Home>Gardening News and Trends>Latest News>How Many Pesticides Are On Apples


Latest News
How Many Pesticides Are On Apples
Modified: January 22, 2024
Get the latest news on how many pesticides are found on apples and the potential risks associated with consumption. Stay informed and make healthier food choices.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What are pesticides?
- The use of pesticides in apple farming
- Impact of pesticides on human health
- Common types of pesticides found on apples
- The potential risks of consuming pesticide residues on apples
- Regulations and safety standards regarding pesticide use on apples
- How to reduce pesticide residues on apples
- Conclusion
Introduction
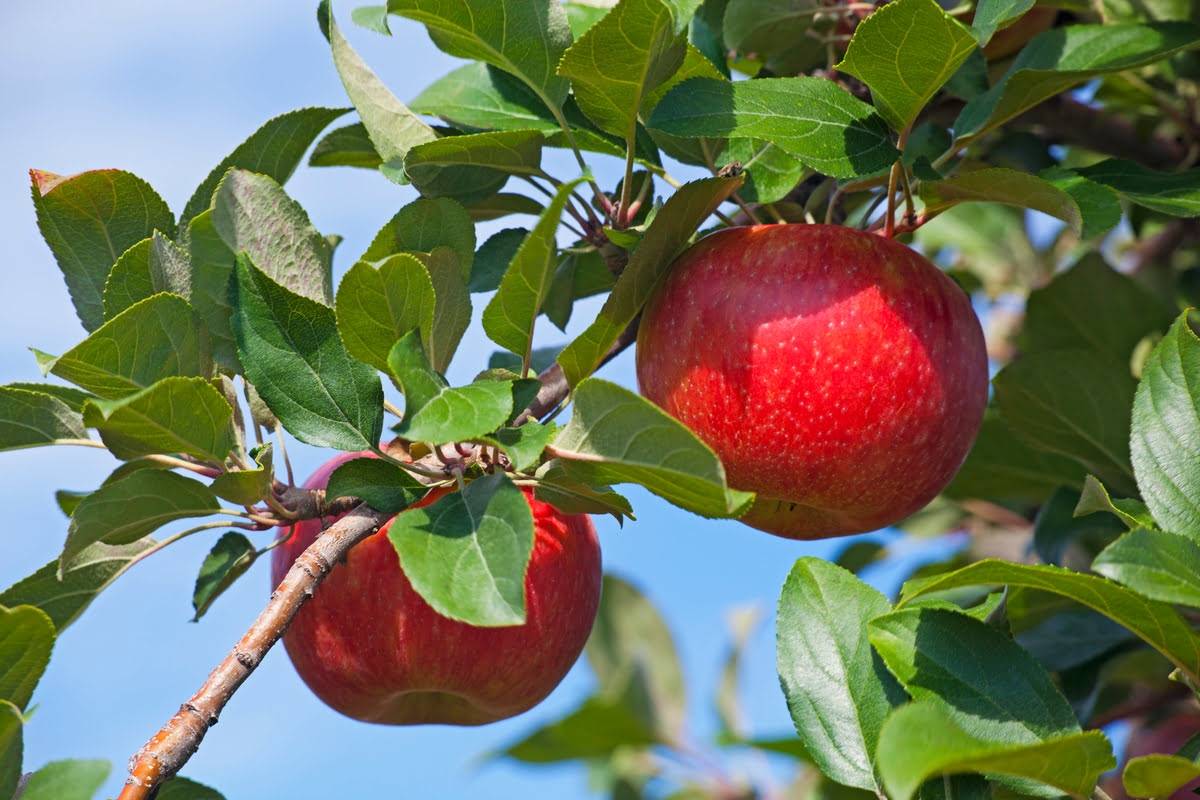
Apples, with their crunchy texture and sweet-tart flavor, are a beloved fruit enjoyed by many people around the world. They are not only a delicious snack but also a versatile ingredient in various dishes. However, have you ever wondered how many pesticides are on the apples you consume? This question has become a growing concern in recent years as the use of pesticides in agriculture continues to rise.
