Home>Gardening Tips and Tricks>Eco-Friendly Gardening>How To Compost Grass Clippings
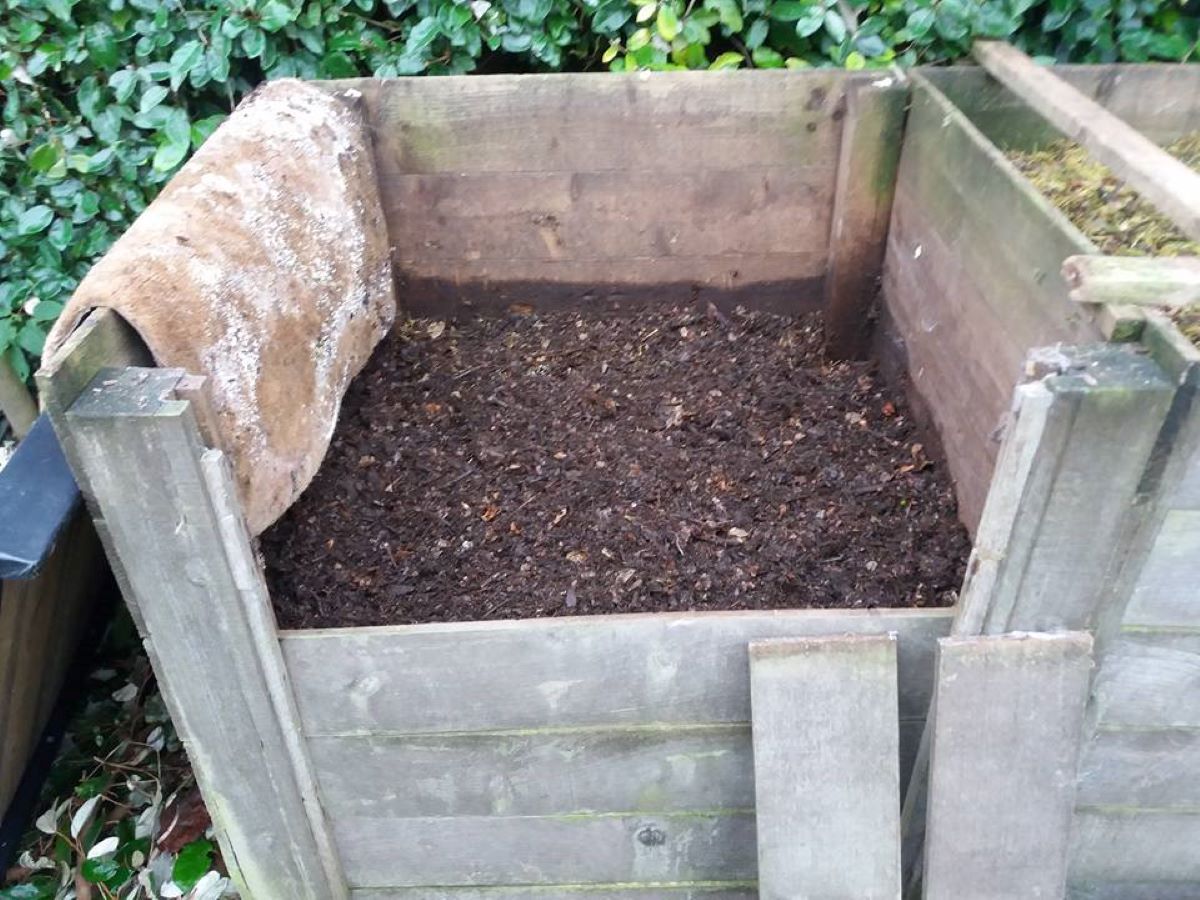


Eco-Friendly Gardening
How To Compost Grass Clippings
Modified: January 22, 2024
Learn how to compost grass clippings and embrace eco-friendly gardening practices for a healthier and sustainable garden.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Chicagolandgardening.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Benefits of Composting Grass Clippings
- Preparing Your Compost Bin
- Collecting and Storing Grass Clippings
- Balancing the Carbon-Nitrogen Ratio
- Layering Grass Clippings in Your Compost Bin
- Turning and Maintaining Your Compost Pile
- Using Composted Grass Clippings in Your Garden
- Troubleshooting Common Composting Issues
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to the world of eco-friendly gardening! If you’re passionate about creating a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly garden, composting grass clippings is a fantastic way to start. Not only is it a simple and cost-effective method, but it also provides numerous benefits for your garden and the planet.
