Home>Gardening Basics>Tools and Equipment>When Should You Turn Off Irrigation System


Tools and Equipment
When Should You Turn Off Irrigation System
Published: November 17, 2023
Learn when to turn off your irrigation system with our comprehensive guide. Get expert advice on maintaining your tools and equipment for optimal efficiency.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding Irrigation Systems
Welcome to the world of irrigation systems! Whether you are a homeowner with a lush garden or a farmer tending to your crops, having a well-designed irrigation system is essential for maintaining healthy plants and maximizing their growth potential. An irrigation system is a network of pipes, valves, sprinklers, and other components that delivers water to plants on a regular basis. By providing water directly to the root zone, irrigation systems ensure that plants receive the right amount of moisture, helping them thrive and produce a bountiful harvest.
However, it’s important to strike a balance in watering your plants. Too much water can lead to waterlogged soil, root rot, and nutrient leaching, while too little water can result in wilting, stunted growth, and reduced yield. So, when should you turn off your irrigation system? This article will explore the various factors to consider in order to make an informed decision.
Understanding Irrigation Systems
Irrigation systems are a crucial tool for providing plants with the water they need to thrive. They come in various types, including drip irrigation, sprinkler systems, and soaker hoses, each suited to different applications and plant needs.
Drip irrigation delivers water slowly and directly to the plant’s root zone, minimizing evaporation and ensuring efficient water use. Sprinkler systems, on the other hand, distribute water through a network of sprinkler heads, mimicking natural rainfall. Soaker hoses release water along their length, allowing for deep root penetration.
When designing an irrigation system, it’s important to consider factors such as water source, water pressure, and the specific needs of your plants. Proper installation and maintenance are essential to ensure the system operates effectively and efficiently. Regular inspections of valves, pipes, and sprinkler heads can prevent leaks and ensure even distribution of water.
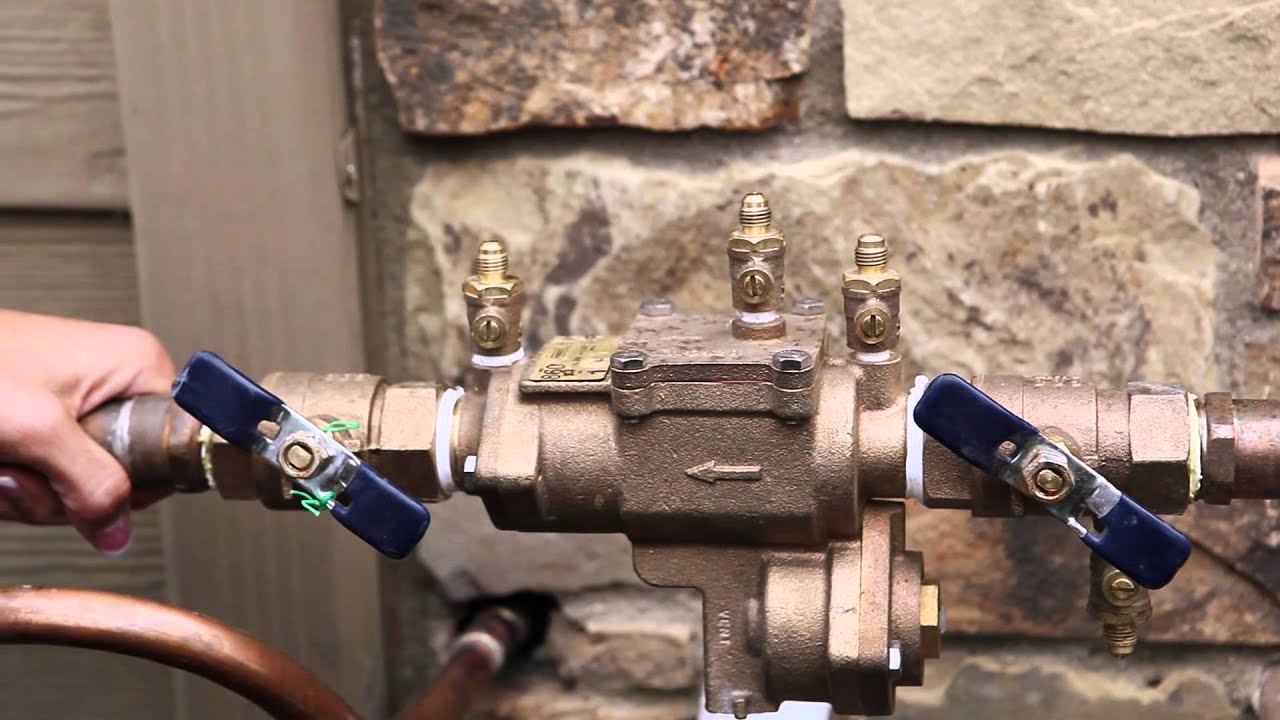
An understanding of the different components of an irrigation system is crucial. Valves control the flow of water, while timers automate the irrigation schedule. Filters remove debris and prevent clogging, and backflow preventers protect the water supply from contamination.
