Home>Gardening Techniques>Plant Care>What Are Rubber Trees


Plant Care
What Are Rubber Trees
Published: October 24, 2023
Learn essential plant care tips for rubber trees to help them thrive. Discover how to properly water, fertilize, and care for these popular indoor houseplants.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of rubber trees! If you’re looking to bring a touch of nature into your home or garden, rubber trees are a fantastic choice. These versatile and resilient plants are known for their glossy leaves, which can add a vibrant and lush feel to any space. Not only are they visually appealing, but they also offer a range of benefits and can even be grown as a source of rubber production.
Originally native to the rainforests of South America, rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) have gained popularity around the world for their unique characteristics and easy-care nature. They belong to the Euphorbiaceae family and are known for their ability to produce latex, which is used to make various rubber-based products.
Whether you’re a seasoned plant enthusiast or a beginner looking to dip your toes into gardening, rubber trees are an excellent choice. With a little knowledge and care, you can enjoy the beauty and benefits they offer.
In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating world of rubber trees, from their history and characteristics to cultivation tips and the products they yield. We’ll also discuss the benefits of having rubber trees in your surroundings and touch upon any concerns or challenges you may face along the way.
So, let’s dive in and discover the wonders of rubber trees!
History of Rubber Trees
The history of rubber trees dates back centuries and is intertwined with the exploration and discovery of the Americas. The native people of South America were the first to utilize the latex produced by rubber trees for a variety of purposes.
Ancient civilizations, such as the Mayans and Aztecs, used latex from rubber trees to create waterproof materials, shoes, and even ancient Mesoamerican ball games. However, it wasn’t until the arrival of Europeans in the 15th century that rubber became known to the rest of the world.
In the late 18th century, botanists and explorers began to investigate the properties of rubber trees, leading to increased interest in the plant and its potential commercial uses. It was during this time that rubber trees were first cultivated outside of their native habitat.
The real breakthrough in rubber production came in the early 19th century when the British scientist Charles Goodyear discovered the vulcanization process. This revolutionary technique allowed for the transformation of raw rubber into a durable and practical material that could be used in various industries.
The demand for rubber surged during the industrial revolution, as it became an essential component in the production of tires, belts, seals, and a wide range of consumer products. This led to the establishment of rubber plantations in countries such as Brazil, Malaysia, and Indonesia, which became the leading producers of rubber.
However, the rubber industry faced challenges during World War II when the supply of natural rubber was cut off due to the Japanese occupation of Southeast Asian rubber plantations. This prompted the development of synthetic rubber as an alternative, which impacted the global rubber market.
Today, rubber trees are cultivated worldwide, with major rubber-producing countries including Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and India. The flexibility and versatility of rubber continue to make it an indispensable material in various sectors, from automotive and manufacturing to healthcare and construction.
The history of rubber trees is a testament to human ingenuity and the continuous quest for new materials. Their cultivation and commercial use have evolved over time, making rubber trees a fascinating part of our natural and industrial heritage.
Characteristics of Rubber Trees
Rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) are known for their distinctive characteristics that make them a popular choice among plant enthusiasts. Here are some key features that set rubber trees apart:
- Large Leaves: One of the defining features of rubber trees is their large, glossy leaves. These leaves can grow up to 12 inches long and have a rich green color, adding a touch of elegance to any space.
- Indoor and Outdoor Varieties: Rubber trees can be grown both indoors and outdoors, making them versatile options for different environments. Indoor rubber trees are typically smaller and compact, while outdoor varieties can grow into impressive trees reaching heights of up to 50 feet.