Grass clippings are a valuable resource that often goes to waste. Many homeowners simply dispose of them in the trash or leave them on the lawn, unknowingly missing out on the opportunity to recycle and transform them into nutrient-rich compost.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of composting grass clippings and provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to effectively incorporate them into your composting routine. We will cover everything from preparing your compost bin to troubleshooting common issues, so you can make the most of this eco-friendly gardening practice.
By composting your grass clippings, you will not only reduce waste but also improve the health of your garden. The rich compost produced from grass clippings can be used as a natural fertilizer, enhancing the soil’s fertility and promoting healthy plant growth. It also helps retain moisture and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, making it a sustainable and environmentally conscious choice.
So, let’s delve into the world of composting grass clippings and discover how you can harness the power of nature to create a more vibrant and thriving garden. Get ready to dive into the exciting world of eco-friendly gardening!
Benefits of Composting Grass Clippings
Composting grass clippings offers a multitude of benefits for both your garden and the environment. Here are some reasons why you should consider incorporating this practice into your eco-friendly gardening routine:
- Nutrient-rich soil amendment: Grass clippings contain a high concentration of nitrogen, which is vital for plant growth. By composting them, you can transform them into a nutrient-rich soil amendment that will enhance the fertility of your garden soil. This means healthier, more vibrant plants.
- Reduces waste: Recycling your grass clippings through composting helps divert them from landfills, reducing organic waste. This is not only beneficial for the environment but also for local waste management systems. Plus, it saves you the trouble of bagging and disposing of the clippings.
- Improves soil structure: Composted grass clippings improve the structure of your soil by promoting better drainage and aeration. They help loosen compacted soil, allowing roots to access oxygen and nutrients more easily. This, in turn, leads to healthier plant growth and increased water retention.
- Suppresses weeds: A layer of composted grass clippings can act as a natural weed suppressant by smothering weed growth and preventing the germination of weed seeds. This reduces the need for using harmful herbicides in your garden.
- Enhances microbial activity: Grass clippings are teeming with beneficial microorganisms that break down organic matter and release nutrients. Adding composted grass clippings to your soil fosters a thriving microbial community, contributing to a healthier and more balanced ecosystem in your garden.
- Reduces water usage: Composted grass clippings improve the water-holding capacity of the soil, reducing the frequency of irrigation. They act as a natural mulch, helping to conserve moisture and prevent evaporation, thereby saving both water and time for gardeners.
- Promotes sustainable gardening practices: Composting grass clippings aligns with principles of sustainability and eco-friendly gardening. By recycling organic matter, you are minimizing your impact on the environment and embracing a natural and holistic approach to gardening.
These are just a few of the many benefits that come from composting grass clippings. It is a simple yet effective way to make a positive impact on your garden’s health while reducing waste. Now that we’ve explored the advantages, let’s move on to how you can prepare your compost bin to accommodate grass clippings.
Preparing Your Compost Bin
Before you start composting grass clippings, it’s essential to prepare your compost bin or pile properly. Follow these steps to ensure that your composting process is efficient and effective:
- Select the right composting system: Choose a composting system that suits your needs and space availability. You can opt for a traditional compost bin, a compost tumbler, or even a homemade compost pile. Make sure it has adequate airflow and drainage to facilitate decomposition.
- Choose a suitable location: Place your compost bin in an area that receives partial sunlight or shade. This will prevent excessive drying out or waterlogging of your compost. Ensure it is easily accessible for adding and turning materials.
- Prepare a base: Lay down a layer of twigs, straw, or dry leaves at the bottom of your compost bin. This creates airflow and drainage, preventing the compost from becoming waterlogged.
- Consider a compost bin with compartments: If possible, choose a compost bin with compartments or separate areas. This allows you to have separate sections for filling, turning, and curing compost. This makes the process more organized and efficient.
