Home>Gardening Techniques>Seasonal Gardening>What Temperature Is Too Cold For Seedlings


Seasonal Gardening
What Temperature Is Too Cold For Seedlings
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the ideal temperature for seedlings with our seasonal gardening guide. Don't let your seedlings freeze - learn what temperature is too cold for seedlings.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Factors Affecting Seedling Growth
- The Importance of Temperature for Seedlings
- Optimal Temperature Range for Seedling Growth
- Low-Temperature Stress on Seedlings
- How Cold Temperature Affects Seedling Development
- Signs of Cold Stress in Seedlings
- Strategies to Protect Seedlings from Cold Temperatures
- Tips for Germinating Seedlings in Cool Conditions
- Conclusion
Introduction
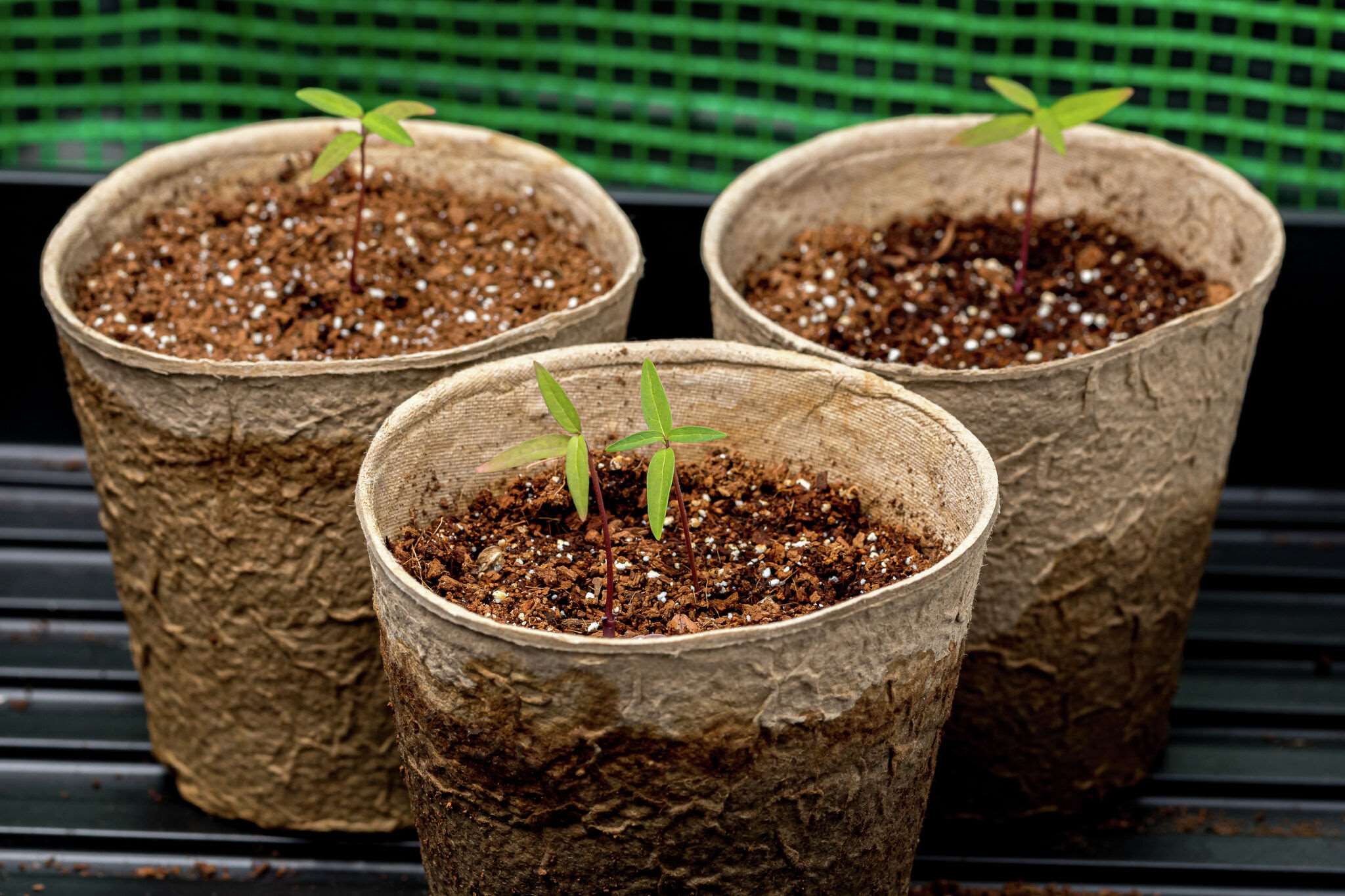
When it comes to seasonal gardening, understanding the temperature requirements for seedlings is crucial for successful growth and development. Seedlings are delicate and vulnerable to changes in temperature, and extreme cold can be detrimental to their survival. As a seasonal gardener, it’s important to know what temperature is too cold for seedlings and how to protect them from adverse weather conditions.
