Home>Gardening News and Trends>Latest News>How To Avoid Pesticides In Food


Latest News
How To Avoid Pesticides In Food
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the latest news and tips on how to avoid harmful pesticides in your food. Stay informed and make healthier choices for you and your family.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Impact of Pesticides on Food
- The Dangers of Consuming Pesticide-Laden Foods
- Tips for Avoiding Pesticides in Your Food
- Buy Organic Produce
- Grow Your Own Food
- Wash and Scrub Produce Thoroughly
- Peel Fruits and Vegetables
- Choose Locally Sourced and Seasonal Foods
- Read Labels and Look for Pesticide-Free or Low Pesticide Options
- Support Farmers Using Sustainable Farming Practices
- Choose Packaged Foods with Organic Certifications
- Limit Consumption of High Pesticide Residue Foods
- Opt for Natural Pest Control Methods in Your Garden
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to our guide on how to avoid pesticides in food. In today’s world, where the use of pesticides has become commonplace in conventional farming practices, it is crucial to be aware of the potential risks and take steps to minimize our exposure to these harmful chemicals. This article aims to provide you with practical tips and insights on how to make informed choices when it comes to the food you consume.
It is no secret that pesticides are extensively used in modern agriculture to protect crops from pests, diseases, and weeds. While they serve the purpose of increasing food production and ensuring crops reach our tables, the presence of pesticides in our food has raised concerns about the long-term health effects they may have on our bodies.
Exposure to pesticides has been linked to various health problems, including cancer, reproductive issues, neurodevelopmental disorders, and hormone disruption. This is particularly concerning for vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, infants, and children, as they are more susceptible to the toxic effects of these chemicals.
Fortunately, there are strategies that can help you reduce your exposure to pesticides and make healthier choices for you and your family. By following some simple guidelines and adopting conscious consumer habits, you can minimize your intake of pesticide residues and promote a healthier lifestyle.
In the following sections, we will explore practical tips for avoiding pesticides in your food, ranging from buying organic produce to growing your own food and opting for natural pest control methods. These recommendations will empower you to make informed decisions and take control of your dietary choices. Let’s dive in and discover how you can protect yourself and your loved ones from the potential risks associated with pesticide-laden foods.
Understanding the Impact of Pesticides on Food
Pesticides are chemical substances that are used to control pests, diseases, and unwanted weeds in agricultural practices. While they play an important role in protecting crops and increasing food production, their use comes with potential risks. Pesticides can leave residues on the surface of fruits, vegetables, and other crops, which can be ingested when we consume these foods.
The impact of pesticides on food can be detrimental to our health. Studies have shown that long-term exposure to pesticides through food consumption can lead to various health issues. One of the main concerns is the potential link between pesticide exposure and certain types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and lung cancer. Additionally, pesticides have been associated with reproductive problems, such as infertility and birth defects, as well as neurological disorders and developmental delays in children.
It’s important to note that the effects of pesticides can vary depending on the specific pesticide used, the level of exposure, and individual susceptibility. However, the cumulative exposure to multiple pesticides from different sources can pose a significant risk to our health.
Furthermore, pesticide residues can persist on crops even after they have been harvested, transported, and prepared for consumption. This means that simply washing or peeling fruits and vegetables may not completely remove these residues. Additionally, processed foods, such as canned goods and packaged snacks, may also contain pesticide residues from the ingredients used.
It’s crucial to understand that the impact of pesticides on food goes beyond our individual health. Pesticide use in conventional farming practices can also have negative effects on the environment, including depleting soil quality, contaminating water sources, and harming beneficial insects and wildlife.
By gaining a better understanding of the potential impact of pesticides on our food, we can become more aware and make informed choices to reduce our exposure and protect our overall well-being. In the next sections, we will explore practical tips to help you avoid pesticides in your food and minimize the potential risks associated with their consumption.
The Dangers of Consuming Pesticide-Laden Foods
Consuming pesticide-laden foods can have serious implications for our health and well-being. Pesticides are designed to be toxic substances that target and eliminate pests, but when we consume foods that have been treated with these chemicals, we are inadvertently exposing ourselves to potential harm.
One of the primary concerns of consuming pesticide-laden foods is the risk of developing various health problems. Pesticides have been linked to an increased risk of cancer, as certain pesticides have been classified as carcinogens by leading health organizations. Prolonged exposure to these chemicals through food consumption can contribute to the development of different types of cancers, including breast, prostate, lung, and stomach cancer.
In addition to cancer, pesticides can also disrupt our hormonal balance. Many pesticides act as endocrine disruptors, interfering with the normal functioning of our hormonal system. This disruption can lead to reproductive issues, such as infertility, and can also affect fetal development, potentially leading to birth defects and developmental delays in children.
Furthermore, pesticides have been associated with neurological disorders. Studies have shown that chronic exposure to certain pesticides can increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions. These chemicals can also affect cognitive function and contribute to learning and behavior problems, particularly in children.
It’s important to note that the effects of consuming pesticide-laden foods can be more pronounced in vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, infants, and children. Their smaller size and still-developing systems make them more susceptible to the harmful effects of pesticides.