- Add a compost activator: To kickstart decomposition, add a compost activator to your compost bin. This can be in the form of finished compost, garden soil, or a commercial compost accelerator. Activators introduce beneficial microorganisms into the mix, speeding up the composting process.
- Ensure proper ventilation: Good airflow is crucial for successful composting. If using a traditional compost bin, make sure it has ventilation ports or drill holes in the sides for aeration. Turning the pile regularly also helps with the circulation of air.
- Consider a compost thermometer: Monitoring the temperature of your compost can help gauge its progress. Using a compost thermometer enables you to maintain optimal temperatures for decomposition, typically between 120-160°F (49-71°C).
- Keep compost moist: Adequate moisture is essential for composting. Aim for a moisture level similar to a damp sponge. Water the compost pile regularly, especially during dry periods, to ensure the decomposition process is not hindered.
By taking the time to properly prepare your compost bin, you set the stage for successful composting of grass clippings. With a well-designed and maintained composting system, you can effectively transform your organic waste into nutrient-rich compost for your garden. The next step is to collect and store your grass clippings for optimal composting.
Collecting and Storing Grass Clippings
Collecting and storing grass clippings correctly is crucial for successful composting. Here are some tips to help you gather and store your grass clippings effectively:
- Use a mulching lawn mower: Consider investing in a mulching lawn mower, which cuts the grass into fine pieces and leaves them on your lawn. This method eliminates the need for collecting and storing clippings separately.
- Collect grass clippings after mowing: If you prefer not to use a mulching mower, collect the grass clippings immediately after mowing. Leaving them on your lawn for an extended period can lead to clumping and hinder proper decomposition.
- Avoid collecting clippings from treated lawns: If you have recently applied herbicides or pesticides to your lawn, avoid collecting those clippings. These chemicals can negatively impact the composting process and harm beneficial organisms in the compost.
- Ensure a good mix of green and brown materials: Grass clippings are considered “green” materials in composting due to their high moisture and nitrogen content. To achieve a balanced compost, mix grass clippings with “brown” materials such as dried leaves, straw, or shredded newspaper. This helps maintain the ideal carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in your compost pile.
- Do not let clippings become compacted: When collecting grass clippings, avoid compacting them tightly in bags or containers. This can lead to anaerobic decomposition, producing unpleasant odors. Instead, loosely layer the clippings in your storage container to allow for air circulation.
- Dry clippings before storage (optional): If your grass clippings are excessively wet, you might want to spread them out and allow them to dry for a day or two before storing. This reduces the risk of compacting and helps maintain proper moisture levels in your compost pile.
- Store clippings in a covered container: Use a covered compost bin, container, or trash can to store your grass clippings. Make sure the container has adequate airflow to prevent the buildup of excessive moisture or foul odors.
- Avoid storing clippings for too long: It is best to use grass clippings for composting within a few days of collection. Fresh clippings decompose rapidly and retain more of their nutrients. Storing them for extended periods can lead to nutrient loss.
- Layer clippings in your compost bin: When you are ready to add the grass clippings to your compost pile, layer them with other compostable materials such as kitchen scraps, leaves, and garden trimmings. This helps create a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio for optimal composting.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your grass clippings are collected and stored properly, setting the stage for successful composting. Now, let’s move on to understanding how to achieve the right carbon-nitrogen ratio in your compost pile.
Balancing the Carbon-Nitrogen Ratio
When composting grass clippings, it’s important to maintain a balanced carbon-nitrogen ratio for optimal decomposition. This ratio ensures that the microorganisms responsible for breaking down the materials in your compost pile have the necessary nutrients. Here’s how you can achieve the right balance:
- Understanding carbon and nitrogen: Carbon-rich materials, also known as “brown” materials, provide a source of energy for the microorganisms. Examples include dried leaves, straw, wood chips, and shredded newspaper. Nitrogen-rich materials, also called “green” materials, provide the necessary proteins for the microorganisms. Grass clippings, kitchen scraps, and fresh plant trimmings are good sources of nitrogen.
- The ideal ratio: The ideal carbon-nitrogen ratio for efficient composting is around 25-30 parts carbon to 1 part nitrogen. This balance allows the microorganisms to break down the organic matter effectively.