Seedlings are the young, tender plants that are just starting their journey to become mature plants. They are particularly susceptible to fluctuations in temperature, as they have not yet developed robust root systems to absorb nutrients and water effectively. Moreover, their small size makes them more prone to heat loss and damage from harsh conditions.
Understanding the factors that affect seedling growth is essential for creating a suitable environment for their development. Factors such as moisture, light, soil quality, and temperature all play a significant role in determining the success of your seedlings. While we often focus on providing adequate moisture and light, it’s important not to overlook the impact of temperature on seedling health.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of temperature for seedlings, the optimal temperature range for their growth, the effects of cold temperatures on seedling development, and strategies to protect seedlings from low-temperature stress. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of how temperature impacts seedling growth and the necessary steps to ensure their well-being.
Factors Affecting Seedling Growth
Several factors influence the growth and development of seedlings. By understanding these factors, you can create an ideal environment that promotes healthy seedling growth. Let’s explore some of the key factors:
- Moisture: Adequate moisture is essential for seed germination and the establishment of healthy seedlings. It provides the necessary hydration for seedlings to uptake nutrients from the soil. Insufficient moisture can lead to stunted growth and even death of the seedlings.
- Light: Seedlings rely on light for photosynthesis, which is crucial for energy production and growth. Providing sufficient light to seedlings is vital, as insufficient light can result in weak and leggy growth.
- Soil quality: The quality of the soil determines the availability of nutrients and water to seedlings. Well-draining soil with good fertility provides a conducive environment for root development and nutrient uptake.
- Air circulation: Proper air circulation is important for seedling health. Stagnant air can lead to mold and disease issues, while a gentle breeze promotes strong stem growth and prevents fungal infections.
- Temperature: The temperature plays a significant role in seedling growth and development. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can cause stress and negatively impact the seedlings’ health.
While all these factors are essential, in this article, we will focus on the temperature requirements for seedlings and how to manage temperature fluctuations to ensure their success.
The Importance of Temperature for Seedlings
Temperature is a critical factor that directly influences seedling growth and development. The right temperature range is essential for optimal germination, root growth, leaf expansion, and overall plant vigor. Understanding the importance of temperature for seedlings can help you create the ideal growing conditions for their success.
Temperature affects various physiological processes in seedlings. It influences the rate of seed germination, enzymatic activity, nutrient uptake, and photosynthesis. When the temperature is within the suitable range, these processes occur efficiently, leading to healthy seedling growth.
Seedlings have specific temperature requirements that vary by plant species. Some plants thrive in warmer temperatures, while others prefer cooler conditions. It’s important to research and understand the specific temperature preferences of the seedlings you are cultivating.
Temperature also affects the speed of plant growth. Warmer temperatures generally promote faster growth, while cooler temperatures slow down growth. Balancing the rate of growth is crucial to avoid weak and spindly seedlings that are prone to disease and damage.
Additionally, temperature plays a vital role in determining the development of the root system. Cool temperatures can delay root growth, resulting in limited nutrient and water absorption. On the other hand, excessively high temperatures can inhibit root development and lead to shallow roots that are susceptible to drought stress.
By providing the right temperature conditions, you can optimize the growth and development of your seedlings. It’s important to maintain a balance between warmth and coolness, ensuring that the seedlings are not exposed to extreme temperature fluctuations that can cause stress and hinder their growth.
Understanding the importance of temperature for seedlings allows you to make informed decisions about where and when to start your seeds and how to provide the ideal growing conditions. With the right temperature management, you can set your seedlings up for success and create a strong foundation for a fruitful growing season.