The dangers of consuming pesticide-laden foods extend beyond the immediate health risks. The widespread use of pesticides in agricultural practices has detrimental effects on the environment. Pesticides can contaminate soil, water sources, and the air we breathe. They can also harm beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife, disrupting delicate ecological balance and biodiversity.
Given the potential dangers associated with consuming pesticide-laden foods, it is essential to take proactive steps to minimize our exposure. In the next section, we will explore practical tips to help you reduce your intake of pesticides and make healthier choices for you and your family.
Tips for Avoiding Pesticides in Your Food
Reducing your exposure to pesticides and making healthier choices for your food can be achieved through simple and practical strategies. By following these tips, you can minimize your intake of pesticide residues and protect your well-being:
- Buy organic produce: Choosing organic fruits, vegetables, and other products is one of the best ways to avoid pesticides. Organic farming practices prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides, ensuring that the food you consume is free from harmful chemical residues.
- Grow your own food: If feasible, consider growing your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs. By having control over the cultivation process, you can ensure that your crops are free from pesticides and other chemical interventions.
- Wash and scrub produce thoroughly: Even if you are unable to buy organic, washing and scrubbing produce under running water can help remove some pesticide residues from the surface. Use a clean brush or scrubbing tool for fruits and vegetables with tougher skins.
- Peel fruits and vegetables: Peeling the outer layers of fruits and vegetables can help reduce pesticide exposure, as many pesticide residues accumulate on the surface. However, keep in mind that removing the peel also means losing some valuable nutrients.
- Choose locally sourced and seasonal foods: Local and seasonal produce often requires fewer pesticides, as they are more adapted to the local environment and less prone to pests and diseases. Supporting local farmers also helps promote sustainable agriculture practices.
- Read labels and look for pesticide-free or low pesticide options: When purchasing packaged foods, carefully read labels and look for products that are labeled as pesticide-free or low pesticide. Some food companies provide certification or labels that indicate their commitment to using safer agricultural practices.
- Support farmers using sustainable farming practices: Seek out farmers who implement sustainable farming methods, such as integrated pest management (IPM) and organic practices. By supporting these farmers, you contribute to the growth of a healthier and more sustainable food system.
- Choose packaged foods with organic certifications: When buying packaged foods, look for those that have organic certifications. These certifications ensure that the ingredients used in the food were grown without the use of synthetic pesticides.
- Limit consumption of high pesticide residue foods: Some fruits and vegetables tend to have higher pesticide residues than others. It is advisable to limit your intake of these foods or opt for organic options. The Environmental Working Group (EWG) publishes an annual “Dirty Dozen” and “Clean Fifteen” list, which highlights the produce with the highest and lowest pesticide residues, respectively.
- Opt for natural pest control methods in your garden: If you have a garden, consider using natural pest control methods, such as companion planting, biological pest control, and organic fertilizers. These methods help maintain a healthy ecosystem in your garden without relying on chemical interventions.
By incorporating these tips into your daily life, you can take significant steps towards minimizing your exposure to pesticides and enjoying a healthier, pesticide-free diet. Remember to be mindful of the choices you make and always prioritize your health and the well-being of your loved ones.
Buy Organic Produce
One of the most effective ways to avoid pesticides in your food is to choose organic produce. Organic farming practices prioritize the use of natural methods to grow crops, eliminating the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
When you buy organic produce, you can have confidence that the food you’re consuming is free from potentially harmful chemical residues. Organic farmers use alternative pest management techniques, such as crop rotation, natural predators, and beneficial insects, to promote a healthy and balanced ecosystem within their farms.
The USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) and other certification bodies regulate organic farming practices and set strict guidelines for labeling products as organic. Look for the USDA Organic seal or other credible organic certifications to ensure the produce you’re purchasing meets these standards.
While buying organic produce can be more expensive than conventionally grown options, the benefits to your health and the environment outweigh the cost. If budget constraints are a concern, you can prioritize buying organic for the produce that tends to have higher pesticide residues, such as berries, leafy greens, and apples, and opt for conventionally grown versions of produce with lower pesticide residues.
Shopping at local farmers markets or joining a community-supported agriculture (CSA) program can also be a great way to access fresh, organic produce while supporting local farmers who practice sustainable farming methods.
Keep in mind that organic certification extends beyond fruits and vegetables. You can also find organic options for meat, dairy, eggs, grains, and other food items. By choosing organic across different food categories, you create a well-rounded, pesticide-free diet.
Buying organic goes beyond promoting your own health; it also supports a more sustainable food system. Organic farming practices prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and water conservation, which contribute to long-term environmental sustainability.
In summary, buying organic produce is a powerful step you can take to minimize your exposure to pesticides in food. Look for trusted organic certifications, prioritize your purchases based on the produce with higher pesticide residues, and consider supporting local, organic farmers. By making these choices, you can enjoy the benefits of a healthier diet while advocating for a more sustainable and pesticide-free food system.
Grow Your Own Food
Growing your own food is not only a rewarding and satisfying experience, but it also allows you to have complete control over the cultivation process and ensures that your produce is free from pesticides. Whether you have a small backyard, a balcony, or even just a sunny windowsill, there are plenty of opportunities to grow your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
When you grow your own food, you have the power to decide how your crops are raised. You can choose to follow organic farming practices, avoiding the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. Instead, opt for natural pest control methods like companion planting, which involves planting complementary crops that discourage pests, or organic pest control products made from natural ingredients.
