Home>Gardening News and Trends>Latest News>Why Do You Blanch Vegetables Before Freezing


Latest News
Why Do You Blanch Vegetables Before Freezing
Modified: January 22, 2024
Discover the reasons behind blanching vegetables before freezing in the latest news. Preserve freshness and maintain nutrient content for longer storage.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding the Blanching Process
- The Importance of Blanching Vegetables Before Freezing
- Retaining Color and Texture Through Blanching
- Enzyme Inactivation and Microbial Safety
- Nutrient Preservation with Blanching
- Step-by-Step Guide to Blanching Vegetables Before Freezing
- Common Mistakes to Avoid While Blanching
- Alternative Methods to Blanching
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to preserving the freshness and flavor of vegetables for an extended period, freezing is a popular method. Freezing not only allows you to enjoy your favorite vegetables year-round, but it also helps minimize food waste. However, before you throw your vegetables into the freezer, it’s essential to blanch them.
Blanching involves briefly cooking vegetables in boiling water and then quickly cooling them in ice water. This process may seem like an unnecessary step, but it plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and safety of your frozen vegetables. By blanching, you can preserve the color, texture, flavor, and nutritional value of the vegetables during the freezing process.
In this article, we will delve into the reasons why blanching vegetables before freezing is so important. We will explore how blanching helps retain color and texture, ensures microbial safety, and preserves essential nutrients. Additionally, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide to blanching vegetables and discuss common mistakes to avoid. Furthermore, we will explore alternative methods you can try if blanching is not your preferred technique.
So, if you’re ready to enhance your freezing game and enjoy delicious, high-quality vegetables even when they are out of season, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets behind blanching vegetables before freezing!
Understanding the Blanching Process
Before we explore the reasons why blanching vegetables is crucial before freezing them, it’s essential to understand the blanching process itself. Blanching involves two key steps: boiling and cooling. Let’s break it down:
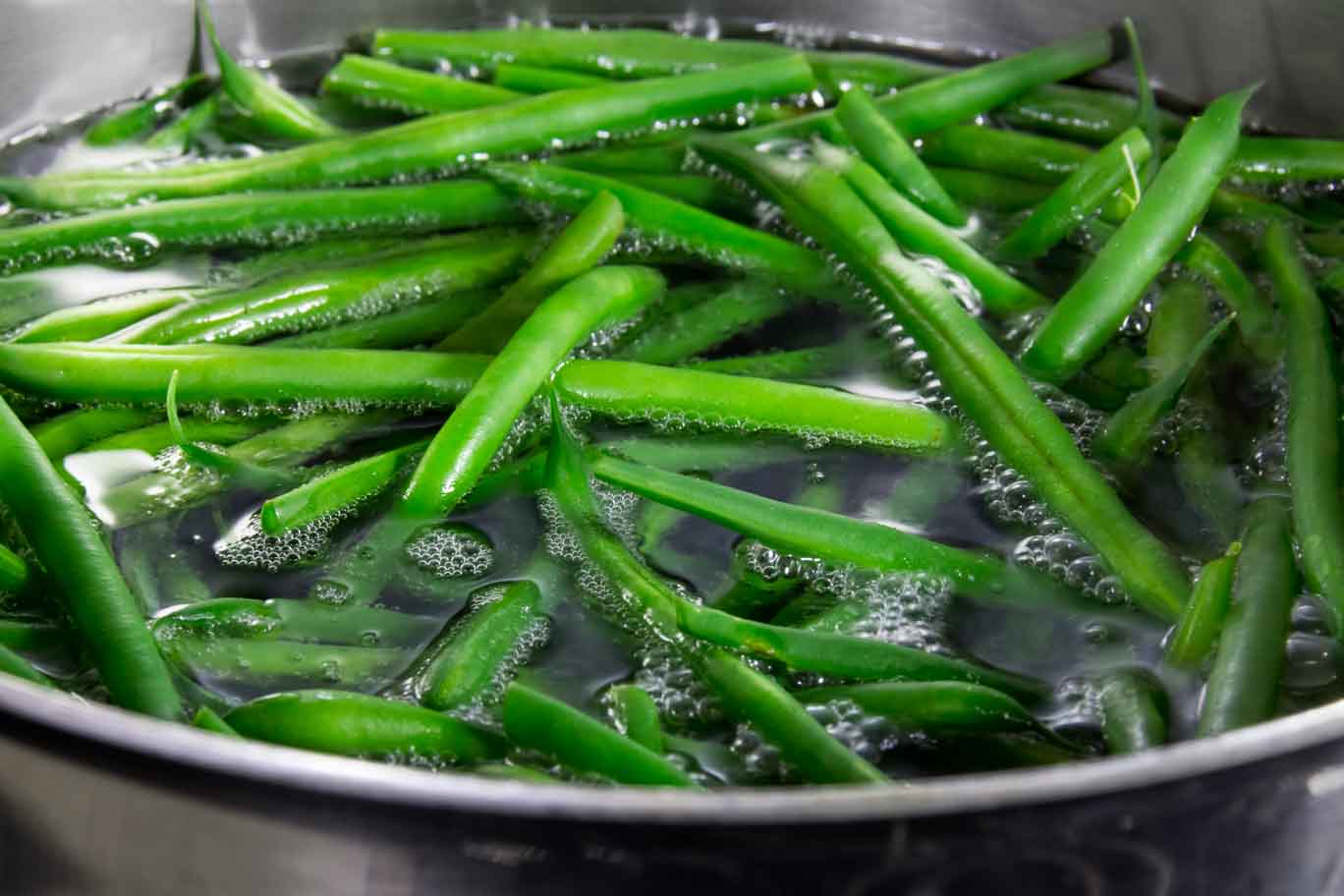
1. Boiling: The first step in blanching is to bring a pot of water to a rolling boil. The amount of water you use should be enough to submerge the vegetables completely. You may also add a small amount of salt to enhance the flavor, but it is purely optional.