Optimal Temperature Range for Seedling Growth
Each plant species has its own preferred temperature range for optimal seedling growth. Understanding the optimal temperature range for your specific seedlings is crucial to ensure their healthy development. Here are some general guidelines:
- Warm-season seedlings: Warm-season plants, such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers, thrive in temperatures between 70°F (21°C) and 85°F (29°C) during the day. Nighttime temperatures should ideally be around 60°F (15°C) to 70°F (21°C).
- Cool-season seedlings: Cool-season crops, including lettuce, spinach, and kale, prefer cooler temperatures. They perform best with daytime temperatures around 60°F (15°C) to 70°F (21°C) and nighttime temperatures between 50°F (10°C) and 60°F (15°C).
- Some plants tolerate colder temperatures: Certain hardy plants, like cabbage, broccoli, and onions, can withstand even lower temperatures. They can tolerate daytime temperatures as low as 50°F (10°C) and nighttime temperatures around 40°F (4°C).
It’s crucial to monitor the temperature fluctuations both indoors and outdoors, as seedlings can be sensitive to sudden changes. Investing in a thermometer or using weather monitoring tools can help you track the temperature accurately.
Keep in mind that providing a consistent temperature range within the plant’s preferred range is essential for fostering healthy growth. Fluctuating temperatures can cause stress and affect seedling vigor. If the temperature consistently falls outside the optimal range, it may be necessary to adjust your growing methods, such as using heat mats or cold frames, to provide the necessary conditions.
Understanding the optimal temperature range for seedling growth allows you to make informed decisions about when to start your seeds and how to create the ideal environment for their success. By providing the right temperature conditions, you can promote vigorous growth, strong root development, and ultimately, increase the chances of your seedlings thriving.
Low-Temperature Stress on Seedlings
Low temperatures can pose significant challenges for seedlings and have detrimental effects on their growth and overall health. When exposed to cold temperatures, seedlings can experience various forms of stress. Understanding the impact of low-temperature stress is crucial for implementing strategies to protect your seedlings.
One common form of low-temperature stress is chilling injury. Chilling injury occurs when seedlings are exposed to temperatures below their optimal range, typically between 32°F (0°C) and 50°F (10°C). Chilling injury can result in cell damage, inhibited growth, and even death of the seedlings.
In addition to cell damage, cold temperatures can also affect the seedlings’ metabolic processes. While some metabolic activities slow down in colder conditions, others may be disrupted entirely. These disruptions can lead to nutrient deficiencies and imbalances, hindering the seedlings’ growth and development.
Cold temperatures can also affect the seedling’s water uptake and transpiration processes. In colder conditions, root activity decreases, resulting in reduced water absorption. As a result, seedlings may experience water stress, further impacting their growth and overall vigor.
Furthermore, cold temperatures can lead to poor nutrient uptake and utilization. Nutrient absorption and metabolic processes are generally slower in low-temperature conditions, leading to deficiencies and imbalances in essential nutrients. This can result in yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and decreased plant vitality.
Seedlings that experience prolonged exposure to cold temperatures may exhibit delayed growth and development. The chilling effects can cause dormancy, inhibiting their ability to grow and thrive. In extreme cases, seedlings may fail to recover from the cold stress, leading to their ultimate demise.
It’s important to note that different plant species have varying degrees of tolerance to cold temperatures. Some seedlings are more resilient and can withstand low temperatures for short periods, while others are highly sensitive and require careful protection.
By understanding the potential effects of low-temperature stress on seedlings, you can take proactive measures to protect them and minimize the risk of damage. Implementing strategies such as providing adequate insulation, utilizing protective coverings, and adjusting planting times can help mitigate the impact of cold temperatures on your seedlings.
How Cold Temperature Affects Seedling Development
Cold temperatures can severely impact seedling development, affecting various physiological processes essential for their growth and survival. Understanding how cold temperatures affect seedlings can help you take necessary precautions to protect them from potential damage.
One of the primary ways cold temperatures affect seedling development is by inhibiting germination. When temperatures drop below a certain threshold, it can slow down or even prevent seed germination altogether. The cold temperature interferes with the metabolic processes required for the seed to break dormancy and start the germination process.
Cold temperatures can also impede root growth in seedlings. Roots are responsible for nutrient and water uptake, as well as providing stability to the plant. When exposed to cold conditions, root growth slows down, limiting nutrient and water absorption. This can lead to nutritional deficiencies and hinder overall seedling development.