Controllers allow you to set watering schedules and adjust for seasonal changes. The choice of controller will depend on the complexity of your system and your specific needs. Some controllers even have weather sensors that adjust watering based on rainfall and soil moisture levels.
It’s important to note that irrigation systems are not a one-size-fits-all solution. The water needs of plants vary depending on factors such as their species, stage of growth, and environmental conditions. It’s essential to research the watering requirements of your specific plants to ensure they receive the optimal amount of water.
Understanding the purpose and functionality of irrigation systems is the first step towards effectively managing the watering needs of your plants. By providing the right amount of water at the right time, irrigation systems can help maintain healthy and vibrant gardens.
Factors to Consider
When deciding when to turn off your irrigation system, there are several important factors to consider. By evaluating these factors, you can ensure that your plants receive the appropriate amount of water, promoting their overall health and reducing the risk of overwatering or underwatering.
#### Seasonal Changes
One of the primary factors to consider is the seasonal changes that occur throughout the year. Different seasons bring varying weather conditions and temperature fluctuations, which affect the water requirements of your plants. For example, during the hot summer months, plants may require more frequent watering due to increased evaporation and higher temperatures. Conversely, during the cooler and wetter months, plants may need less water as soil moisture levels naturally increase.
#### Rainfall Amounts
Monitoring rainfall amounts is crucial when determining the watering needs of your plants. If you live in an area that receives regular and substantial rainfall, it may be unnecessary to run your irrigation system. However, in drier regions or during periods of drought, supplementing rainfall with irrigation may be necessary to maintain adequate moisture levels.
#### Soil Moisture Levels
Understanding the moisture levels in your soil is fundamental in deciding when to turn off your irrigation system. Overwatered plants can develop root rot, while underwatered plants can experience stress and wilt. Use a soil moisture meter or simply dig a small hole to assess the moisture content. If the soil is consistently moist, it may be time to give your irrigation system a break.
#### Plant Types and Watering Needs
Different plants have varying watering needs. Some plants, such as succulents and cacti, are well-adapted to arid conditions and can tolerate drought. On the other hand, plants with shallow root systems or those that are in the early stages of growth may require more frequent watering. Research the specific watering requirements of your plants to ensure you meet their individual needs.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision about when to turn off your irrigation system. This will not only conserve water but also prevent potential issues associated with overwatering or underwatering your plants.
Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes play a significant role in determining when to turn off your irrigation system. As the weather shifts throughout the year, the water requirements of your plants will naturally fluctuate. Understanding these seasonal changes will help you adjust your irrigation schedule accordingly.
#### Spring
Spring is a season of growth and renewal for plants. As temperatures rise, plants begin to emerge from their dormant state and actively grow. During this time, it’s important to gradually increase the frequency and duration of irrigation to support the plants’ developing root systems. Keep an eye on the weather and adjust your irrigation schedule accordingly, considering factors such as rainfall and temperature.
#### Summer
Summer is typically characterized by hot and dry conditions. The increased evaporation and higher temperatures during this season can lead to faster moisture evaporation from the soil. As a result, your plants may require more frequent watering. Monitor soil moisture levels and consider watering during the cooler parts of the day, such as early morning or late evening, to reduce water loss due to evaporation.
#### Fall
In fall, temperatures begin to cool down, and plants enter a period of dormancy. During this time, plants require less water as their growth slows down. Monitor rainfall and adjust your irrigation schedule accordingly. As the leaves fall, clear them away from your irrigation system components to prevent clogging or damage.
#### Winter
Winter is a time of rest for most plants. Precipitation levels tend to increase during this season, providing natural moisture to the soil. In regions where winters have mild temperatures and occasional frosts, occasional irrigation may still be necessary to ensure the soil does not dry out completely. However, in areas with freezing temperatures or heavy snowfall, it is best to turn off your irrigation system and protect it from potential damage caused by freezing water.
