciduous trees provide essential habitats for a diverse range of wildlife. The branches and foliage offer shelter and nesting sites for birds, while the hollows and crevices in their trunks act as homes for small mammals and insects. The fruits, seeds, and leaves of deciduous trees serve as a crucial food source for various animals, contributing to the balance and biodiversity of ecosystems.
3. Shade and Cooling: One of the most obvious benefits of deciduous trees is their ability to provide shade during the hot summer months. The broad canopy of leaves creates a natural umbrella, reducing heat absorption and creating cooler microclimates. This shade not only benefits humans, providing a comfortable area for outdoor activities, but also helps to cool surrounding buildings, reducing the need for excessive air conditioning.
4. Seasonal Aesthetics: The changing foliage of deciduous trees offers a striking display of colors, creating a visual spectacle during the fall season. The vibrant hues of red, orange, and yellow create a picturesque landscape that enchants and captivates. This seasonal show not only brings joy and aesthetic delight, but also draws visitors and enhances the attractiveness of public spaces.
5. Energy Conservation: Deciduous trees are known for their energy-saving properties. When strategically planted around homes and buildings, they act as natural insulation, reducing the need for heating and cooling. During summer, their shade helps to reduce temperatures in buildings, minimizing the need for energy-intensive air conditioning. In winter, when their leaves have shed, they allow sunlight to penetrate and warm surrounding areas.
6. Sound and Visual Barrier: Deciduous trees can also provide a barrier against noise pollution. Their dense foliage helps to absorb sound, reducing traffic noise and other disturbances. Additionally, they can act as visual screens, offering privacy and blocking unsightly views, thereby improving the aesthetics and ambiance of outdoor spaces.
7. Human Health and Well-being: Numerous studies have shown that exposure to nature and green spaces has a positive impact on mental and physical well-being. Deciduous trees, with their calming presence and connection to the changing seasons, provide a sense of tranquility and rejuvenation. They have been shown to reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance overall quality of life.
The multitude of benefits provided by deciduous trees highlights their significance in creating sustainable and healthy environments. Whether used in urban or rural settings, their importance cannot be overstated. By appreciating and nurturing these remarkable trees, we can contribute to a greener future and a healthier planet.
Environmental Impact of Deciduous Trees
Deciduous trees have a significant environmental impact, playing a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of our ecosystems. Through various mechanisms and processes, these trees contribute to biodiversity, carbon sequestration, water management, and overall environmental resilience. Let’s explore the environmental impact of deciduous trees:
1. Carbon Sequestration: One of the key environmental benefits of deciduous trees is their ability to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in their trunks, branches, and leaves. Through the process of photosynthesis, these trees convert carbon dioxide into oxygen while simultaneously storing carbon in their biomass. This carbon sequestration helps to mitigate climate change by reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and slowing down global warming.
2. Air Purification: Deciduous trees act as natural air filters, improving air quality by absorbing pollutants and releasing clean oxygen. Their leaves capture particulate matter and trap harmful gases, such as nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide, mitigating the impact of air pollution. The broad canopies of deciduous trees provide extensive surface area for this purification process, creating a healthier and more breathable environment for both humans and wildlife.
3. Water Management: The root systems of deciduous trees are instrumental in managing water resources. These trees have deep and extensive roots that help to anchor the soil, prevent erosion, and enhance water infiltration. By absorbing excess water during periods of heavy rainfall and releasing it slowly, deciduous trees contribute to natural flood prevention. Conversely, during drier periods, their roots help to conserve moisture by reducing water runoff and maintaining soil moisture levels.
4. Biodiversity Support: Deciduous trees provide vital habitats and food sources for a diverse range of plant and animal species. Their foliage and branches offer shelter for birds, small mammals, and insects. Tree cavities and hollows provide nesting sites for birds and bats. The fruits, seeds, and leaves of deciduous trees serve as a source of food for various animals, contributing to the overall biodiversity and ecological balance of the area.
5. Soil Enrichment: As deciduous trees shed their leaves, these leaves decompose and contribute to the enrichment of soil nutrients. This natural process, known as leaf litter decomposition, adds organic matter to the soil, improving its fertility and health. The decomposed leaves also enhance soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability, promoting the growth of other plants and organisms.
6. Temperature Regulation: Through their shading ability, deciduous trees have a considerable impact on temperature regulation in urban and suburban areas. They help reduce the urban heat island effect, which refers to the higher temperatures experienced in built-up, concrete-heavy environments. Their canopy provides shade, lowering surrounding temperatures, and reducing the energy requirements for cooling buildings. This, in turn, helps to conserve energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
7. Water Quality Protection: The root systems of deciduous trees play a vital role in preventing soil erosion and protecting water quality. Their extensive network of roots helps to stabilize soil, preventing sediment runoff into nearby water bodies. This reduces the amount of pollutants, such as pesticides and fertilizers, that are carried into streams, rivers, and lakes, thus preserving water quality and supporting aquatic ecosystems.