Cold temperature stress can also negatively impact photosynthesis, a vital process for seedling growth. As temperatures decrease, the rate of photosynthesis decreases as well. Reduced photosynthesis leads to a decrease in energy production, resulting in poor plant growth and weakened seedlings.
Additionally, cold temperatures can cause cellular damage to seedlings. Ice crystals may form within the plant cells, causing them to rupture and disrupt cellular structures. This can lead to cell death and irreversible damage to the seedlings.
Furthermore, cold temperatures can affect the hormone balance within seedlings. Hormones play a crucial role in regulating plant growth and development. Cold temperatures can disrupt hormone production and signaling, resulting in abnormal growth patterns and decreased seedling vigor.
Seedlings exposed to prolonged periods of cold temperatures may also exhibit delayed growth and development. The chilling effects can induce dormancy and restrict the seedlings’ ability to reach their full potential. In extreme cases, seedlings may fail to recover from the cold stress and may not survive.
Understanding how cold temperatures affect seedling development allows you to anticipate potential challenges and take preventative measures. By providing appropriate protection and ensuring that seedlings are not exposed to prolonged periods of extreme cold, you can help promote healthy seedling growth and increase their chances of thriving.
Signs of Cold Stress in Seedlings
Cold stress can manifest in various ways in seedlings, and recognizing the signs of cold stress is crucial for taking timely actions to protect your plants. By observing these signs, you can address the issue promptly and minimize the potential damage caused by low temperatures.
One common sign of cold stress in seedlings is stunted growth. Cold temperatures can hinder the plant’s metabolic processes and slow down its growth rate. As a result, seedlings may appear smaller and underdeveloped compared to their counterparts in more favorable conditions.
Another noticeable sign is discoloration of the leaves. Cold stress can cause yellowing or browning of the leaves, particularly around the edges. This discoloration may indicate nutrient deficiencies or reduced chlorophyll production due to the slowed metabolic activity caused by the cold.
In some cases, cold stress can cause the seedlings to exhibit a purplish or reddish coloration. This discoloration is often a result of the accumulation of pigments called anthocyanins, which are produced as a protective response to the cold stress. While the presence of these pigments does provide some level of protection, it also signifies that the plant is experiencing stress.
Frost damage is another visible sign of cold stress. When seedlings are exposed to freezing temperatures, ice crystals can form on the plant’s tissues, causing physical damage. This can result in wilted and blackened foliage, with the affected parts becoming slimy or mushy to the touch.
In severe cases, cold stress can lead to the death of the seedlings. If the temperatures drop to extremely low levels or if the seedlings experience prolonged exposure to cold conditions, they may fail to recover and perish. In such cases, the seedlings may become limp, shriveled, and eventually wither away.
It’s important to note that different plant species have different levels of tolerance to cold temperatures. Some seedlings may show signs of stress more quickly and be more susceptible to damage than others. Understanding the specific requirements and sensitivities of the seedlings you are growing will help you recognize signs of cold stress more accurately.
By being observant and regularly inspecting your seedlings, you can identify the signs of cold stress early on and take necessary measures to mitigate the damage. Prompt actions, such as providing protective coverings, adjusting temperature controls, or relocating seedlings to a warmer area, can help alleviate the stress and improve the chances of seedling survival.
Strategies to Protect Seedlings from Cold Temperatures
Protecting seedlings from cold temperatures is crucial to ensure their survival and promote healthy growth. By implementing effective strategies, you can create a favorable environment for seedlings and shield them from the damaging effects of low temperatures. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Start seeds indoors: Starting seeds indoors allows you to have better control over temperature conditions. It gives seedlings a head start and allows them to establish a stronger root system before being exposed to outdoor conditions.
- Use protective coverings: Protective coverings such as row covers, frost blankets, and cold frames can help create a microclimate around the seedlings, shielding them from cold winds and extreme temperatures.
- Provide insulation: Adding a layer of mulch around the seedlings can help insulate the soil and retain heat. Mulch acts as a protective barrier, preventing rapid temperature fluctuations and providing insulation for the roots.
- Utilize heat sources: Using heat sources like heat mats or portable heaters in greenhouse or indoor growing environments can provide supplemental warmth to seedlings. These heat sources help maintain a consistent temperature range, particularly during cold nights.
- Adjust planting times: Timing your seedling planting can also help protect them from cold temperatures. Delaying planting until after the last frost date or starting seeds earlier indoors can minimize the risk of exposing seedlings to extreme cold conditions.