Pesticides are chemical substances used to manage and control pests, including insects, weeds, and diseases, that can damage crops and reduce yields. While the use of pesticides is intended to protect crops, including apples, from various threats, there is a growing concern about the potential health risks associated with pesticide residues on food.
Apple farming, like many other forms of agriculture, relies heavily on the use of pesticides to protect the crops from pests and diseases. Pesticides are used at various stages of apple production, from the early stages of growth to the preservation and storage of the fruit. This ensures that the apples are visually appealing, free from pests, and have a longer shelf life.
However, the use of pesticides comes with potential risks. Studies have shown that some pesticides found on apples can have adverse effects on human health. Prolonged exposure to these chemicals can lead to various health issues, including neurological disorders, hormonal imbalances, and even an increased risk of certain cancers.
While pesticide residues can be found on many fruits and vegetables, apples have been identified as one of the most heavily contaminated crops when it comes to pesticide residues. This is mainly due to the thin and permeable skin of apples, making them more susceptible to absorbing and retaining pesticide residues.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the types of pesticides commonly found on apples, the potential risks associated with consuming pesticide residues on apples, the regulations and safety standards regarding pesticide use on apples, and steps you can take to reduce the pesticide residue on the apples you consume.
What are pesticides?
Pesticides are chemical substances used to manage and control pests that can cause damage to crops. They are widely used in agriculture to protect plants from insects, weeds, fungi, and other forms of pests. Pesticides can be classified into different categories based on their target pests and their mode of action.
Insecticides, as the name suggests, are pesticides specifically designed to target and eliminate insects. They work by interfering with the nervous system of the insects, leading to paralysis or death. Common types of insecticides used in apple farming include organophosphates, carbamates, and pyrethroids.
Herbicides, on the other hand, are pesticides used to control the growth and spread of weeds in apple orchards. They work by disrupting the metabolic processes of the weeds, eventually causing them to wither and die. Glyphosate is a commonly used herbicide in apple farming, although there has been growing concern about its potential health effects.
Fungicides are pesticides used to prevent or treat fungal infections in apple trees. Fungi can cause diseases such as apple scab, powdery mildew, and black rot, which can significantly reduce yield and quality. Fungicides contain chemical compounds that inhibit the growth and reproduction of fungi, thereby protecting the apple trees. Captan, thiabendazole, and mancozeb are some of the fungicides commonly used in apple farming.
In addition to insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, there are also other types of pesticides used in apple farming. These include rodenticides, which are used to control rodent populations, and miticides, which are used to manage mites that can damage apple trees.
It is important to note that while pesticides serve a crucial role in protecting crops from pests and diseases, their use also poses potential risks to human health and the environment. Pesticides can accumulate in the soil, water, and air, affecting ecosystems and potentially harming non-target organisms. Therefore, it is essential to ensure responsible and controlled pesticide use in agriculture to minimize these adverse effects.
The use of pesticides in apple farming
The cultivation of apples involves various challenges, including pest infestations and diseases that can impact the yield and quality of the crop. To address these challenges, farmers rely on the use of pesticides as an integral part of their crop management strategies.
Pesticides are used in apple farming at different stages of the crop’s growth cycle. They are applied during the early stages to protect young apple trees from insects and diseases. As the trees mature, pesticides are used to control pests such as codling moths, apple maggots, and aphids, which can cause significant damage to the fruit. Additionally, fungicides are utilized to prevent and manage common apple diseases like apple scab and powdery mildew.
The application of pesticides in apple orchards can be done through various methods. Spraying is the most common method, where pesticides are evenly distributed using specialized equipment. This ensures that the entire tree, including its leaves, branches, and fruit, is adequately covered. In some cases, pesticides are applied directly to the soil or injected into the tree trunk to target specific pests or diseases.
To ensure effective pest and disease management, farmers often follow integrated pest management (IPM) practices. IPM is a holistic approach that combines various pest control techniques, including cultural, biological, and chemical methods. The goal is to reduce pesticide use by utilizing natural predators, introducing beneficial insects, implementing crop rotation, and maintaining proper orchard sanitation. When pesticides are used, it is done so in a targeted and strategic manner, minimizing their impact on the environment and non-target organisms.