By staying attuned to the seasonal changes and adjusting your irrigation system accordingly, you can ensure that your plants receive the right amount of water throughout the year. This will help promote healthy plant growth and conserve water resources.
Rainfall Amounts
Rainfall plays a crucial role in determining when to turn off your irrigation system. Monitoring the amount of rainfall your area receives is essential for making informed decisions about watering your plants. By keeping track of rainfall amounts, you can avoid overwatering and conserve water resources.
#### Regular Rainfall
If you live in an area that receives regular and substantial rainfall, it may not be necessary to run your irrigation system frequently or at all. Assess the rainfall patterns in your region and consider the average rainfall amounts. If the soil consistently remains moist and your plants appear healthy, you can turn off your irrigation system and rely on natural rainfall to meet the water requirements of your plants.
#### Dry and Drought Conditions
In regions where drought or dry spells are common, supplementing rainfall with irrigation is necessary to ensure the health and survival of your plants. In such cases, it’s important to closely monitor rainfall amounts and soil moisture levels. If rainfall is limited or insufficient to meet the water needs of your plants, continue using your irrigation system as needed to provide the necessary moisture.
#### Seasonal Rainfall Variations
Seasonal variations in rainfall also impact the watering needs of your plants. For example, during the rainy season, you might have to reduce the frequency and duration of your irrigation cycles to avoid waterlogging the soil. On the other hand, during dry seasons or periods of low rainfall, you may need to increase irrigation to compensate for the lack of moisture in the soil.
#### Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is an eco-friendly practice that allows you to collect and store rainwater for later use. By implementing rainwater harvesting systems, you can reduce your reliance on municipal water supplies and effectively use rainwater to irrigate your plants. By utilizing this stored rainwater during dry periods, you can further conserve water resources and minimize the need for excessive irrigation.
By understanding the rainfall amounts in your area and adjusting your irrigation system accordingly, you can ensure that your plants receive the appropriate amount of water. This not only promotes plant health and growth but also helps to conserve water resources and reduce your overall water consumption.
Soil Moisture Levels
Monitoring soil moisture levels is crucial for determining when to turn off your irrigation system. Proper moisture management is essential to ensure the health and well-being of your plants. By understanding the moisture content of the soil, you can avoid overwatering or underwatering your plants, promoting their overall growth and vitality.
#### Assessing Soil Moisture
There are several methods to assess soil moisture levels. One common approach is to use a soil moisture meter, which provides a quantified reading of the moisture content in the soil. Simply insert the probe into the soil and read the moisture level indicated on the meter. This can help you determine whether the soil is adequately moist or if additional irrigation is necessary.
#### Visual Inspection
In addition to using a soil moisture meter, a visual inspection of the soil can also provide valuable information about its moisture content. If the soil appears dark and feels damp to the touch, it is an indication of sufficient moisture. However, if the soil appears light in color and feels dry, it may be an indication that your plants require watering.
#### Monitoring Plant Health
The health and appearance of your plants can also serve as indicators of soil moisture levels. Overwatered plants may exhibit signs of root rot, such as wilting, yellowing leaves, or the presence of fungi. On the other hand, underwatered plants may appear wilted, with dry and brittle leaves. Monitoring these visual cues can help you determine if your plants require additional watering or if it’s time to turn off your irrigation system.
#### Consider Different Soil Types
It’s important to note that different soil types have varying water-holding capacities. Sandy soils tend to drain water quickly, requiring more frequent watering, while clay soils retain moisture for longer periods, requiring less frequent irrigation. Understanding your soil type and its unique characteristics will help you determine the appropriate watering schedule for your plants.
#### Irrigation Strategies
Understanding soil moisture levels will help you develop effective irrigation strategies. If the soil is consistently moist, it’s a sign that your plants are receiving sufficient water, and you can consider turning off your irrigation system temporarily. However, if the soil is dry or moisture levels are too low, it’s an indication that your plants need additional irrigation to thrive.
By monitoring soil moisture levels, you can ensure that your plants receive the ideal amount of water. Finding the right balance will support their growth and minimize the risk of water-related problems, such as root rot or drought stress.