Starting a garden may seem intimidating, but it can be done on any scale. Begin by assessing the space you have available and the amount of sunlight it receives. You can start small with potted herbs or container gardens, which are perfect for individuals or those with limited space. If you have more room, consider creating raised beds or even converting a section of your yard into a vegetable garden.
Do some research on the types of crops that are well-suited for your region and climate. Plan your garden layout, taking into account factors like crop rotation, proper spacing, and pest prevention techniques. You can also explore the option of heirloom or organic seeds to ensure the highest quality and genetic diversity of your plants.
In addition to the health benefits of homegrown, pesticide-free produce, growing your own food has other advantages as well. It can help reduce your grocery bills, provide you with fresh, flavorful produce at your convenience, and promote a stronger connection to nature and the food you eat.
If you’re new to gardening, there are plenty of resources available to help you get started. Look for local gardening workshops, join online gardening communities, or seek advice from experienced gardeners in your area. Many gardening enthusiasts love to share their knowledge and can provide guidance on plant care, soil preparation, and organic gardening practices.
Growing your own food is a fulfilling and empowering endeavor that allows you to take control of what goes into your meals. By cultivating pesticide-free crops, you can enjoy the peace of mind knowing that you are consuming fresh, healthy produce. So, roll up your sleeves, get your hands dirty, and start growing your own pesticide-free food.
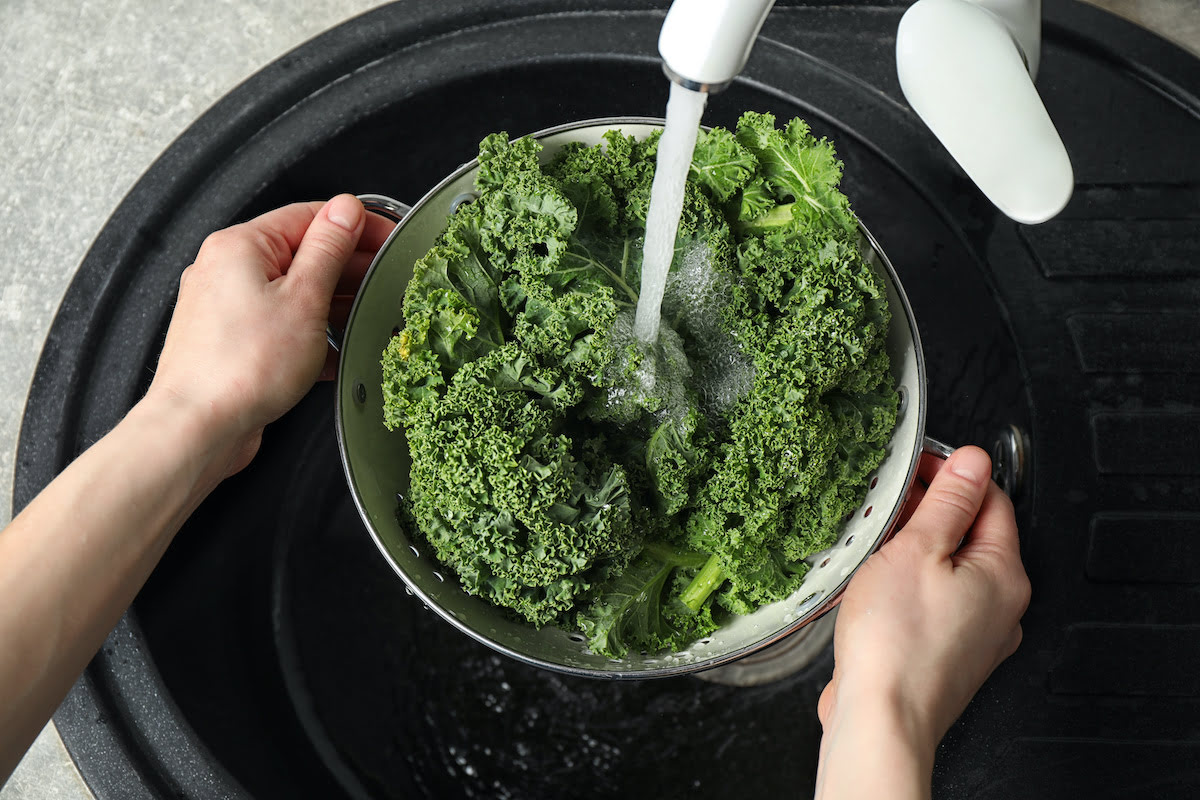
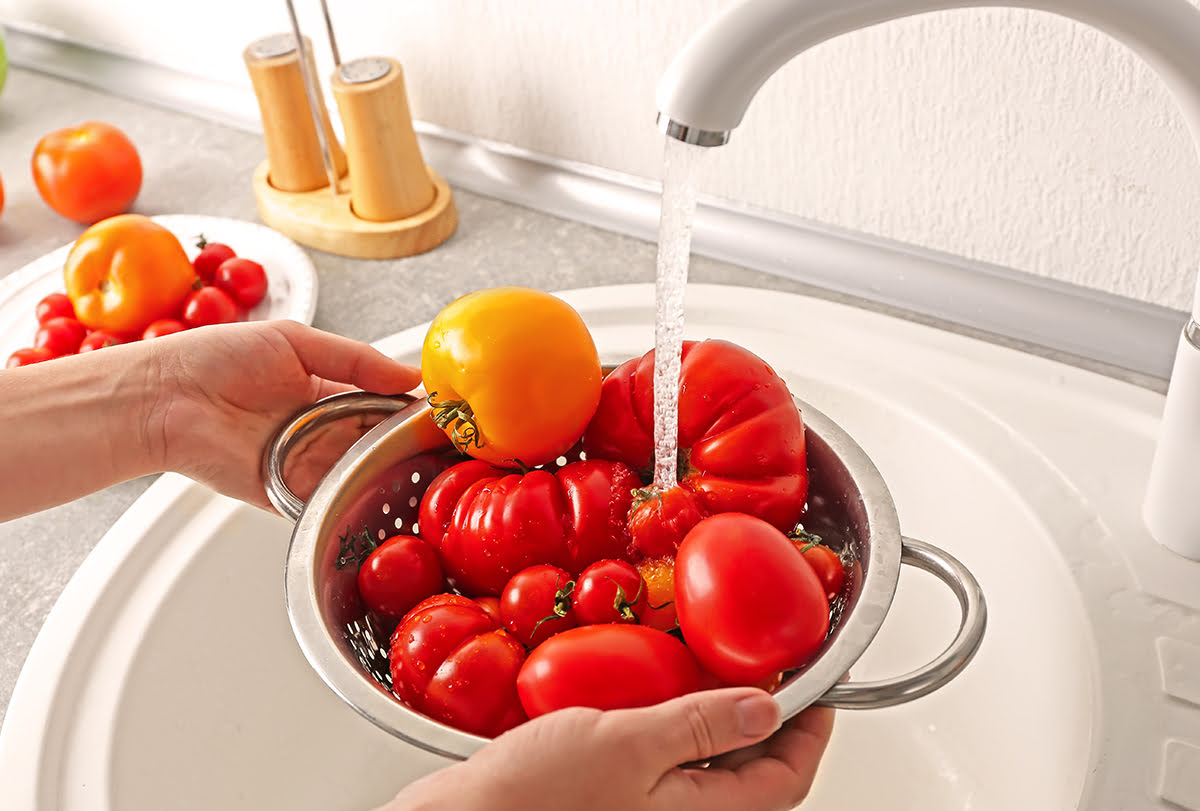
Wash and Scrub Produce Thoroughly
Washing and scrubbing produce thoroughly is an essential step in reducing pesticide residues and other contaminants on the surface of fruits and vegetables. While it may not completely eliminate all pesticide residues, it does help to minimize your exposure. Here are some tips to ensure you thoroughly clean your produce:
- Use running water: Rinse fruits and vegetables under cool, running water to remove dirt, debris, and any pesticide residues present. Avoid using soap or detergents as they may leave a residue or alter the taste of the produce.