While the use of pesticides in apple farming is essential for maintaining healthy and productive orchards, there are concerns regarding their potential effects on human health and the environment. Pesticides can leave residues on the fruit, which can be ingested when consumed. Additionally, excessive use or misuse of pesticides can lead to the build-up of chemical residues in the soil and water sources, potentially affecting ecosystems and wildlife.
To address these concerns, regulatory agencies establish maximum residue limits (MRLs) for pesticides on apples and other crops. These limits ensure that the levels of pesticide residues in food are within safe and acceptable ranges. Farmers are required to adhere to these regulations and follow good agricultural practices to minimize pesticide residues on apples.
Impact of pesticides on human health
While pesticides play a crucial role in protecting apple crops from pests and diseases, their potential impact on human health has raised concerns. The residues of these chemical compounds can find their way into the apples we consume and may have adverse effects on our well-being.
Exposure to pesticides has been linked to various health issues, ranging from acute effects to long-term consequences. Acutely, pesticide exposure can cause symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, headaches, and skin irritations. These effects are more common among farmers and farmworkers who handle and apply pesticides directly.
However, even at lower levels of exposure, pesticides can have long-term health implications. Some pesticides are categorized as endocrine disruptors, which means they can interfere with the hormonal balance in our bodies. This disruption can lead to reproductive disorders, developmental delays in children, and even an increased risk of certain cancers, including breast, prostate, and lung cancer.
Certain groups, such as pregnant women, children, and those with compromised immune systems, are particularly vulnerable to the effects of pesticide exposure. For example, prenatal exposure to certain pesticides has been associated with an increased risk of developmental disorders and neurobehavioral problems in children.
It’s important to note that the effects of pesticide exposure on human health can vary depending on factors such as the type and concentration of pesticides, the duration and frequency of exposure, and individual susceptibility. Nevertheless, it is crucial to minimize exposure to pesticides whenever possible to reduce potential health risks.
To protect consumers, regulatory bodies in many countries establish maximum residue limits (MRLs) for pesticides on food, including apples. These limits are based on extensive scientific research and are set at levels considered safe for most individuals. Compliance with these MRLs is crucial for ensuring that consumers are not exposed to excessive pesticide residues in their food.
Furthermore, organic farming practices offer an alternative for those concerned about pesticide exposure. Organic apples are grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, relying instead on natural methods such as beneficial insects, crop rotation, and biological controls to manage pests and diseases. By choosing organic apples, consumers can reduce their exposure to pesticide residues while supporting environmentally sustainable farming practices.
Common types of pesticides found on apples
When it comes to apples, several types of pesticides are commonly used to protect the fruit from pests and diseases. These pesticides can leave residues on the apple skin, which can be ingested when we consume the fruit. Understanding these common types of pesticides can help us make informed choices about the apples we consume.
One commonly used group of pesticides on apples is organophosphates. These are highly effective insecticides that target a wide range of pests, including aphids, mites, and leafhoppers. Although effective, organophosphates have raised concerns due to their potential toxicity. Some studies have linked long-term exposure to organophosphates with neurological effects and developmental disorders in children.
Another group of pesticides used in apple farming is carbamates. Similar to organophosphates, carbamates are insecticides that target various apple pests. They work by disrupting the nervous system of insects. However, carbamates are generally considered to be less toxic than organophosphates. Still, there is a need to minimize exposure and adhere to safety guidelines when using these pesticides.
Pyrethroids are another group of pesticides commonly found on apples. These insecticides are derived from natural compounds found in chrysanthemum flowers and are effective against a range of pests like apple maggots, codling moths, and aphids. Pyrethroids are often preferred due to their lower toxicity to humans and animals compared to other insecticides. However, it is still important to follow safety precautions and use them responsibly.
In addition to insecticides, fungicides are also used to protect apples from fungal diseases. Captan is a commonly used fungicide in apple farming. It is effective against apple scab, a common fungal disease that can cause blemishes on the fruit. In recent years, there has been a shift towards using less toxic and environmentally friendly alternatives to captan, such as biological controls and other organic methods.