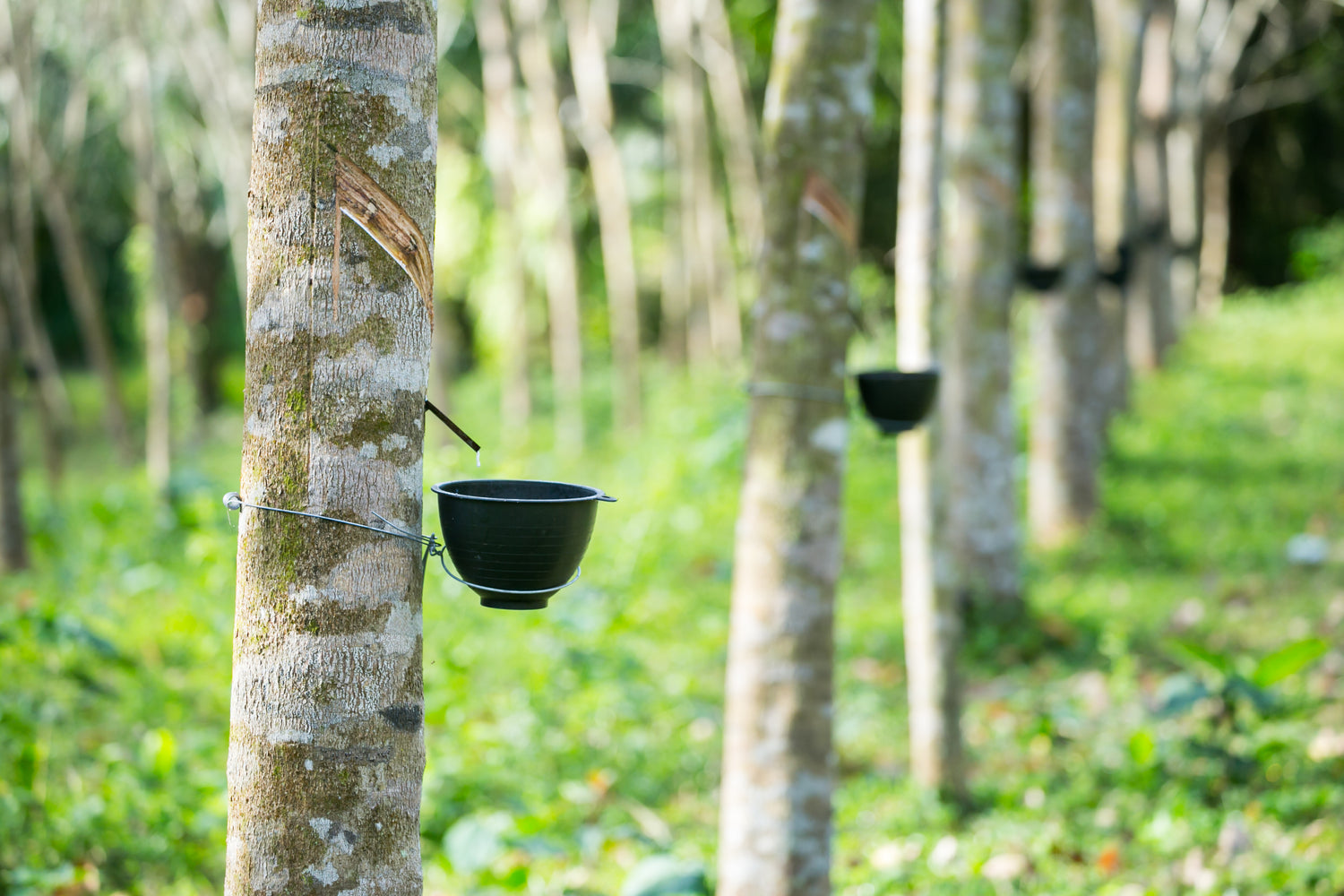
- Latex Production: Rubber trees have the remarkable ability to produce latex, a milky white sap found in the layers beneath their bark. This latex is rich in rubber compounds and can be harvested and processed to create various rubber-based products.
- Fast-Growing: Rubber trees are known for their rapid growth, especially in warm and humid climates. With proper care and favorable conditions, these trees can grow several feet in just a year.
- Low Maintenance: Another appealing characteristic of rubber trees is their relatively low maintenance requirements. They are resilient plants that can tolerate a range of light conditions and are generally resistant to pests and diseases.
- Air Purifying: Like many houseplants, rubber trees have air purifying properties. They can help remove pollutants from the air, making them ideal choices for indoor spaces.
It’s important to note that while rubber trees have many desirable characteristics, they also have some considerations to keep in mind. The latex produced by rubber trees can cause allergic reactions in some individuals, so it’s recommended to handle them with caution if you have latex allergies. Additionally, the sap of rubber trees is mildly toxic to pets, so if you have furry friends, it’s best to keep them away from the plant.
Overall, the unique characteristics of rubber trees make them visually appealing, resilient, and versatile plants suitable for a range of environments.
Cultivation and Growing Conditions
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner, growing rubber trees can be a rewarding and successful endeavor. Here are some key factors to consider when cultivating rubber trees:
- Light: Rubber trees thrive in bright, indirect light. They can tolerate some shade, but too little light can result in leggy growth and smaller leaves. Place them near a window with filtered sunlight for optimal growth.