The environmental impact of deciduous trees is profound and far-reaching. These trees contribute to climate resilience, biodiversity conservation, water management, and overall environmental well-being. Protecting and planting deciduous trees is an essential component of sustainable land management and an investment in a greener future.
Seasonal Changes in Deciduous Trees
The seasonal changes in deciduous trees are a remarkable spectacle that adds beauty and dynamism to our natural surroundings. These changes occur in response to the shifting seasons and are characterized by the transformation of foliage color, leaf shedding, and the eventual regrowth of new leaves. Let’s delve into the fascinating journey of seasonal changes in deciduous trees:
1. Spring: As winter fades away and temperatures rise, deciduous trees begin to awaken from their dormant state. Buds that formed during the previous year start to swell and open, heralding the arrival of spring. The emerging leaves are often bright green and tender, as they energize the tree through the process of photosynthesis. Spring is a time of rejuvenation and growth, as deciduous trees burst with fresh foliage, adding vibrant hues to the landscape.
2. Summer: With the canopy of leaves fully developed, deciduous trees reach their peak during the summer months. The leaves are lush and richly green, capturing sunlight and converting it into energy through photosynthesis. The dense foliage acts as a natural umbrella, providing shade and relief from the summer heat. During this season, deciduous trees also produce flowers and fruits, adding splashes of color and attracting pollinators and wildlife to their branches.
3. Fall: As temperatures cool and daylight hours decrease, deciduous trees prepare for the stunning transformation of fall. It is during this season that the leaves of deciduous trees undergo a dramatic change in color. Chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis, breaks down and reveals the underlying pigments within the leaves. This leads to a display of captivating colors, including shades of red, orange, yellow, and even purple. The intensity of these colors varies depending on factors such as tree species and environmental conditions.
4. Leaf Shedding: The vibrant foliage of fall eventually gives way to the characteristic leaf shedding of deciduous trees. The trees enter a phase of preparation for the winter months by withdrawing valuable nutrients from the leaves and sealing off the leaf stems to form a protective layer. The leaves gradually change from brilliant colors to a dry, brown hue before being shed from the tree. Leaf litter covers the ground below, providing a natural mulch and contributing to soil health and fertility.
5. Winter Dormancy: With the arrival of winter, deciduous trees enter a period of dormancy. The branches appear bare, and the once vibrant canopy of leaves is absent. The tree conserves energy and rests until the arrival of spring. Deciduous trees withstand the cold by employing various survival mechanisms, including reducing water content in their tissues and relying on stored energy reserves. Winter dormancy is a time for regeneration and preparation for the cycle to begin anew.
The seasonal changes in deciduous trees are a testament to the resilience and adaptability of these incredible plants. They demonstrate the cyclical nature of life and the ever-changing beauty of our natural world. Observing and appreciating these seasonal shifts can provide us with a deeper connection to nature and a sense of wonder and awe.
Common Deciduous Trees in Different Regions
Deciduous trees are found in various regions around the world, each with its own unique climate and environmental conditions. As a result, different species of deciduous trees thrive in different regions, showcasing a diverse array of tree types and characteristics. Let’s explore some of the common deciduous trees found in different regions:
1. North America:
- Maple (Acer spp.): Maples are abundant in North America, with species such as the sugar maple (Acer saccharum) and red maple (Acer rubrum) being particularly common. Known for their spectacular fall colors, maples are prized for their shade and are often tapped for their sap to produce maple syrup.
- Oak (Quercus spp.): Oaks are another prominent deciduous tree in North America, with species like the white oak (Quercus alba) and red oak (Quercus rubra) being widespread. Oaks are renowned for their strength and longevity and provide crucial habitats for many wildlife species.
- Poplar (Populus spp.): Poplars are fast-growing deciduous trees found throughout North America. Species such as the quaking aspen (Populus tremuloides) and cottonwood (Populus deltoides) are known for their distinctive trembling leaves and offer quick shade and screening benefits.
2. Europe:
- Beech (Fagus sylvatica): Beech trees are native to Europe and are known for their smooth gray bark and glossy, deep green leaves. They are prevalent in forests and provide a majestic appearance and dense shade.