Glyphosate, a herbicide, is also used in apple farming to control weeds. However, the use of glyphosate has become a subject of controversy due to concerns about its potential health effects. Some studies have linked glyphosate exposure to an increased risk of certain cancers and other health problems. As a result, there is a growing demand for alternative weed control methods in apple farming, especially those that are more organic and environmentally friendly.
It’s important to note that while these are some of the commonly used pesticides on apples, there are many other pesticides and active ingredients that may be used depending on specific pests and diseases prevalent in the region. Understanding these pesticides and their potential effects can help consumers make informed choices and seek out apples with lower pesticide residues whenever possible.
The potential risks of consuming pesticide residues on apples
Consuming apples that contain pesticide residues can pose potential risks to our health. While the levels of pesticide residues found on apples are regulated and considered safe for consumption, long-term exposure to these residues can still have adverse effects on our well-being.
One concern is the potential impact of pesticide residues on our neurological health. Some pesticides, such as organophosphates and certain fungicides, have been linked to neurological disorders and developmental delays, especially in children. Prolonged exposure to these pesticides may disrupt the normal function of the nervous system, leading to issues such as impaired cognitive function, learning disabilities, and behavioral problems.
Pesticide residues on apples and other fruits have also raised concerns related to hormonal disruption. Certain pesticides, including some fungicides and insecticides, are known to act as endocrine disruptors. These compounds can interfere with the hormonal balance in our bodies, potentially leading to reproductive disorders, hormonal imbalances, and even an increased risk of certain cancers.
Furthermore, individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing health conditions may be more susceptible to the potential risks associated with pesticide residues. Consuming apples with higher pesticide residue levels may further compromise their health and well-being.
It is worth noting that the risks associated with pesticide residues on apples are generally considered low in comparison to the potential health benefits of consuming fruits. It is important to maintain a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, including apples, while also considering strategies to reduce pesticide exposure.
Additionally, it is important to remember that washing and peeling apples can help reduce pesticide residue levels. While washing with water alone may not completely remove all traces of pesticides, gently scrubbing the surface can help remove dirt and some surface residues. Peeling the skin can further reduce pesticide exposure, although it is worth noting that many of the beneficial nutrients and fiber in apples are found in the skin.
To further minimize pesticide exposure, consumers can also consider purchasing organic apples. Organic farming practices prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides, relying instead on natural methods and environmentally friendly approaches. Choosing organic apples can significantly reduce pesticide residue intake while supporting sustainable and environmentally conscious agricultural practices.
Lastly, it is essential to stay informed and aware of the latest research on pesticide residues in apples and other fruits. By understanding and considering the potential risks, consumers can make more informed choices about the apples they consume and take steps to minimize their exposure to pesticide residues.
Regulations and safety standards regarding pesticide use on apples
The use of pesticides in apple farming is strictly regulated to ensure the safety of consumers and the environment. Regulatory bodies around the world have established comprehensive guidelines and safety standards to govern the use of pesticides in agriculture, including the cultivation of apples.
Maximum residue limits (MRLs) are set for pesticides on apples and other crops to ensure that the levels of pesticide residues in food are within safe and acceptable ranges. These limits are determined through rigorous scientific assessments and take into account factors such as toxicology, dietary exposure, and cumulative effects. MRLs are regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the latest scientific findings.
Farmers who grow apples are required to follow good agricultural practices (GAPs) to minimize pesticide residues on their produce. This includes using approved pesticides at recommended dosages, following proper application techniques, and adhering to pre-harvest intervals to allow sufficient time for pesticide degradation.
To enforce compliance with safety standards, regulatory agencies conduct regular inspections, sample testing, and residue analysis of apples and other agricultural products. Any exceedance of MRLs can result in penalties, withdrawal of products from the market, or the requirement for additional safety measures to be implemented.