- Scrub firm produce: For produce like apples, cucumbers, and potatoes, use a clean vegetable brush or your hands to gently scrub the surface. This can help remove any pesticide residues that may be clinging to the skin.
- Pay attention to leafy greens: Leafy greens like lettuce and spinach can trap pesticide residues in their crevices. Separate the leaves and rinse them thoroughly, making sure to remove any dirt or bugs that may be present.
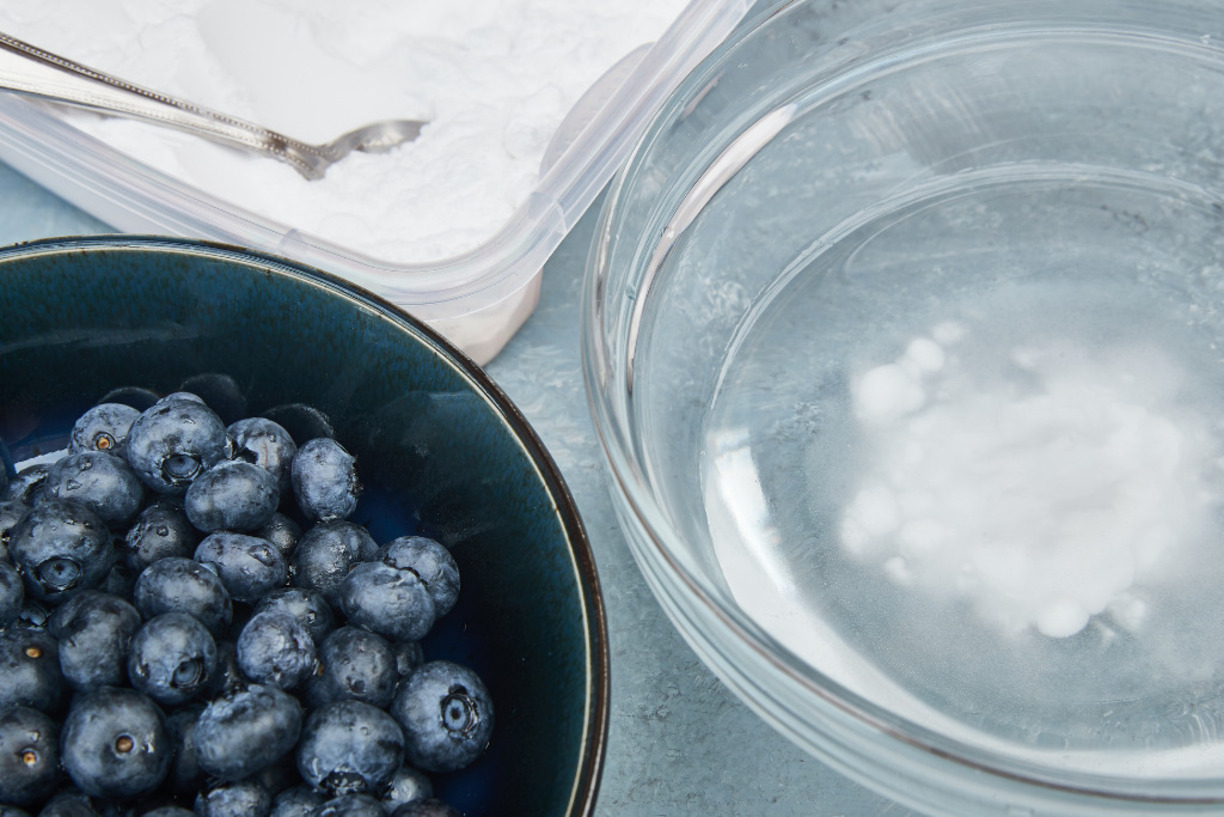
- Soak certain produce: Some fruits and vegetables, like berries, grapes, and broccoli, can benefit from a short soak in a mixture of water and vinegar. Fill a bowl with a solution of 1 part vinegar to 3 parts water, gently place the produce into the mixture, and let it soak for a few minutes. Rinse thoroughly afterwards.
- Pat dry: After washing, gently pat dry produce with a clean cloth or paper towel to remove excess moisture. This can help prevent mold growth and maintain the freshness of the produce.
It’s important to note that washing and scrubbing produce is more effective in removing external residues rather than those that have been absorbed into the flesh of the fruit or vegetable. However, every effort counts, and by following these cleaning practices, you can significantly reduce your exposure to pesticide residues on the surface of your food.
In addition to washing and scrubbing, it’s worth considering the source of your produce. Locally sourced and organically grown fruits and vegetables are likely to have lower pesticide residues, making them a preferable choice. By supporting local farmers who practice sustainable farming methods, you can further reduce your exposure to pesticides.
Lastly, remember that washing and scrubbing produce is not limited to fresh fruits and vegetables. It’s equally important to clean canned or packaged fruits and vegetables, as pesticide residues can still be present, especially in processed foods. Pay attention to labels and opt for organic or pesticide-free options whenever possible.
By incorporating thorough washing and scrubbing into your food preparation routine, you can ensure that you are reducing pesticide residues on the surface of your produce and promoting a healthier diet.
Peel Fruits and Vegetables