- Temperature: Rubber trees prefer warm temperatures between 60-80°F (15-27°C). Avoid exposing them to temperatures below 50°F (10°C) as it can damage the leaves. They are not frost-tolerant plants.
- Humidity: Rubber trees are native to tropical and subtropical regions, so they appreciate higher humidity levels. If the air in your home is dry, consider using a humidifier or placing a tray of water near the plant to increase humidity.
- Watering: It’s important to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Water your rubber tree when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot. In winter, reduce the frequency of watering.
- Soil: Rubber trees prefer well-draining soil that retains some moisture. A good potting mix formulated for tropical plants or a blend of peat moss, perlite, and sand works well. A slightly acidic to neutral pH range is ideal.
- Fertilization: Regular fertilization is necessary to promote healthy growth. Use a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength every month during the growing season (spring and summer). Avoid fertilizing in winter when the plant is dormant.
- Pruning: Pruning is not necessary for rubber trees, but you can trim back any leggy or unruly growth to maintain a compact shape. Be cautious when handling the milky sap as it can be irritating to the skin and eyes.
- Propagation: Rubber trees can be propagated through stem cuttings. Take a 6-8 inch cutting from a healthy, mature plant and place it in a container with a well-draining potting mix. Keep the cutting warm and moist until it develops roots.
Remember that each rubber tree is unique, and its specific care requirements can vary. Monitor your plant closely and make adjustments as needed to provide the best growing conditions.
With the right care and attention, your rubber tree will thrive and bring joy with its beautiful foliage.
Rubber Tree Products
Rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) are not only admired for their beauty and versatility in the world of plants but also for their valuable contribution to various industries. Let’s explore some of the key products derived from rubber trees:
- Natural Rubber: The primary product obtained from rubber trees is natural rubber. The latex collected from the trees is processed to remove impurities and generate rubber in its raw state. Natural rubber is widely used in the production of tires, industrial belts, gloves, footwear, and countless other rubber-based products.
- Latex Products: The latex extracted from rubber trees has numerous applications beyond natural rubber production. It is used in the manufacturing of latex gloves, balloons, rubber toys, foam mattresses, medical equipment, adhesives, and even some food products.
- Rubberwood: After a rubber tree reaches the end of its latex-producing life cycle (usually after 25-30 years), the wood from the tree can be harvested and repurposed. Rubberwood is highly valued in the furniture industry and is known for its durability, attractive grain patterns, and eco-friendliness.
- Rubber Seeds: Rubber tree seeds can also be utilized commercially. The seeds contain oil that is rich in essential fatty acids and is used in the production of soaps, cosmetics, lubricants, and biodiesel.
- Landscape and Ornamental Use: Rubber trees are often utilized for their aesthetic appeal in landscapes and gardens. The large, glossy leaves and striking form of the tree make it an attractive focal point in outdoor spaces.
- Air Purification: Rubber trees, like many other plants, have the ability to improve air quality by filtering out pollutants and releasing oxygen. Having a rubber tree indoors can contribute to a healthier, more pleasant environment.
The diverse range of products derived from rubber trees highlights their economic significance and the importance of sustainable rubber production. As the demand for rubber continues to grow, it becomes crucial to explore sustainable cultivation methods and alternative sources to meet global needs.
From tires to furniture, rubber trees provide an array of valuable products that touch many aspects of our daily lives.
Benefits of Rubber Trees
Rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) offer numerous benefits, making them a valuable addition to any home, garden, or natural environment. Let’s explore some of the advantages of having rubber trees:
- Aesthetically Pleasing: With their large and glossy leaves, rubber trees add a touch of elegance and a tropical vibe to any space. Whether indoors or outdoors, they can enhance the visual appeal of your surroundings.
- Air Purification: Like many other houseplants, rubber trees have the ability to purify the air by removing toxins and releasing oxygen. They can help improve indoor air quality and create a healthier living environment.
- Indoor and Outdoor Versatility: Rubber trees can be grown both indoors and outdoors, providing flexibility in placement options. They make excellent houseplants and can thrive in gardens, landscapes, or as shade trees in suitable climates.
- Low Maintenance: Rubber trees are relatively low maintenance compared to some other plants. They are resilient and can tolerate different light conditions, making them suitable for those new to gardening or with busy lifestyles.