- Sycamore (Acer pseudoplatanus): Sycamore trees, also known as plane trees, are common throughout Europe. They have distinctive palmate leaves and a characteristic mottled bark. Sycamores are often planted for their decorative value in urban and rural settings.
- Birch (Betula spp.): Birch trees can be found across Europe, known for their slender trunks and striking white bark. Species like the silver birch (Betula pendula) and downy birch (Betula pubescens) add a touch of elegance to the landscape.
3. Asia:
- Cherry Blossoms (Prunus spp.): Cherry blossom trees are famous throughout Asia, particularly in Japan. These deciduous trees, with their delicate pink or white flowers, create stunning displays during the springtime, symbolizing the beauty and transience of life.
- Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba): Ginkgo trees, also known as the maidenhair tree, are native to Asia and are well-known for their fan-shaped leaves that turn a beautiful golden hue in the fall. They are highly valued for their medicinal properties and are often planted near temples and shrines.
- Japanese Maple (Acer palmatum): Japanese maple trees are prized for their stunning foliage colors and delicate, often intricately cut leaves. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, from dwarf shrubs to larger trees, adding elegance and beauty to Japanese gardens and landscapes.
4. Australia:
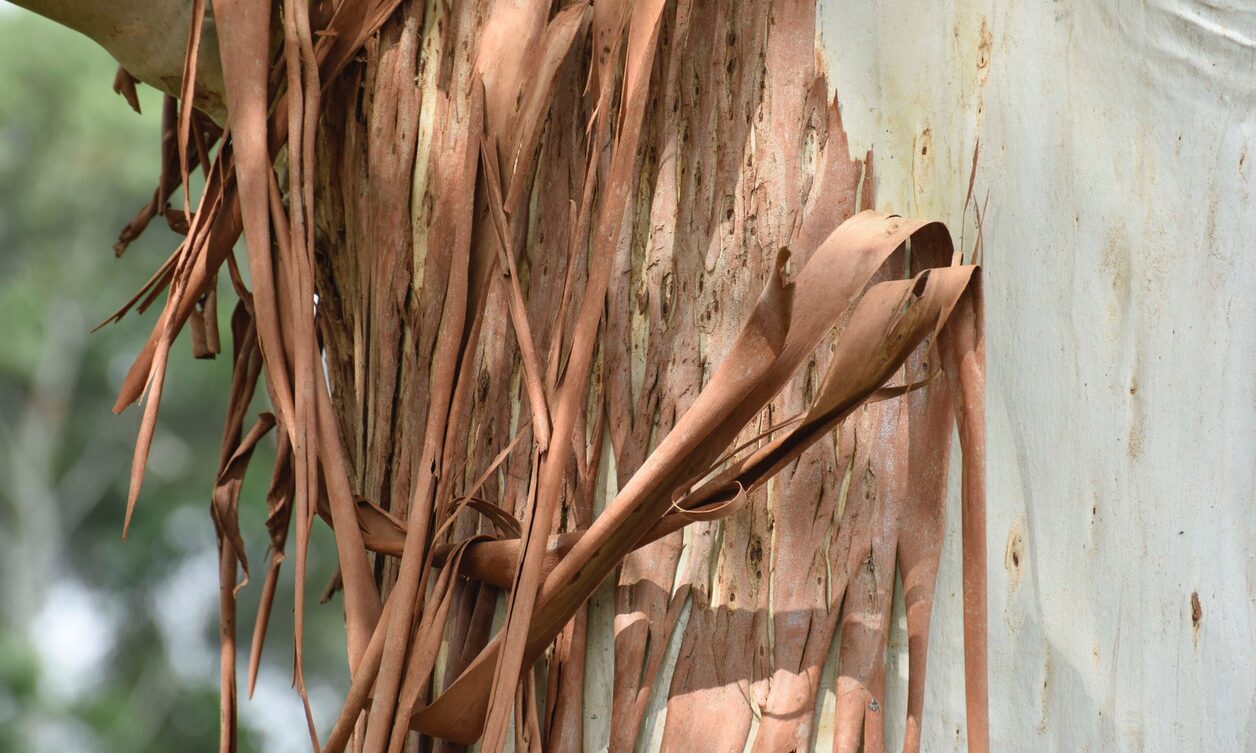
- Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus spp.): Australian eucalyptus trees are known for their distinctive fragrance, smooth bark, and slender leaves. They are vital components of Australian ecosystems, providing food, shelter, and nesting sites for a diverse range of wildlife.