Peeling fruits and vegetables is an effective way to further reduce pesticide exposure, as many pesticide residues accumulate on the surface of produce. While this method may result in some nutrient loss, it can significantly reduce your intake of pesticide residues. Here are some key points to consider when peeling fruits and vegetables:
- Focus on thicker-skinned produce: Thicker-skinned fruits and vegetables tend to have higher pesticide residues on their outer layers. Examples include apples, cucumbers, bell peppers, and carrots. Peeling these fruits and vegetables can help remove a significant portion of pesticide residues.
- Wash before peeling: Before peeling, it’s important to wash the produce under running water and use a clean vegetable brush to remove any dirt or debris. This step helps to prevent contaminants from transferring from the skin to the flesh of the fruit or vegetable during the peeling process.
- Be mindful of nutrient loss: Keep in mind that some nutrients are concentrated in the skin of fruits and vegetables. Peeling them may result in some loss of vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. To compensate, include a variety of whole, unpeeled fruits and vegetables in your diet to maximize nutritional benefits.
- Consider the source of your produce: If you’re unable to buy organic produce or prefer not to peel, choosing locally sourced and organically grown fruits and vegetables can provide an alternative solution. Organic produce is cultivated without the use of synthetic pesticides, reducing the need for peeling to remove residues.
- Utilize peels creatively: While it’s common to discard peels, some can be used in other culinary applications. For example, citrus peels can be used to infuse flavor into dishes or as a garnish. Consider incorporating peels into recipes or using them in homemade stocks or compost.
It’s worth noting that not all fruits and vegetables need to be peeled. Thin-skinned produce such as berries, grapes, and leafy greens can be difficult to peel and may not have high levels of pesticide residues on their surfaces. In such cases, thorough washing and using alternative cleaning methods may be more effective in reducing contamination.
Remember that the decision to peel fruits and vegetables ultimately depends on your personal preference and circumstances. If you’re unsure or concerned about pesticide residues, reach out to local farmers or sellers who can provide information on their growing practices and pesticide usage.