- Choose cold-tolerant varieties: Selecting plant varieties that are known for their cold tolerance can increase the chances of seedling survival. These varieties are adapted to withstand lower temperatures and are better equipped to endure cold stress.
- Monitor weather conditions: Stay informed about weather forecasts, especially during critical periods when seedlings are vulnerable. By keeping an eye on changing weather conditions, you can take proactive measures to protect your seedlings in advance.
Implementing a combination of these strategies can greatly improve the chances of your seedlings surviving and thriving in cold temperatures. Remember to tailor the methods to fit the specific needs of your seedlings and the environmental conditions in your area.
By taking proactive steps to protect seedlings from cold temperatures, you can ensure a successful growing season and enjoy healthy, robust plants in your garden.
Tips for Germinating Seedlings in Cool Conditions
Gardening in cool conditions requires special attention to ensure successful seed germination. Cool temperatures can pose challenges for seedlings, but with the right strategies, you can increase the likelihood of successful germination and healthy seedling development. Here are some tips to help you germinate seedlings in cool conditions:
- Pre-warm the soil: Before sowing seeds, warm up the soil using techniques like applying black plastic mulch or utilizing cold frames. This helps create a warmer microclimate for the seeds.
- Use bottom heat: Providing bottom heat to germinating seed trays can encourage faster and more uniform germination. Heat mats or propagators can maintain the optimum temperature range for seed germination.
- Protect seed trays: Covering seed trays with plastic wrap or using a plastic dome helps retain heat and moisture, creating ideal conditions for germination.
- Choose quick-maturing varieties: Selecting varieties with shorter maturity times can increase the chances of successful seed germination and growth, especially in cooler conditions.
- Soak seeds before planting: Soaking seeds in warm water before planting can help soften the seed coat and may expedite germination.
- Provide ample light: Even in cool conditions, seedlings need sufficient light for healthy growth. Ensure they receive at least 12-14 hours of bright light daily through the use of grow lights if natural sunlight is limited.
- Monitor soil moisture: Keep the soil consistently moist, but avoid overwatering which can lead to damping-off disease. Use a spray bottle or misting system to provide gentle moisture to the seedlings.
- Adjust planting depths: Plant seeds slightly shallower in cool conditions as the germination process may take longer. Check the specific planting depth recommendations for each seed variety.
- Protect from frost: Be cautious of late frosts in cool conditions. Covering seedlings with protective fabric or temporarily moving them indoors can safeguard against frost damage.
- Prioritize air circulation: Proper air circulation is crucial to prevent fungal diseases. Use a fan on low speed or carefully open vents in cold frames or greenhouses to ensure adequate airflow.
By implementing these tips, you can optimize seed germination and promote healthy seedling development, even in cool conditions. Remember to monitor the progress of your seedlings closely and make adjustments as needed to ensure their success and resilience.
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of temperature on seedlings is essential for successful seasonal gardening. Cold temperatures can pose challenges for seedling growth and development, but with proper knowledge and strategies, you can protect your seedlings and set them up for a fruitful growing season.
Factors such as moisture, light, soil quality, and air circulation all play a significant role in seedling growth. However, temperature is a critical factor that directly influences seedling health and vitality. Providing the optimal temperature range for your seedlings promotes efficient germination, root development, leaf expansion, and overall plant vigor.
Low temperatures and cold stress can have detrimental effects on seedlings, including stunted growth, discoloration, reduced metabolic activity, water and nutrient imbalances, and, in severe cases, plant death. Understanding the signs of cold stress is crucial for taking timely actions to protect your seedlings and minimize damage.
Implementing strategies such as starting seeds indoors, using protective coverings, providing insulation, utilizing heat sources, adjusting planting times, and selecting cold-tolerant varieties can help protect seedlings from cold temperatures. Regularly monitoring weather conditions and observing seedlings for signs of stress allows for proactive measures to be taken before any significant damage occurs.
When germinating seedlings in cool conditions, pre-warming the soil, using bottom heat, protecting seed trays, choosing quick-maturing varieties, providing ample light, monitoring soil moisture, adjusting planting depths, protecting from frost, and ensuring proper air circulation are all key considerations to promote successful germination and healthy seedling growth.
By incorporating these practices and understanding the unique temperature requirements of your seedlings, you can cultivate a thriving garden, even in the face of challenging seasonal temperatures. With proper care and attention, your seedlings will flourish and set the stage for a bountiful harvest.