2. Cooling: Once the vegetables have been blanched in boiling water for a specific amount of time, they must be rapidly cooled to stop the cooking process. This is achieved by transferring the vegetables into a bowl of ice water. The ice water helps maintain their vibrant color and crisp texture.
Blanching time may vary depending on the type of vegetable, its size, and whether it’s whole or cut. Generally, most vegetables require blanching times between one to five minutes. Blanching times for specific vegetables can be found in reputable sources or guides.
During the blanching process, several changes occur within the vegetables. The heat from boiling water activates enzymes present in the vegetables, which can lead to deterioration in color, texture, flavor, and nutritional quality over time. The rapid cooling step halts the enzyme activity, preserving the vegetable’s characteristics.
Additionally, blanching helps eliminate dirt, surface bacteria, and other microorganisms present on the vegetables. It reduces the risk of spoilage and foodborne illness during storage. By understanding the blanching process, you can ensure that you follow the correct steps to achieve optimal results.
Now that we have a good grasp on the blanching process, let’s explore why blanching vegetables is essential before freezing them.
The Importance of Blanching Vegetables Before Freezing
Blanching is a crucial step to ensure the quality, safety, and longevity of your frozen vegetables. Let’s examine why blanching is so important:
1. Retaining Color and Texture: Blanching helps preserve the vibrant color and appealing texture of vegetables. By quickly heating the vegetables, enzymes that cause loss of color, texture, and flavor are inactivated. The rapid cooling step prevents overcooking and helps maintain the natural firmness and crispness of the vegetables. As a result, when you thaw and cook your frozen vegetables, they will retain their brightness and texture, providing a delightful visual and sensory experience.
2. Ensuring Microbial Safety: Blanching helps eliminate surface bacteria and microorganisms that can lead to spoilage and foodborne illnesses. The brief exposure to boiling water effectively reduces the microbial load, ensuring that your frozen vegetables remain safe for consumption throughout their storage period. By blanching, you significantly reduce the risk of contamination and ensure that your vegetables stay fresh and safe to eat.
3. Nutrient Preservation: Blanching plays a crucial role in preserving the nutritional value of vegetables. While some loss of nutrients is inevitable during the blanching process, it is minimal compared to the potential nutrient degradation that can occur during freezing and prolonged storage. By blanching, you lock in the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants present in the vegetables, ensuring that they remain intact and available for your body’s nourishment when you consume them.