By peeling fruits and vegetables, you can reduce your exposure to pesticide residues while still enjoying the nutritional benefits of these produce items. Consider incorporating a variety of both peeled and unpeeled fruits and vegetables into your diet to ensure a balance between pesticide reduction and nutrient intake.
Choose Locally Sourced and Seasonal Foods
Opting for locally sourced and seasonal foods can significantly reduce your exposure to pesticides. Local and seasonal produce often requires fewer pesticides, as they are more adapted to the local environment and less prone to pests and diseases that would require extensive chemical interventions. Here’s why choosing locally sourced and seasonal foods is beneficial:
- Reduced pesticide use: Local farmers who practice sustainable or organic farming methods often prioritize natural pest control techniques and minimize the use of synthetic pesticides. By supporting these farmers, you are indirectly reducing your intake of pesticide residues.
- Fresher and more flavorful: Locally sourced produce is harvested at peak ripeness and consumed within a shorter timeframe. This ensures that you’re getting the freshest and most flavorful fruits and vegetables, which often require fewer preservatives or synthetic coatings that conventional produce may have.
- Support for local economy: By choosing local foods, you support farmers in your community. This helps to strengthen local food systems, reduce carbon emissions associated with long-distance transportation, and promotes a more sustainable and resilient community.
- Connection to your food: Buying locally sourced produce allows you to connect with the seasons and the natural agricultural rhythms of your region. It encourages a deeper appreciation for the variety and diversity of locally grown foods, reconnecting you with the land and the environment.
- Access to heirloom and unique varieties: Local farmers often cultivate heirloom or unique produce varieties that may not be readily available in large-scale supermarkets. By choosing local, you have the opportunity to explore and taste a wider range of flavors, textures, and colors.
When shopping for locally sourced and seasonal foods, consider visiting farmers markets, joining a community-supported agriculture (CSA) program, or participating in farm-to-table initiatives. These provide direct access to fresh produce while allowing you to engage with local farmers and learn more about their farming practices.
Seasonality plays a crucial role in determining which fruits and vegetables are available at a given time. Familiarize yourself with the seasonal produce in your area, and plan your meals accordingly. Take advantage of the abundance of fresh options during the growing season, and find ways to preserve or store produce for the off-season.
Additionally, local grocery stores and supermarkets may label the origin of their produce, indicating whether it is locally sourced or imported from other regions. Look for signs or ask store associates to help you identify locally sourced options.
By choosing locally sourced and seasonal foods, you support sustainable farming practices, reduce pesticide exposure, and enjoy the freshest and most flavorful produce available. It’s a win-win situation for your health, the environment, and your local community.
Read Labels and Look for Pesticide-Free or Low Pesticide Options
When it comes to purchasing packaged foods, one way to avoid pesticides is by carefully reading labels and looking for products that are pesticide-free or have low pesticide residue levels. While this may require some extra time and effort, it can significantly contribute to reducing your overall pesticide exposure. Here’s how you can make informed choices:
- Look for organic certifications: Organic certifications ensure that the ingredients used in the product were grown without the use of synthetic pesticides. Look for labels indicating that the product is certified organic, such as the USDA Organic seal or other reputable organic certifications.
- Check for “pesticide-free” or “low pesticide” claims: Some food companies may label their products as “pesticide-free” or “low pesticide.” These claims indicate that the company has taken measures to minimize pesticide use in their production process. Look for these labels as an additional indication of a product’s reduced pesticide content.
- Prioritize natural and clean ingredient lists: Even if a product doesn’t have specific pesticide-related claims, focus on choosing packaged foods with minimal ingredients and those that use natural preservatives or those labeled as “clean” or “all-natural.” These products are more likely to contain fewer synthetic pesticides or chemical additives.
- Research company practices: If you’re concerned about pesticide use in specific brands or products, research the company’s practices. Look for information on their website or reach out to them directly to inquire about their farming or sourcing practices. Some companies pride themselves on their commitment to pesticide reduction or sustainability.
- Consider environmentally friendly certifications: Some certifications focus on environmentally friendly growing practices, which often include reduced pesticide use. Look for certifications like “Rainforest Alliance,” “Fair Trade,” or “Non-GMO Project Verified,” as these can indicate a commitment to more sustainable agricultural practices and potentially lower pesticide residues.
It’s important to note that while reading labels can be helpful, it’s still advisable to prioritize whole, fresh, and unprocessed foods whenever possible. These foods are less likely to contain hidden pesticide residues and offer greater nutritional benefits.
Additionally, remember that labels provide only a limited amount of information. They may not disclose the specific pesticides used or the actual amount of residue present. Therefore, it’s always best to prioritize organic produce and to grow your own food when feasible, as these options offer the highest level of control over pesticide exposure.
By reading labels and seeking out pesticide-free or low pesticide options, you can make more informed choices about the packaged foods you consume. This approach allows you to reduce your overall pesticide intake and promote a healthier diet for yourself and your family.
Support Farmers Using Sustainable Farming Practices
Supporting farmers who use sustainable farming practices is not only beneficial to the environment but also helps to reduce your exposure to pesticides in food. These farmers prioritize the use of natural, environmentally friendly methods to grow their crops, reducing the need for synthetic pesticides and promoting a healthier and more sustainable food system. Here’s how you can support farmers using sustainable farming practices:
- Shop at farmers markets: Farmers markets are a great way to directly connect with local farmers who practice sustainable farming. By purchasing your produce and other food items from farmers markets, you support their efforts in reducing pesticide use and promoting ecological balance.