Plant Types and Watering Needs
Understanding the watering needs of different plant types is essential when deciding when to turn off your irrigation system. Different plants have varying water requirements based on factors such as their species, stage of growth, and environmental conditions. By considering these factors, you can ensure that your plants receive the right amount of water to thrive.
#### Researching Plant Watering Requirements
Before planting new vegetation or maintaining existing ones, it’s crucial to research and understand the specific watering needs of each plant species. Some plants, such as cacti and succulents, have adapted to arid conditions and require infrequent watering. On the other hand, plants with shallow root systems or those in the early stages of growth may require more frequent irrigation to establish strong root systems.
#### Matching Watering Frequency
The watering frequency and duration should align with the specific needs of your plants. For example, drought-tolerant plants may only require watering once a week, while plants with high water needs might need to be watered multiple times a week. Additionally, potted plants tend to dry out faster than those planted in the ground, so they may need more frequent watering.
#### Adjusting Watering Based on Growth Stage
Plants have different water requirements at various stages of growth. Newly planted seedlings require more frequent and gentle irrigation to help them establish strong root systems. Once established, they can transition to a regular watering schedule based on the specific needs of their species. Flowering plants may require additional water during blooming to support healthy flower production.
#### Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to sunlight can also influence the water needs of your plants. In hot and dry climates, plants may require more frequent watering to combat evaporation and aid in regulating their temperature. Take into account the prevailing weather conditions and adjust your irrigation system accordingly.
#### Observing Plant Response
Monitoring the health and appearance of your plants is crucial in determining their watering needs. Signs of dehydration, such as wilted or drooping leaves, are indicators that the plants require more water. Conversely, if the plants show signs of overwatering, such as yellowing leaves or root rot, it may be necessary to reduce or temporarily turn off the irrigation system.
By understanding the unique watering needs of your plants, you can tailor the irrigation schedule to meet their specific requirements. This not only promotes healthy growth but also conserves water resources by avoiding unnecessary irrigation.
Signs of Overwatering
Overwatering is a common mistake that can detrimentally affect the health and vitality of your plants. Knowing the signs of overwatering is essential for identifying and addressing this issue promptly. By recognizing these signs, you can adjust your irrigation practices and prevent further damage to your plants.
#### Wilting
Ironically, one of the most common signs of overwatering is wilting. Overwatered plants may exhibit wilting because their roots are suffocating due to excessive moisture, which inhibits the absorption of nutrients. However, it’s important to differentiate between wilting caused by overwatering and wilting caused by underwatering or other factors, such as heat stress.
#### Yellowing or Dying Leaves
If your plants’ leaves are turning yellow or brown and are falling off, it may indicate overwatering. Excess moisture can lead to root rot or fungal diseases, resulting in leaf discoloration and decay. This typically occurs in the lower leaves first, progressing upward as the problem becomes more severe.
#### Mold or Fungus Growth
Overwatered soil creates a favorable environment for mold and fungus growth. If you notice a white, fuzzy substance or greenish mold on the surface of the soil or around the base of your plants, it is a strong indication of excessive moisture. These fungal growths can prevent proper airflow and further damage the roots.
#### Slow Growth and Root Health
Overwatering can lead to stunted growth and poor root health. When the soil is constantly saturated, it deprives plants of the oxygen needed for root development. You may notice that the plant’s overall growth is slower than usual, and upon inspection, the roots may appear mushy, discolored, or have a foul odor.
#### Pests and Disease Infestation
Overwatered plants are more susceptible to pests and diseases. Excessive moisture weakens plant defenses and attracts unwanted visitors, such as aphids, slugs, and plant-attacking bacteria. If you notice an increase in pest activity or signs of disease, it could be a result of overwatering.
#### Waterlogged Soil
Another clear sign of overwatering is waterlogged soil. If the soil feels constantly wet or muddy, even days after watering, it means that the soil is not draining properly and is retaining too much water. This can lead to oxygen deprivation and root suffocation.
When you observe signs of overwatering, it’s crucial to adjust your irrigation practices accordingly. Allow the soil to dry out before watering again and consider improving drainage in the affected areas. Remember, watering should always be based on the specific needs of your plants and not on a predetermined schedule.
Signs of Underwatering
Underwatering can have detrimental effects on the health and vitality of your plants. It’s essential to recognize the signs of underwatering to promptly address the issue and prevent further damage. By understanding these signs, you can adjust your watering practices and ensure your plants receive adequate moisture.