4. Enzyme Inactivation: Enzymes naturally present in vegetables can continue to cause chemical changes even at freezing temperatures. These changes can lead to loss of flavor, texture, and nutritional quality. Blanching effectively inactivates these enzymes, preserving the overall quality of the vegetables throughout their time in the freezer. By blanching, you minimize the degradation and maintain the natural characteristics of the vegetables.
5. Improved Freezer Storage: Properly blanched vegetables are less likely to develop freezer burn or become soggy and mushy during storage. The blanching process helps create a protective barrier around the vegetables, preventing moisture loss and maintaining their overall quality. By blanching, you enhance the freezing process, resulting in superior texture and taste when you eventually cook the vegetables.
As you can see, blanching plays a crucial role in ensuring that your frozen vegetables retain their color, texture, flavor, and nutritional value. By taking the time to blanch your vegetables before freezing, you can enjoy high-quality, delicious vegetables any time of the year.
Retaining Color and Texture Through Blanching
One of the primary reasons why blanching is a crucial step before freezing vegetables is its ability to help retain their color and texture. Let’s explore how blanching accomplishes this:
1. Enzyme Inactivation: Vegetables contain enzymes that are responsible for natural changes in color, texture, and flavor. These enzymes can continue to be active even at freezing temperatures, leading to deterioration of the vegetables. By blanching, the enzymes are quickly inactivated, preserving the natural characteristics of the vegetables. This process helps retain the color intensity and texture that we associate with fresh vegetables.
2. Retention of Chlorophyll: Chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the vibrant green color in many vegetables, is sensitive to heat and light. Without blanching, the enzymes in vegetables can cause chlorophyll to break down, resulting in a loss of color. Blanching effectively halts this enzymatic activity, preserving the green color and ensuring that your frozen vegetables remain visually appealing.
3. Prevention of Texture Loss: Blanching helps maintain the crispness and firmness of vegetables. It slows down the breakdown of cell walls and the loss of water-soluble components that contribute to texture. By blanching, you protect the vegetables’ structural integrity, ensuring that they remain firm and succulent even after freezing and thawing.
4. Improving Visual Appeal: Properly blanched vegetables retain their vibrant colors, making them visually appealing when added to dishes. Whether it’s the bright orange of carrots or the deep purple of eggplants, blanching helps preserve the natural beauty of vegetables. This visual appeal not only makes your meals look more appetizing but also adds an element of freshness and health to your plate.
5. Enhanced Taste Experience: The color and texture of vegetables greatly influence our perception of their taste. By retaining the color and texture through blanching, the overall taste experience of the vegetables is significantly improved. Blanching helps preserve the delicate flavors and crisp texture, ensuring that your frozen vegetables taste as close to freshly harvested ones as possible.
Blanching is a simple yet effective technique that ensures the color and texture of your vegetables remain vibrant and appealing even after freezing. By investing a few minutes in blanching before freezing, you can elevate the visual and sensory experience of your meals, making them more enjoyable and satisfying.
Enzyme Inactivation and Microbial Safety
Blanching vegetables before freezing not only helps with retaining color and texture but also plays a vital role in enzyme inactivation and ensuring microbial safety. Let’s explore these aspects in more detail:
1. Enzyme Inactivation: Enzymes are present in vegetables and can cause undesirable changes over time, such as discoloration, loss of texture, and deterioration of flavor. Blanching involves briefly exposing the vegetables to boiling water, which effectively inactivates these enzymes. By quickly heating the vegetables, the enzymatic activity is disrupted, preserving the vegetables’ quality and preventing the enzymatic degradation during freezer storage. This step ensures that your frozen vegetables retain their freshness and taste when you eventually cook and consume them.
2. Microbial Safety: Vegetables can harbor surface bacteria and other microorganisms that may lead to spoilage and foodborne illnesses. Blanching helps eliminate or significantly reduce the microbial load by subjecting the vegetables to high-temperature water. The heat kills or inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria, reducing the risk of contamination during storage. Rapidly cooling the vegetables in ice water further prevents bacterial growth, ensuring the safety of your frozen vegetables. By blanching, you can store your vegetables with confidence, knowing that they are less likely to harbor harmful microorganisms.