- Join community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs: CSA programs allow you to invest in a local farm and receive a share of its produce throughout the growing season. CSAs support sustainable farming practices and provide a direct relationship with the farmers who grow your food.
- Look for sustainable farming certifications: Some farms may carry certifications such as “Certified Naturally Grown” or “Biodynamic” that indicate their commitment to sustainable and organic farming practices. These certifications ensure that the produce you buy is grown with minimal pesticide use and follows sustainable principles.
- Engage in farm-to-table initiatives: Participate in initiatives that connect consumers with local farmers, such as farm-to-table programs or farm cooperatives. These initiatives promote transparency and allow you to directly support farmers who prioritize sustainable practices.
- Get to know your local farmers: Building relationships with local farmers is a wonderful way to support sustainable farming. Visit their farms, ask questions about their practices, and develop an understanding of their commitment to minimizing pesticide use. Many farmers are eager to share their knowledge and love to educate consumers about their farming methods.
- Advocate for policy changes: Support policies and regulations that promote sustainable farming practices and reduce reliance on pesticides. Stay informed about local and national agricultural policies and use your voice to advocate for a more sustainable and pesticide-free food system.
Supporting farmers who practice sustainable farming methods not only helps to reduce pesticide exposure but also contributes to the conservation of soil health, water quality, and biodiversity. By encouraging sustainable practices, we can build a more resilient and environmentally friendly agricultural system.
Remember that every purchasing decision you make has an impact. By actively seeking out and supporting farmers who prioritize sustainable practices, you are contributing to a healthier and more sustainable future.
Choose Packaged Foods with Organic Certifications
When it comes to choosing packaged foods, one effective way to avoid pesticides is to look for products with organic certifications. Organic certifications ensure that the ingredients used in the product were grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, making them a safer and healthier option for consumption. Here’s why you should choose packaged foods with organic certifications:
- Avoidance of synthetic pesticides: Organic certifications guarantee that the ingredients used in the product were cultivated using organic farming practices, which prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides. By choosing organic-certified packaged foods, you minimize your exposure to harmful chemical residues.
- Maintaining nutritional integrity: Organic farming practices not only eliminate synthetic pesticides but also promote soil health and biodiversity. The use of natural fertilizers and sustainable farming methods helps to maintain the nutritional integrity of the ingredients used in organic products.
- Reduced environmental impact: Organic farming practices prioritize the use of natural resources, conserve biodiversity, and protect the environment. By choosing packaged foods with organic certifications, you contribute to the reduction of water pollution, soil degradation, and the overall ecological footprint associated with conventional farming.
- Stringent regulations and standards: Organic certifications are backed by stringent regulations and standards that ensure the integrity of organic products. Certifying bodies, such as the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) or other reputable organic certification organizations, monitor and verify that the products comply with organic farming guidelines.
- Diverse range of options: The availability of organic-certified packaged foods has greatly expanded in recent years. Whether you’re looking for snacks, canned goods, condiments, or other pantry staples, you can find organic alternatives for a wide range of products.
When purchasing packaged foods, always look for credible organic certifications on the label. The USDA Organic seal is one of the most well-known organic certifications, indicating that the product meets the USDA’s strict organic standards. Additionally, other reputable organic certifications, such as those from independent organic certification organizations, can provide further assurance of the product’s organic status.
While choosing packaged foods with organic certifications is a valuable strategy, it’s important to remember that whole, fresh, and unprocessed foods should always be prioritized whenever possible. These foods offer greater nutritional value and are less likely to contain hidden additives or pesticide residues.
By selecting packaged foods with organic certifications, you can make informed choices that prioritize your health, support sustainable farming practices, and contribute to a more environmentally friendly food system.
Limit Consumption of High Pesticide Residue Foods
While it may not be feasible to completely eliminate exposure to pesticide residues in food, you can minimize your intake by limiting the consumption of high pesticide residue foods. Some fruits and vegetables tend to have higher levels of pesticide residues than others, making it important to prioritize organic options or reduce intake. Here’s how you can make informed choices to reduce exposure:
- Refer to the “Dirty Dozen” and “Clean Fifteen” lists: The Environmental Working Group (EWG) produces an annual list known as the “Dirty Dozen” and “Clean Fifteen,” which identifies the fruits and vegetables with the highest and lowest levels of pesticide residues, respectively. Consult these lists to prioritize organic options for the produce on the “Dirty Dozen” list.
- Choose organic for high pesticide residue foods: When possible, opt for organic varieties of fruits and vegetables that tend to have higher pesticide residues, such as strawberries, spinach, kale, and apples. By choosing organic, you can significantly reduce your exposure to these harmful chemicals.
- Explore alternative options: If organic options are not readily available or within your budget, consider choosing different fruits and vegetables. For example, if strawberries are on the “Dirty Dozen” list, opt for fruits with lower pesticide residues, such as pineapples or mangoes.