- Too much carbon: If your compost pile has too much carbon, it can slow down the decomposition process. The microorganisms will struggle to break down the materials efficiently. Signs of excess carbon include a slow decomposition rate and a pile that is dry and lacks moisture.
- Too much nitrogen: Conversely, if your compost pile has an excessive amount of nitrogen, it can become overly wet and start to emit unpleasant odors. This is known as a “hot” pile. In this case, the microorganisms are consuming nitrogen faster than it can be supplied, resulting in an imbalanced compost pile.
- Adjusting the ratio: To balance the carbon-nitrogen ratio, mix carbon-rich and nitrogen-rich materials in appropriate proportions. For grass clippings, which are high in nitrogen, add an equal amount of carbon-rich materials like dried leaves or shredded newspaper. Alternatively, layer grass clippings with other carbon-rich materials in your compost pile to maintain the balance.
- Testing the ratio: To ensure the carbon-nitrogen ratio is balanced, you can use a compost thermometer to monitor the temperature of your compost pile. A properly balanced pile will generate heat, indicating active microbial activity and decomposition.
- Adjusting as needed: If you find that your compost pile is too dry and decomposition is slow, add more nitrogen-rich materials such as grass clippings or kitchen scraps. On the other hand, if your pile is too wet and emits a foul odor, add more carbon-rich materials to absorb excess moisture.
- Regular turning: Turning your compost pile regularly also helps distribute the carbon and nitrogen materials evenly, promoting effective decomposition and preventing any imbalances from occurring.
By understanding and balancing the carbon-nitrogen ratio in your compost pile, you ensure that the microorganisms responsible for decomposition have the ideal conditions to work efficiently. Now that you know how to achieve the right ratio, let’s move on to how to layer your grass clippings in the compost bin.
Layering Grass Clippings in Your Compost Bin
Layering grass clippings properly in your compost bin is key to creating a well-balanced and productive compost pile. Here are some steps to help you effectively layer your grass clippings:
- Start with a layer of carbon-rich materials: Begin by adding a layer of carbon-rich “brown” materials, such as dried leaves, straw, or shredded newspaper, at the bottom of your compost bin. This acts as a base and helps absorb excess moisture.
- Add a layer of grass clippings: On top of the carbon-rich layer, add a layer of fresh grass clippings. Ensure that they are spread out evenly and not piled too thickly, as this can lead to compaction and hinder airflow. A thickness of 1 to 2 inches is ideal.
- Incorporate nitrogen-rich materials: To maintain the carbon-nitrogen balance, add a layer of nitrogen-rich materials, such as kitchen scraps or fresh plant trimmings, on top of the grass clippings. Aim for a thickness of about ½ inch to 1 inch.
- Repeat the layers: Continue layering in this manner, alternating between carbon-rich and nitrogen-rich materials. The ratio of carbon to nitrogen materials should be approximately 25-30 parts carbon to 1 part nitrogen.
- Moisten each layer: As you add each layer, lightly moisten it with water. The layers should be damp, similar to a well wrung-out sponge. This helps activate the decomposition process and provides the necessary moisture for the microorganisms to thrive.
- Continue layering until your compost bin is full: Repeat the process of layering grass clippings, carbon-rich materials, and nitrogen-rich materials until your compost bin is full. Remember to maintain a balanced ratio and avoid adding too many grass clippings at once, as this can cause the pile to become compacted and slow down decomposition.
- Finish with a layer of carbon-rich materials: To prevent odor and maintain moisture levels, finish the compost pile with a final layer of carbon-rich materials, such as dried leaves or straw. This acts as a cover and helps insulate the pile.
- Optional: Mix the top layer: If desired, you can lightly mix the top layer of grass clippings and carbon-rich materials using a garden fork or compost turning tool. This helps incorporate air and aids in the decomposition process.
Remember to regularly monitor the moisture levels and temperature of your compost pile. If the pile becomes too dry, water it lightly. Conversely, if it appears too wet, add some additional carbon-rich materials to absorb the excess moisture.
By layering your grass clippings properly in your compost bin, you create an environment conducive to decomposition and the efficient breakdown of organic matter. Now, let’s move on to understanding how to maintain and turn your compost pile.