3. Prevention of Enzymatic Reactions: Freezing alone is not sufficient to halt the activity of enzymes in vegetables. Cold temperatures slow down enzymatic reactions but do not completely stop them. This means that even when vegetables are frozen, enzymes can still contribute to the deterioration of color, texture, and flavor. By blanching before freezing, you effectively neutralize the enzymes and minimize their impact. This step ensures that your frozen vegetables maintain their desired qualities and extend their shelf life.
4. Retention of Nutritional Value: Enzymes can also contribute to the loss of nutrients in vegetables over time. Blanching helps inactivate these enzymes, minimizing nutrient degradation during freezer storage. While blanching itself may cause slight nutrient loss, it is minimal compared to the potential nutrient loss that can occur during freezing and prolonged storage without blanching. Blanching helps preserve the essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in vegetables, ensuring that they remain nutritious even after freezing.
By blanching your vegetables before freezing, you not only ensure the inactivation of enzymes that can cause deterioration but also enhance the microbial safety of the frozen vegetables. These critical steps help maintain the quality, flavor, and nutritional value of your vegetables, offering you peace of mind and a safe and enjoyable culinary experience.
Nutrient Preservation with Blanching
One of the key benefits of blanching vegetables before freezing is the preservation of their nutritional value. Let’s explore how blanching helps maintain the nutrients in vegetables:
1. Minimizing Nutrient Loss: Blanching involves a short exposure to heat, which helps inactivate enzymes that can degrade nutrients over time. While blanching can cause some slight nutrient loss, the overall impact is minimal compared to the potential loss that can occur during freezing and prolonged storage without blanching. By blanching, you preserve a significant portion of the essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants present in the vegetables.
2. Retaining Water-Soluble Vitamins: Water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin C and the B vitamins, are susceptible to degradation during cooking and storage. Blanching, being a brief cooking process, helps limit the loss of these vitamins. The rapid heat and cooling process of blanching helps to preserve water-soluble vitamins, ensuring their availability when you consume the frozen vegetables later on.
3. Preserving Antioxidants: Vegetables are rich in antioxidants that play a vital role in protecting the body against oxidative stress and various diseases. Some antioxidants, like carotenoids and flavonoids, can be sensitive to heat and oxygen exposure. Blanching helps preserve these valuable antioxidants by quickly heating and cooling the vegetables, reducing the risk of degradation. By blanching, you ensure that your frozen vegetables retain their antioxidant content and the associated health benefits.
4. Maintaining Phytochemicals: Phytochemicals are natural compounds found in plants that offer numerous health benefits. These compounds can vary depending on the type of vegetable. Blanching helps preserve the phytochemicals present in vegetables, ensuring that you still benefit from their potential anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and immune-enhancing properties when consuming the frozen vegetables.
5. Retaining Dietary Fiber: Dietary fiber is essential for a healthy digestive system and plays a role in managing weight and controlling blood sugar levels. Blanching helps preserve the fiber content of vegetables, ensuring that the frozen vegetables continue to provide the necessary dietary fiber when consumed. Maintaining the fiber content also contributes to the texture and overall mouthfeel of the vegetables when cooked.
Blanching plays a crucial role in nutrient preservation. While there may be some slight nutrient loss, blanching significantly minimizes degradation compared to freezing vegetables without blanching. By preserving the essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, phytochemicals, and dietary fiber, blanching helps ensure that your frozen vegetables continue to offer optimal nutritional value and contribute to a healthy diet.
Step-by-Step Guide to Blanching Vegetables Before Freezing
Blanching vegetables before freezing is a simple process that ensures optimal results. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you through the blanching process:
Step 1: Preparation: Start by selecting fresh and high-quality vegetables. Wash them thoroughly to remove any dirt or debris. If the vegetables are large, such as broccoli or cauliflower, cut them into smaller, uniform-sized pieces.
Step 2: Boiling Water: Fill a large pot with water and bring it to a vigorous boil. The amount of water should be sufficient to completely submerge the vegetables.