- Enhancing Biodiversity: Rubber trees, when grown outdoors, can contribute to increasing biodiversity in their surroundings. They provide shelter and food sources for various birds, insects, and other wildlife.
- Source of Rubber Production: Rubber trees are primarily cultivated for their latex, which is used to produce rubber. The rubber industry plays a vital role in numerous sectors, including transportation, manufacturing, and healthcare.
- Renewable Resource: Rubber trees are a renewable resource as they can be tapped for latex multiple times throughout their lifespan. With sustainable cultivation practices, rubber production can be environmentally friendly and economically sustainable.
- Supporting Rural Communities: Rubber plantations often provide employment opportunities for people in rural areas, thereby contributing to local economies and livelihoods.
Whether you appreciate the aesthetic appeal, the air-purifying qualities, or the economic benefits, rubber trees offer a wide range of advantages. By incorporating rubber trees into your surroundings, you can enjoy both the beauty they bring and the positive impact they have on the environment.
Concerns and Challenges in Rubber Tree Cultivation
While rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) offer many benefits, there are also some concerns and challenges to consider when cultivating them. Let’s explore some of the potential issues that rubber tree growers may face:
- Latex Allergies: The latex produced by rubber trees can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. If you have latex allergies, it’s essential to take precautions when handling the plant, such as wearing gloves and avoiding contact with the sap.
- Pest and Disease Management: Rubber trees are generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, they can still be susceptible to issues like scale insects, mealybugs, leaf spots, and fungal infections. Regular monitoring, proper hygiene, and appropriate pest control measures are key to maintaining healthy trees.
- Environmental Impact: In regions where rubber plantations are extensive, there can be concerns about deforestation, habitat loss, and the impact on local ecosystems. Sustainable cultivation practices, including responsible land management and biodiversity conservation, are crucial to mitigating these concerns.
- Water Requirements: Rubber trees require consistent moisture but can be sensitive to overwatering. Improper irrigation practices can lead to waterlogging, root rot, or nutrient leaching. Balancing watering needs with proper drainage is essential for maintaining healthy trees.
- Frost and Cold Sensitivity: Rubber trees are sensitive to cold temperatures and frost. If you live in a region with harsh winters, protecting your rubber tree from extreme cold is necessary. Consider bringing potted rubber trees indoors during colder months or providing adequate frost protection for outdoor trees.
- Longevity of Latex Production: Rubber trees have a finite period of latex production, usually around 25-30 years. Once a rubber tree reaches the end of its productive life, the latex yield declines significantly. Proper planning for replanting or transitioning to alternate crops is necessary for sustained rubber production.
- Economic Volatility: The rubber industry can be influenced by fluctuations in global demand and market prices. Growers may face challenges in maintaining profitability due to changing market dynamics, making careful financial planning and diversification crucial for long-term success.
Despite these challenges, with proper care, attention, and sustainable practices, many of these concerns can be addressed or minimized. By staying informed and implementing best practices, rubber tree growers can overcome obstacles and enjoy the many benefits that rubber trees have to offer.
Conclusion
Rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis) are remarkable plants with a rich history, unique characteristics, and a range of benefits. Whether you’re looking to enhance your indoor space, add beauty to your garden, or contribute to the rubber industry, rubber trees are an excellent choice.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the journey of rubber trees from their origins in South America to their cultivation worldwide. We’ve delved into their distinct characteristics, such as their large glossy leaves and latex production capabilities. We’ve also discussed the optimal growing conditions and care requirements necessary to ensure their health and vitality.
Furthermore, we’ve examined the various products that rubber trees offer, from natural rubber for tires and industrial applications to latex products, rubberwood, and even the oil-rich seeds. The versatility and sustainability of rubber tree cultivation make it an essential industry globally.
However, we must also be mindful of the concerns and challenges that come with rubber tree cultivation, such as latex allergies, pest management, environmental impact, and the finite lifespan of latex production. By addressing these challenges with proper precautions, sustainable practices, and responsible management, we can navigate them effectively.
In conclusion, rubber trees have a significant place in the plant world, offering not only aesthetic appeal but also economic and environmental benefits. Whether you choose to grow them for their beauty, their rubber production potential, or their air-purifying properties, rubber trees can bring joy, sustainability, and a touch of nature to your life.
So, why not embark on a rubber tree journey of your own? With proper knowledge, care, and a little bit of green-thumb magic, you can cultivate these fascinating trees and enjoy the many benefits they have to offer.