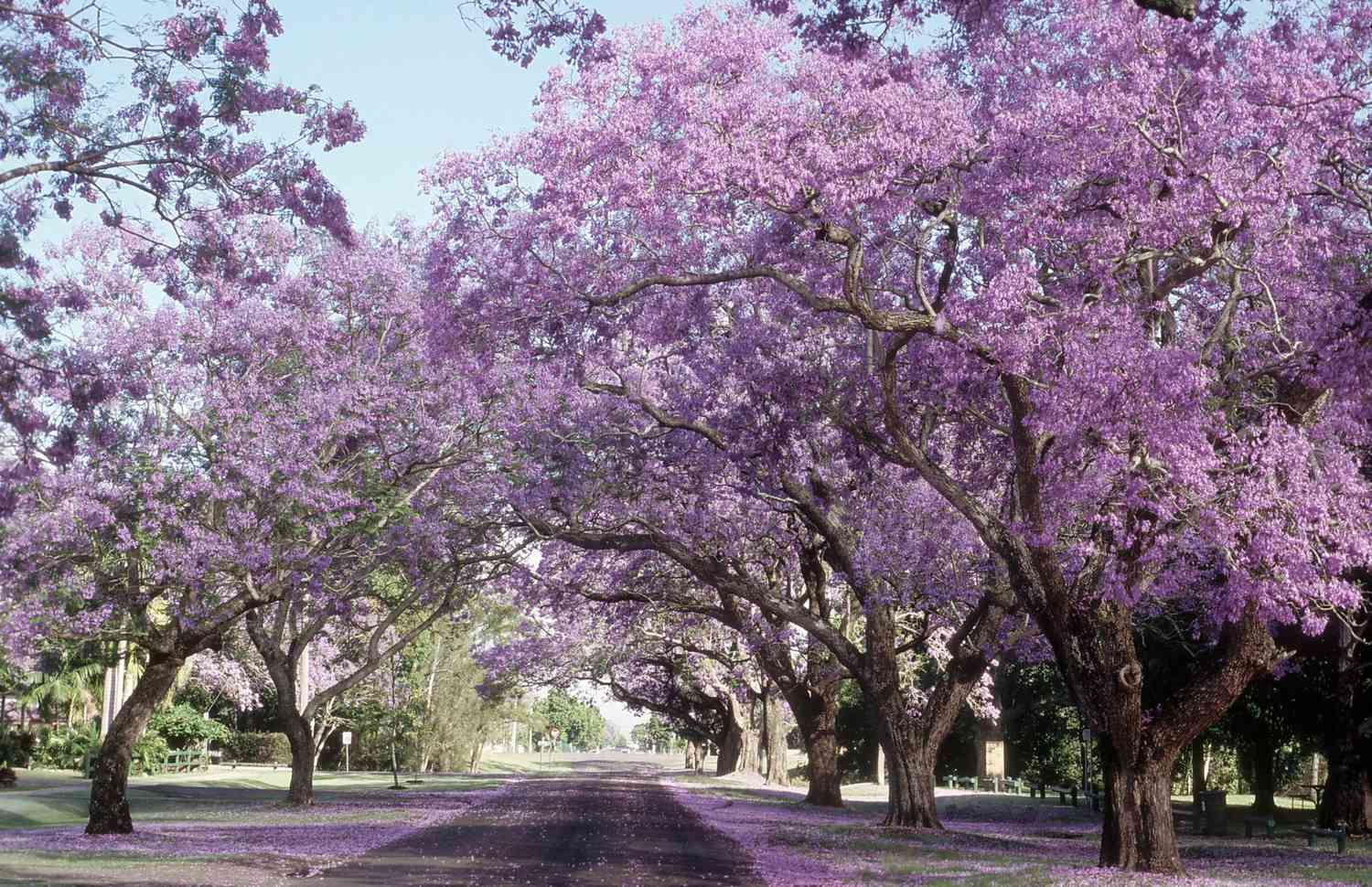
- Jacaranda (Jacaranda mimosifolia): Jacaranda trees are beloved for their stunning display of purple or blue flowers, which blanket the branches during the spring. They are commonly found in parts of Australia, particularly in city landscapes where their vibrant blooms create an enchanting sight.
- Gum trees (Corymbia spp. and Eucalyptus spp.): Gum trees, also known as eucalyptus trees, are iconic symbols of the Australian landscape. They have unique foliage and often shed strips of bark, revealing striking, often colorful bark beneath. Gum trees are highly adaptable, with various species found across different habitats in Australia.
These are just a few examples of the common deciduous trees found in different regions around the world. Each region has its own unique collection of deciduous trees that contribute to the beauty, biodiversity, and cultural significance of the area. Exploring these diverse tree species enhances our appreciation for the wonders of nature and highlights the importance of preserving and protecting these valuable natural resources.