Step 3: Salt (Optional): If desired, add a small amount of salt to the boiling water. This step is optional but can enhance the flavor of the vegetables.
Step 4: Blanching Time: Place the vegetables into the boiling water and allow them to cook for a specific amount of time. The blanching time can vary depending on the type and size of the vegetables. Consult a reliable source or blanching guide for specific times.
Step 5: Ice Water Bath: After the blanching time is complete, quickly remove the vegetables from the boiling water using a slotted spoon or tongs. Immediately transfer them to a bowl or sink filled with ice water. The ice water bath helps cool the vegetables rapidly and halt the cooking process.
Step 6: Cooling: Allow the vegetables to cool in the ice water for the same duration as the blanching time. This step ensures that the vegetables are completely cooled and helps preserve their color and texture.
Step 7: Drain and Dry: Once the vegetables are fully cooled, remove them from the ice water and drain them well. Use a colander or paper towels to remove excess moisture from the vegetables. Excess moisture can lead to ice crystals during freezing, which may affect the quality of the vegetables.
Step 8: Packaging: Place the blanched and drained vegetables into freezer-safe containers or bags. Remove as much air as possible before sealing the containers or bags tightly. Proper packaging helps protect the vegetables from freezer burn and maintains their quality during storage.
Step 9: Freezing: Place the packaged vegetables in the freezer and ensure they are stored in a single layer until fully frozen. Once frozen, you can stack the packages to save space. Label the containers or bags with the date to keep track of their freshness.
Step 10: Cooking: When you’re ready to use the frozen vegetables, simply thaw them in the refrigerator or immerse them in cold water. Once thawed, you can cook them according to your preference, whether it’s boiling, steaming, sautéing, or adding them to soups and stir-fries.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can successfully blanch your vegetables before freezing, ensuring optimal color, texture, and flavor preservation for your frozen vegetables.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Blanching
While blanching is a relatively straightforward process, there are some common mistakes that can affect the quality of your blanched vegetables. By being aware of these mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can ensure optimal results. Here are some common mistakes to avoid while blanching vegetables:
1. Overcooking: One of the most common mistakes is overcooking the vegetables during the blanching process. Overcooking can lead to loss of color, texture, and nutrients. It’s important to follow the recommended blanching times for each type of vegetable and adjust accordingly based on the size and thickness of the pieces.
2. Undercooking: On the other hand, undercooking the vegetables can result in enzymes not being fully inactivated and microbial safety not being ensured. Make sure to adhere to the recommended blanching times to achieve the proper level of heat treatment.
3. Not Using Enough Water: Using insufficient water can lead to uneven blanching and inadequate heat transfer. Ensure that there is enough water in the pot to fully submerge the vegetables and allow for even cooking.
4. Not Rapidly Cooling: Failure to rapidly cool the blanched vegetables can lead to continued cooking and loss of color and texture. Immerse the vegetables in ice water immediately after blanching to stop the cooking process and lock in the desired qualities.
5. Forgetting to Drain Excess Water: After the vegetables have been blanched and cooled, it’s important to drain them well to remove excess moisture. Excess water can result in freezer burn and degradation of the vegetable quality during storage.
6. Incorrect Packaging: Improper packaging can lead to freezer burn and loss of quality. Ensure that the blanched vegetables are properly sealed in airtight freezer-safe containers or bags. Remove as much air as possible before sealing to minimize the risk of freezer burn.
7. Neglecting Labeling: It’s important to label the containers or bags with the date of blanching. This helps you keep track of the freshness of the vegetables and ensures that you use them within the recommended storage period.
8. Freezing Warm Vegetables: Freezing warm or partially cooled vegetables can lead to the formation of ice crystals and adversely affect the texture. Always ensure that the blanched vegetables are completely cooled before packaging and placing them in the freezer.
9. Assembling Vegetables with Different Blanching Times: If you are blanching a mixture of vegetables that have different blanching times, it’s important to blanch them separately. This ensures that each vegetable receives the appropriate heat treatment and achieves the desired texture and color.