- Grow your own: Growing your own fruits and vegetables allows you to have control over the cultivation process and ensure that your produce is free from pesticide residues. You can prioritize growing high pesticide residue foods yourself, ensuring they are grown without the use of harmful chemicals.
- Rotate your produce: Rotate the types of fruits and vegetables you consume to minimize repeated exposure to the same high residue produce. Variety is key in maintaining a balanced and diverse diet while reducing overall pesticide exposure.
- Focus on whole foods: By placing emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods, you can minimize your exposure to hidden pesticide residues present in processed foods. Cooking from scratch using fresh ingredients allows you to have greater control over the quality of the ingredients you use.
While it’s essential to be mindful of high pesticide residue foods, it’s important not to let concerns about pesticide residues deter you from consuming an abundance of fresh fruits and vegetables. The benefits of a diet rich in plant-based foods far outweigh the risks associated with pesticide exposure.
By incorporating these practices into your diet, such as opting for organic varieties, growing your own produce, and diversifying your choices, you can take proactive steps towards reducing your intake of high pesticide residue foods and promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Opt for Natural Pest Control Methods in Your Garden
Creating a garden free from pests without the use of harmful pesticides is possible by adopting natural pest control methods. These methods prioritize ecological balance, promoting a healthy garden ecosystem that can naturally combat pests. Here are some techniques you can implement to reduce the need for pesticides in your garden:
- Companion planting: Planting certain crops next to each other can help repel pests or attract beneficial insects that act as natural pest controllers. For instance, marigolds can deter aphids, while planting herbs like basil or mint near tomatoes can repel tomato hornworms.
- Biological pest control: Encourage beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and praying mantises to inhabit your garden. These predators feed on common garden pests such as aphids, caterpillars, and mites. Creating habitats like small ponds or installing birdhouses can also attract natural predators to your garden.
- Use crop rotation: Rotating crops each growing season can help disrupt the life cycles of pests and reduce soil-borne diseases. By moving crops to different areas of the garden, you can avoid a buildup of pests that tend to target specific plant families.
- Practice good garden hygiene: Keeping your garden tidy and free of debris can reduce pest habitats. Clear away fallen leaves, weeds, and overripe fruits to discourage pests from taking up residence and minimize the spread of diseases.
- Natural barriers and traps: Create physical barriers, such as netting or row covers, to protect susceptible plants from pests. You can also employ sticky traps or pheromone traps to attract and capture specific pests.
- Organic fertilizers and soil amendments: Maintaining healthy soil and providing balanced nutrition to your plants can make them more resistant to pests and diseases. Use organic fertilizers, compost, and other natural soil amendments to nourish your garden without relying on synthetic chemicals.
- Handpicking pests: For minor pest problems, manually remove insects by handpicking them off plants or using a gentle spray of soapy water to dislodge them.
Implementing these natural pest control methods may require more careful observation and monitoring of your garden. By being attentive to the needs of your plants and the behavior of potential pests, you can take proactive steps to address issues before they become severe.
Engage in continuous learning about natural pest control techniques and seek advice from local gardening experts or fellow gardeners who have experience with organic gardening. This shared knowledge and experience can help you tailor your pest control methods to suit the specific needs of your garden and region.
Remember, a few pests in the garden are usually tolerable and shouldn’t cause alarm. A balanced ecosystem that accommodates both pests and beneficial insects will help maintain the natural harmony of your garden while reducing the need for synthetic pesticides.
By implementing natural pest control methods, you can create a sustainable, pesticide-free garden that is both environmentally friendly and abundant with healthy, thriving plants.
Conclusion
Minimizing exposure to pesticides in our food is crucial for maintaining our health and well-being. The impact of pesticides on our bodies and the environment is a growing concern, but fortunately, there are practical steps we can take to reduce our risk. By following the tips provided in this guide, we can make informed choices and avoid pesticide-laden foods.
We started by understanding the potential dangers of consuming pesticide-laden foods, including the increased risk of cancer, reproductive issues, and neurological disorders. Awareness of these risks motivates us to take proactive measures to protect ourselves and our loved ones.
We explored various strategies for avoiding pesticides in our food, such as buying organic produce, growing our own food, and washing and scrubbing produce thoroughly. These practices not only reduce our exposure to pesticides but also support sustainable farming practices and promote a healthier food system.
Understanding the importance of choosing locally sourced and seasonal foods helps us prioritize freshness, flavor, and reduced pesticide use. By supporting local farmers, we contribute to the community, reduce carbon emissions, and strengthen food security.
By reading labels and choosing packaged foods with organic certifications, we make informed choices that prioritize our health and support a more sustainable food industry. Opting for natural pest control methods in our gardens helps maintain a balanced ecosystem without resorting to harmful pesticides.
Ultimately, our efforts to avoid pesticides in our food require a holistic approach that encompasses our shopping habits, dietary choices, and gardening practices. Every step we take towards reducing pesticide exposure contributes to our overall well-being and the health of the environment.
By prioritizing organic options, supporting farmers who use sustainable practices, and adopting natural solutions, we can enjoy a diet that is both nutritious and free from harmful pesticides. Let us continue to make conscious choices that protect our health, the health of our communities, and the health of our planet.