Turning and Maintaining Your Compost Pile
Turning and maintaining your compost pile is essential for the successful decomposition of grass clippings and other organic materials. Follow these steps to ensure your compost pile remains healthy and productive:
- Regularly turn your compost pile: Turning your compost pile helps create airflow, ensuring the materials decompose evenly. Use a garden fork or compost turning tool to gently mix the layers. Aim to turn the pile every 2-3 weeks to promote decomposition.
- Monitor moisture levels: Your compost pile should be moist, but not overly wet or dry. Check the moisture content regularly by grabbing a handful of material and squeezing it. It should feel damp, similar to a well-wrung sponge. Moisture is crucial for the microorganisms to break down the organic matter effectively.
- Add water if needed: If your compost pile is too dry, lightly water it to ensure adequate moisture. Use a watering can or a hose with a gentle spray nozzle to moisten the materials. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to excess moisture and anaerobic conditions.
- Avoid compacting the pile: When turning the compost, be careful not to compact the materials. Gentle mixing and fluffing help maintain airflow and prevent the pile from becoming too dense. This allows the microorganisms to thrive and speeds up decomposition.
- Monitor temperature: Regularly check the temperature of your compost pile using a compost thermometer. The internal temperature should be between 120-160°F (49-71°C) for optimal decomposition. If the temperature drops significantly, it may indicate a lack of nitrogen or insufficient aeration. Adjust your compost pile accordingly.
- Add additional organic matter: As you collect more grass clippings or other compostable materials, continue adding them to the compost pile. Layer them with existing materials and maintain the carbon-nitrogen balance. This ensures a constant supply of organic matter for decomposition.
- Monitor and manage pests: Keep an eye out for any signs of pests or unwanted visitors in your compost pile. If necessary, cover it with a wire mesh or use compost bin covers to deter animals and prevent them from disturbing the materials.
- Be patient: Composting is a natural process that takes time. It can take several months for grass clippings and other organic materials to fully decompose into rich, dark compost. Be patient and allow nature to work its magic.
By regularly turning and maintaining your compost pile, you create an environment that encourages decomposition and supports the activity of beneficial microorganisms. This helps break down the grass clippings and other organic matter more efficiently, resulting in nutrient-rich compost for your garden.
Now that you have learned how to turn and maintain your compost pile effectively, let’s explore how to utilize the composted grass clippings in your garden.
Using Composted Grass Clippings in Your Garden
Once your grass clippings have decomposed into nutrient-rich compost, you can utilize this valuable resource to enhance your garden. Here are some ways to effectively use composted grass clippings:
- Soil amendment: Incorporate the composted grass clippings into your garden soil to improve its structure and fertility. Spread a layer of compost on top of your soil and gently mix it in using a garden fork or shovel. This will increase the organic matter content and provide essential nutrients for plant growth.
- Top-dressing: Use composted grass clippings as a top-dressing around your existing plants. This helps retain moisture, suppresses weed growth, and adds nutrients to the soil. Spread a thin layer of compost around the base of your plants, taking care not to cover the stem or leaves.
- Mixing with potting soil: Blend composted grass clippings with commercial potting soil to create a nutrient-rich mix for container gardening. This will provide a boost of organic matter and beneficial microorganisms to support healthy plant growth.
- Making compost tea: Use composted grass clippings to create compost tea, a liquid fertilizer that can be applied foliarly or to the soil. Simply place a handful of composted clippings into a porous bag or container and let it steep in water for a day or two. Strain the solution and use it to feed your plants.
- Creating a mulch layer: Spread a layer of composted grass clippings around your plants as a natural mulch. This will help retain moisture, regulate soil temperature, and suppress weed growth. Ensure that the mulch layer is not too thick to allow for proper air circulation.
- Building raised beds: Use composted grass clippings as a component when building raised beds. Mix it with other organic materials like composted leaves and aged manure to create a nutrient-rich growing medium. This provides an excellent foundation for growing vegetables and flowers.
- Amending potting mixes: Improve the quality of your potting mixes by adding composted grass clippings. It adds organic matter and helps retain moisture, promoting healthier root development and plant growth.