Consumer safety is further ensured through quality control measures such as quality grading systems and certification programs. Certain countries and regions have specific grading criteria for apples, which encompass factors such as size, color, shape, and absence of visible defects. Certification programs, such as those for organic produce, provide consumers with assurance that the apples have been grown according to strict standards and without the use of synthetic pesticides.
International organizations, such as the Codex Alimentarius Commission, also play a critical role in establishing global standards for pesticide residues in food. These standards serve as a reference for countries around the world, promoting consistency and harmonization in safety regulations to protect consumers worldwide.
It is important for consumers to stay informed about the regulations and safety standards regarding pesticide use on apples. By understanding these standards and the efforts made to ensure safety, consumers can make educated choices about the apples they purchase and consume. Additionally, supporting organic farming practices and seeking out organic apples can provide an extra layer of assurance for those concerned about pesticide exposure.
How to reduce pesticide residues on apples
Reducing pesticide residues on apples can be achieved by implementing certain practices during cultivation, storage, and preparation. By following these strategies, consumers can minimize their exposure to pesticide residues and enjoy apples that are safer to consume.
1. Choose organic apples: Opting for organic apples ensures that the fruit has been grown without the use of synthetic pesticides. Organic farming practices rely on natural methods and environmentally friendly approaches to manage pests and diseases.
2. Wash apples thoroughly: Washing apples with water can help remove dirt and some surface residues. Although it may not entirely eliminate all pesticide residues, scrubbing the skin gently can help reduce their presence.
3. Consider peeling the apples: Peeling the skin of apples can further reduce pesticide residue intake, as residues tend to accumulate on the outer layer. However, keep in mind that peeling also removes nutrients and fiber found in the skin.
4. Buy local and in-season apples: Purchasing apples from local farmers or markets can reduce the chances of coming into contact with high pesticide residue fruits. In addition, buying apples in-season ensures that they are freshly harvested and have had less time for pesticide residues to accumulate.
5. Diversify your fruit intake: While apples are a healthy and delicious fruit, eating a variety of fruits can help reduce exposure to specific pesticides. Different fruits may have varying pesticide residue levels and types, so including a wide range of fruits in your diet can help distribute your exposure to different pesticides.
6. Grow your own apples: If you have space and resources, consider growing your own apples. This way, you have control over the pesticides used in cultivation and can opt for organic or pesticide-free methods.
7. Support integrated pest management (IPM) practices: IPM combines various pest control techniques, including cultural, biological, and chemical methods. By supporting farmers who employ IPM practices, you contribute to the reduction of pesticide use and the promotion of environmentally sustainable farming.
8. Stay informed: Stay updated with the latest research and information regarding pesticide residues on apples. This awareness will enable you to make informed decisions about the apples you consume and seek out apples with lower pesticide residue levels whenever possible.
By following these practices, individuals can reduce their exposure to pesticide residues on apples. Prioritizing organic options and adopting mindful fruit consumption habits contribute to a healthier diet and support sustainable agricultural practices that aim to minimize pesticide use.
Conclusion
The presence of pesticide residues on apples raises valid concerns about the potential risks to human health. While pesticides play a crucial role in protecting apple crops from pests and diseases, it is essential to be aware of the potential health implications and take steps to minimize exposure to pesticide residues.
Regulatory bodies have established maximum residue limits (MRLs) for pesticides on apples, ensuring that the levels of residues are within safe and acceptable ranges. Farmers adhere to good agricultural practices (GAPs) and undergo regular inspections and residue analysis to comply with these safety standards. Certification programs and quality grading systems provide further assurance for consumers.
To reduce pesticide residues on apples, individuals can choose organic apples grown without synthetic pesticides or opt for locally produced apples in-season. Washing and peeling apples, while considering the loss of nutrients, can also help decrease residue levels. Supporting integrated pest management (IPM) practices and staying informed about pesticide regulations contribute to a safer apple supply chain.
It’s important to remember that apples, with their numerous health benefits, remain a valuable addition to a balanced diet. While the risks associated with pesticide residues should be considered, the overall benefits of consuming fruit should not be overlooked. By making informed choices and practicing mindful fruit consumption, we can enjoy the deliciousness of apples while minimizing potential risks to our health.