Cultivation and Care of Deciduous Trees
Cultivating and caring for deciduous trees is essential to ensure their growth, health, and longevity. Whether you are planting a new tree or maintaining established ones, following proper techniques and providing adequate care will help these trees thrive in your garden. Here are some tips for the cultivation and care of deciduous trees:
1. Site Selection: Choose a suitable location for your deciduous tree, considering factors such as soil type, sun exposure, and available space. Different tree species have specific soil and sunlight requirements, so research the specific needs of your chosen tree to ensure proper growth. Planting in an appropriate site sets the foundation for a healthy tree.
2. Planting: When planting your deciduous tree, dig a hole that is wide and deep enough to accommodate the root system. Gently loosen the roots before planting to encourage outward growth. Make sure the tree is positioned at the same level as it was in the nursery container or root ball, with the root collar slightly above ground level to prevent waterlogging and stem rot.
3. Watering: Newly planted deciduous trees require regular and deep watering to establish strong root systems. Water deeply, allowing water to penetrate the root zone. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot. During dry spells, provide supplementary watering to ensure sufficient moisture. As the tree matures, reduce watering frequency but continue to monitor soil moisture levels.
4. Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree, keeping it a few inches away from the trunk. Mulch helps retain soil moisture, suppresses weed growth, and regulates soil temperature. Use organic materials such as wood chips or bark, and maintain a mulch depth of 2-4 inches. Avoid piling the mulch against the trunk, as it can create a favorable environment for pests and diseases.
5. Pruning: Pruning is essential for maintaining the health and structure of deciduous trees. Remove dead, damaged, or diseased branches to enhance the overall appearance and prevent the spread of pests and diseases. Perform corrective pruning in the early years to shape the tree’s growth. Prune during the dormant season to minimize stress on the tree and promote vigorous growth.
6. Fertilizing: Deciduous trees generally do not require frequent fertilization if planted in healthy soil. However, if the tree shows signs of nutrient deficiency, you can apply a balanced slow-release fertilizer in the spring, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Avoid over-fertilization, as excessive nutrients can cause excessive vegetative growth and weak branches.
7. Pest and Disease Management: Regularly inspect your deciduous trees for signs of pest infestations or disease. Monitor for common pests such as aphids, caterpillars, or scale insects and employ appropriate strategies for their control. In case of disease symptoms, identify the issue and take necessary actions, such as pruning affected branches or applying targeted treatments. Maintaining overall tree health through proper care practices helps in preventing and managing pests and diseases.
8. Tree Support: Young deciduous trees may require staking for support against strong winds or improper growth. Use materials such as soft tree ties and stakes to provide stability without causing damage to the tree. Monitor the tree regularly and remove stakes once the trunk and root system are strong enough to support the tree independently.
By following these cultivation and care practices, you can ensure the optimal growth and health of deciduous trees in your garden. Regular monitoring and timely interventions will help maintain the beauty, functionality, and longevity of these remarkable trees.
Conclusion
Deciduous trees are a captivating and essential component of ornamental gardening. Their ability to undergo seasonal changes, provide shade, enhance biodiversity, and contribute to environmental sustainability makes them highly valued in landscapes around the world. Understanding the characteristics, life cycle, and cultivation practices of deciduous trees allows us to appreciate their beauty and maximize their benefits.
From the vibrant colors of their foliage in the fall to the cooling shade they provide in the summer, deciduous trees bring dynamic and ever-changing aesthetics to gardens and public spaces. Their impact goes beyond visual appeal, as they contribute to carbon sequestration, air purification, water management, and habitat creation for wildlife. Proper care practices, such as site selection, watering, mulching, pruning, and pest management, are crucial for ensuring the health and longevity of deciduous trees.
Whether you are designing a new garden or looking to enhance an existing landscape, the wide variety of deciduous tree species available allows for endless possibilities. From the stately oaks of North America to the captivating cherry blossoms of Asia, deciduous trees provide an opportunity to create a diverse and enchanting outdoor space.
By cultivating and caring for deciduous trees, we not only elevate the beauty of our surroundings but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient environment. Their seasonal changes remind us of the cyclic nature of life and connect us to the rhythms of the natural world. Moreover, the benefits they provide, such as shade, cleaner air, and habitat support, enhance our well-being and create a harmonious coexistence with nature.
So, whether you are seeking to create a peaceful oasis, a vibrant splash of color, or a habitat for wildlife, incorporating deciduous trees into your ornamental garden is a choice that brings lasting beauty and environmental impact. Embrace the wonders of deciduous trees and unleash your creativity to create a truly remarkable and sustainable outdoor space.