- Composting future organic waste: Use composted grass clippings as a “brown” material for future composting projects. Layer it with other kitchen scraps or garden trimmings to maintain a balanced carbon-nitrogen ratio in your compost pile.
By utilizing composted grass clippings in various ways, you can maximize their benefits and promote sustainable gardening practices. Whether it’s amending soil, creating mulch, or enhancing potting mixes, composted grass clippings provide a fantastic source of organic matter and nutrients for your garden.
Now that you are equipped with the knowledge of using composted grass clippings, let’s address some common issues that may arise during the composting process.
Troubleshooting Common Composting Issues
Composting is a natural process, but sometimes issues can arise that hinder the optimal decomposition of grass clippings and other organic materials. Let’s explore some common composting problems and how to troubleshoot them:
- Odor: If your compost pile emits foul odors, it may indicate anaerobic decomposition. To fix this, ensure proper aeration by turning the pile more frequently. Add more carbon-rich materials like dried leaves or straw to absorb excess moisture and balance the pile.
- Slow decomposition: If your compost pile is taking longer than expected to decompose, it may be due to an imbalance in the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Adjust the ratio by adding more carbon-rich or nitrogen-rich materials as needed. Ensure the pile is adequately moist and turn it regularly to provide the necessary conditions for decomposition.
- Pests and critters: Unwanted pests and critters can be attracted to your compost pile. To deter them, avoid adding meat, dairy, oily foods, or invasive plant materials. Cover your pile with a wire mesh or use compost bin covers to prevent animals from accessing the compost.
- Weed seeds: If your compost contains weed seeds, they may still germinate when you use the compost in your garden. To avoid this, ensure your compost pile reaches high temperatures during the decomposition process. Hot composting, where the pile reaches temperatures above 130°F (54°C), helps kill weed seeds and pathogens.
- Excessive moisture: An overly wet compost pile can lead to anaerobic conditions and foul odors. To combat excessive moisture, add more carbon-rich materials like dried leaves or straw to absorb the excess water. Enhance drainage by ensuring your compost bin or pile has proper airflow.
- Insufficient moisture: If your compost pile is too dry, it may hinder decomposition. Water the pile lightly to ensure adequate moisture. Mix the materials to distribute the moisture evenly, and cover the pile with a tarp or compost bin cover to retain moisture.
- Unpleasant smell: A strong and unpleasant odor can indicate a high concentration of nitrogen-rich materials or materials that are slow to decompose, such as animal waste. Balance the compost pile with carbon-rich materials, turn it regularly, and ensure proper aeration to reduce the odor.
- Persistent materials: Some materials in your compost pile, such as woody branches or large chunks of food waste, may take longer to break down. To expedite the process, chop or shred these materials into smaller pieces before adding them to the pile. Turn the pile frequently to ensure the materials decompose more efficiently.
Addressing these common composting issues will help you create a healthier and more productive compost pile. Remember that composting is a continuous learning process, and it may take some experimentation to find the best strategies for your specific composting setup.
Now that you are equipped with troubleshooting knowledge, you are ready to embark on your composting journey and experience the joys of eco-friendly gardening.
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing this comprehensive guide to composting grass clippings! By incorporating eco-friendly practices into your gardening routine, you are not only taking steps towards a more sustainable lifestyle but also reaping the benefits of nutrient-rich compost for your garden.
We have explored the numerous benefits of composting grass clippings, from reducing waste and improving soil health to promoting sustainable gardening practices. Preparing your compost bin, collecting and storing grass clippings, balancing the carbon-nitrogen ratio, layering in the compost bin, turning and maintaining the compost pile, and utilizing the composted grass clippings in your garden have been discussed in detail.
Remember, composting involves patience and experimentation. While troubleshooting common issues may arise, don’t be discouraged. By following the tips and techniques outlined in this guide, you can overcome challenges and continue producing nutrient-rich compost for your garden.
Composting grass clippings is a simple yet impactful way to make a positive environmental contribution while enhancing the health and productivity of your garden. Embrace this eco-friendly gardening practice and enjoy the satisfaction of seeing your garden thrive with the help of your very own compost.
So why wait? Start collecting those grass clippings, prepare your compost bin, and embark on this rewarding journey of composting. Your garden and the environment will thank you!