10. Not Using Fresh Vegetables: Starting with fresh and high-quality vegetables is essential for blanching success. Avoid using vegetables that are spoiled, wilted, or past their prime as they may not retain their quality even after blanching.
By avoiding these common blanching mistakes and following the recommended techniques, you can ensure that your blanched vegetables retain their color, texture, flavor, and nutritional value, providing delicious and healthy additions to your meals.
Alternative Methods to Blanching
While blanching is the traditional method of preparing vegetables for freezing, there are alternative methods you can consider. These methods offer different approaches to preserve the quality of vegetables before freezing. Let’s explore some of these alternatives:
1. Steaming: Steaming is an excellent alternative to blanching as it helps retain the color, flavor, and nutritional value of vegetables. Steaming involves cooking vegetables over boiling water in a steamer basket or pot with a tight-fitting lid. This gentle cooking method minimizes nutrient loss and maintains the vegetables’ texture. Once steamed, the vegetables can be quickly cooled in ice water before freezing.
2. Microwaving: Microwaving is a quick and convenient method of preparing vegetables for freezing. Place the vegetables in a microwave-safe dish with a small amount of water and cover loosely. Microwave on high for a few minutes until the vegetables are slightly tender but still crisp. Once cooked, immerse the vegetables in ice water to cool them rapidly before freezing.
3. Blanching in the Steam: This method combines the benefits of steam and blanching. Bring a few inches of water to a boil in a pot with a tight-fitting lid. Place a steamer basket or colander above the boiling water and add the vegetables. Cover the pot and steam for a short time, ensuring that the vegetables are heated through. Once steamed, cool the vegetables in ice water to halt the cooking process before freezing.
4. Blanche and Sauté: Instead of blanching alone, you can blanch the vegetables briefly and then sauté them in a little oil or butter. This method helps caramelize the vegetables slightly and adds a tasty dimension to their flavor. After sautéing, cool the vegetables before transferring them to freezer-safe containers or bags.
5. Freezing without Pre-Treatment: Alternatively, you can skip the blanching or pre-treatment step altogether and freeze raw vegetables directly. While this method is simple, it may result in changes in color, texture, and flavor over time. Raw freezing is best suited for certain vegetables like peppers, onions, and green beans, which can tolerate freezing without significant quality degradation.
6. Freezing Prepared Dishes: If you prefer to skip the individual blanching or cooking steps, you can also freeze prepared dishes that include vegetables as ingredients. This method, commonly known as batch cooking, involves cooking the vegetables, incorporating them into dishes such as soups, stews, or casseroles, and freezing the entire meal. This allows you to have complete meals ready to reheat and enjoy without the need for separate blanching processes.
While these alternative methods can be effective, it’s important to note that blanching has been widely tested and accepted as the ideal method for most vegetables before freezing. Alternative methods may yield slightly different results, and it’s essential to adjust the cooking or processing times accordingly to achieve the desired texture and quality. Experimentation and personal preference can help determine which alternative method works best for your specific vegetables and freezing needs.
Conclusion
Blanching vegetables before freezing is essential for preserving their color, texture, flavor, and nutritional value. Through the blanching process, enzymes are inactivated, microbial safety is ensured, and nutrient degradation is minimized. The step-by-step guide provided can help you navigate the blanching process successfully, while avoiding common mistakes that may affect the quality of your blanched vegetables.
Alternative methods, such as steaming or microwaving, offer different approaches to preparing vegetables for freezing, but blanching remains the most widely accepted and recommended method. It provides reliable results in terms of maintaining the desired characteristics of the vegetables during freezer storage.
By blanching vegetables before freezing, you can enjoy the convenience of having fresh-tasting and nutrient-rich vegetables available year-round. Whether you’re freezing your homegrown produce or taking advantage of seasonal sales, blanching ensures that your frozen vegetables retain their nutritional value and provide a delicious addition to your meals.
So, the next time you prepare your vegetables for freezing, remember the importance of blanching. Take the time to follow the proper blanching techniques and enjoy the benefits of vibrant colors, appealing textures, and preserved nutrients in your freezer. Blanching is a small investment of time that yields big rewards when it comes to the quality and enjoyment of your frozen vegetables.