#### Wilting
Wilting is one of the most obvious signs of underwatering. When plants don’t receive enough water, they are unable to maintain turgidity, causing their leaves and stems to droop. However, it’s important to differentiate between wilting caused by underwatering and other factors, such as overwatering or heat stress.
#### Dry and Cracked Soil
Underwatering often leads to dry and cracked soil. If the soil feels dry to the touch and pulls away from the sides of the pot or forms cracks, it indicates insufficient moisture. Dry soil can inhibit nutrient uptake and restrict root growth, impacting the overall health of your plants.
#### Yellowing or Browning of Leaves
Leaves turning yellow or brown can be a sign of underwatering. When plants lack water, they prioritize survival over growth, causing leaves to change color as a result of stress. If the problem persists, the leaves may eventually wither, dry out, and fall off.
#### Stunted Growth
Insufficient water supply can stunt a plant’s growth. When plants receive inadequate moisture, their growth rate slows down, and they may appear smaller or less developed compared to healthy plants. Leaves and stems may also be smaller and less vibrant.
#### Dry and Brittle Leaves
Underwatered plants often develop dry and brittle leaves. When there is a lack of water, the leaves lose moisture and become dehydrated, resulting in a crispy or papery texture. This can also make the leaves more prone to damage from environmental stressors.
#### Increased Wilting in Heat
Underwatered plants are more susceptible to wilting in high temperatures. When exposed to hot climates, plants transpire more and require additional water to prevent dehydration. If your plants wilt excessively in the heat, it could be an indication that they are not receiving enough water.
#### Slow Recovery after Watering
Underwatered plants often have a slower recovery time after receiving water. If you notice that your plants don’t bounce back quickly after watering, it may be an indication they are not getting enough water. This can be due to root damage or the plant’s inability to uptake water efficiently.
When you observe signs of underwatering, it’s important to adjust your watering practices accordingly. Ensure that your plants receive adequate water by adjusting the frequency and volume of watering, and monitor soil moisture levels to maintain optimal hydration for your plants.
Benefits of Turning Off Irrigation System
While irrigation systems are essential for providing water to plants, there are several benefits to turning off the system at appropriate times. By knowing when to give your irrigation system a break, you can conserve water, save money, and promote a healthier and more sustainable garden.
#### Water Conservation
One of the primary benefits of turning off your irrigation system is water conservation. By only watering when necessary, you can minimize water waste and ensure responsible usage. This is particularly important in regions that experience water scarcity or where water restrictions are in place. Conserving water not only benefits your own garden but also contributes to the overall conservation of this precious resource.
#### Financial Savings
Reducing water usage by turning off your irrigation system can lead to financial savings. By conserving water, you can reduce your water bills and save money in the long run. Additionally, using water wisely aligns with sustainable practices and reduces the strain on local water supplies, potentially avoiding future price increases or fines for excessive water consumption.
#### Environmental Impact
By practicing responsible irrigation habits and turning off your system when appropriate, you can reduce the environmental impact of your garden. Excessive water use can lead to runoff and water pollution, causing harm to local ecosystems and water bodies. By minimizing water use and preventing overwatering, you can help protect the environment and promote a healthier ecosystem.
#### Plant Health
Giving your plants periodic breaks from constant watering can actually promote healthier root development and overall plant growth. Allowing the soil to dry out between watering cycles encourages plants to develop deep and strong root systems, making them more resilient to drought conditions. This can result in more robust and healthier plants in the long run.
#### Disease Prevention
Constant moisture from overwatering can create a favorable environment for the development of plant diseases, such as root rot and fungal infections. By turning off your irrigation system and allowing the soil to dry out, you can reduce the likelihood of these diseases taking hold and impacting the health of your plants.
#### Improved Soil Structure
Over time, excessive irrigation can lead to compacted soil, reducing its ability to absorb water and nutrients effectively. By turning off your irrigation system and allowing the soil to naturally dry out, you can promote better soil structure, allowing for improved drainage and nutrient availability for your plants.
#### Supporting Native Plants and Pollinators
Turning off your irrigation system can also encourage the growth of native plants that are well-adapted to the local climate. These plants often require less water and support local pollinators and wildlife. By promoting the growth of native species, you can contribute to biodiversity and create a more ecologically friendly garden.
By turning off your irrigation system at appropriate times, you can reap these benefits and create a more sustainable and thriving garden environment.
When to Turn Off the Irrigation System
Deciding when to turn off your irrigation system requires careful consideration of various factors. While each garden and landscape is unique, there are general guidelines to help you determine the appropriate time to give your irrigation system a break.
#### Rainy Days and Periods
If there has been sufficient rainfall in your area, it may be a good time to turn off your irrigation system temporarily. Monitor the amount of rainfall and adjust your watering schedule accordingly. Taking advantage of natural precipitation can help conserve water and prevent overwatering your plants.
#### Soil Moisture Levels
Monitor the moisture content of the soil to determine when to turn off your irrigation system. Use a soil moisture meter or perform a simple visual and tactile inspection of the soil. If the soil feels consistently moist and the plants are showing no signs of wilting, it may be an indication that the irrigation system can be temporarily turned off.
#### Plant Needs and Growth Stage
Consider the specific needs of your plants and their growth stage when deciding when to turn off your irrigation system. Some plants, such as succulents and cacti, are adapted to arid conditions and can tolerate drought. Others may have different moisture requirements based on their growth stage or species. Research the watering needs of your plants and adjust your irrigation system accordingly.
#### Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes play a significant role in determining when to turn off your irrigation system. During cooler seasons or periods of lower evaporation rates, your plants may require less frequent watering. Conversely, during hot and dry summer months, you may need to continue with regular or increased watering to compensate for increased evaporation and higher water needs.
#### Evaluate Plant Health and Performance
Regularly assess the health and performance of your plants as an indicator of their watering needs. Underwatered plants may show signs of wilting, stunted growth, and dry soil. Conversely, overwatered plants may exhibit wilting, yellowing leaves, or signs of root rot. Adjust your irrigation system based on the specific needs of your plants and their overall health and performance.
#### Local Water Restrictions
Be aware of any local water restrictions or guidelines that may affect the use of your irrigation system. Some areas have specific regulations regarding watering schedules, especially during times of drought or water scarcity. Adhering to these restrictions not only ensures compliance with local regulations but also promotes responsible water usage.
#### Using Weather/Soil Moisture Sensors
Consider utilizing weather or soil moisture sensors to automatically control your irrigation system. These devices can provide real-time data on rainfall, temperature, and soil moisture levels, allowing for more accurate and efficient irrigation. With this technology, you can set parameters for when the system should turn on or off based on specific measurements, ensuring that you only irrigate when necessary.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can determine the appropriate timing to turn off your irrigation system. This will help conserve water, maintain the health of your plants, and promote more sustainable and efficient gardening practices.
Conclusion
Understanding when to turn off your irrigation system is crucial for maintaining the health and vitality of your plants while conserving water resources. By considering factors such as seasonal changes, rainfall amounts, soil moisture levels, plant types, and specific watering needs, you can make informed decisions about your irrigation practices.
Seasonal changes play a significant role in determining when to adjust your irrigation system. Different seasons bring varying weather patterns and temperature fluctuations, which affect the water requirements of your plants. Adapting your watering schedule to match these changes ensures optimal growing conditions.
< p >Monitoring rainfall amounts is essential in determining when to turn off your irrigation system temporarily. Sufficient rainfall can provide your plants with the moisture they need, reducing the need for additional watering. Conversely, during dry periods or in regions experiencing drought, supplemental irrigation may be necessary.
Checking soil moisture levels regularly is crucial in avoiding overwatering or underwatering your plants. Different soil types have different water-holding capacities, so understanding your soil composition is key. Assessing the moisture content of the soil using methods such as visual inspection or soil moisture meters helps you adjust watering frequencies accordingly.
Each plant has unique watering needs based on factors such as species, growth stage, and environmental conditions. Researching the specific watering requirements of your plants ensures that they receive the optimal amount of water for their growth and health.
Recognizing signs of overwatering and underwatering is essential for identifying watering issues before they cause significant damage. Wilting, leaf discoloration, fungus growth, stunted growth, and pest infestations are all signs to look out for. Adjusting your irrigation practices based on these signs helps maintain the health of your plants.
Turning off your irrigation system when appropriate offers several benefits. It conserves water resources, saves money on water bills, reduces environmental impact, promotes plant health and root development, prevents diseases, and improves soil structure. Additionally, supporting native plants and pollinators contributes to biodiversity and creates a more sustainable garden environment.
By carefully considering these factors and implementing responsible irrigation practices, you can strike a balance in providing your plants with the right amount of water while conserving water resources and promoting a healthy and vibrant garden.